Practical Networking: Ensuring That All Web Traffic Uses BorderManager Proxy Cache
Articles and Tips:
01 May 1998
Novell's BorderManager includes a feature calledproxy cache, which can significantly reduce the overall traffic on your company's Internet connection and speed up users' access to World-Wide Web documents. In addition, the BorderManager proxy cache enables you to create access controls that enforce your company's policies for using the Internet. For example, you could allow only certain users or groups of users to access the Internet, or you could limit users' Internet access to business hours. However, these access controls apply only to users whose workstations are configured to use the BorderManager IPX-IP gateway and to users whose web browsers are configured to use the BorderManager proxy cache.
If a user's workstation is TCP/IP enabled, the user can bypass the BorderManager proxy cache and its access controls. The user can configure his or her web browser to access the Internet directly (rather than through the BorderManager proxy cache). In this case, the web pages this user accesses bypass the BorderManager proxy cache and go directly to the user's workstation.
Later, when a web browser that is configured to use the BorderManager proxy cache requests the same web pages, the BorderManager server must request these pages from the Internet because the pages have not been cached. As a result, your company's Internet bandwidth is wasted because the same web pages must be downloaded multiple times.
But even worse than wasting Internet bandwidth, users who bypass the BorderManager proxy cache have unlimited access to the Internet because they bypass the access controls you have created. You can then no longer enforce your company's policies for using the Internet.
Fortunately, you can ensure that all web traffic is routed through the BorderManager proxy cache. To route web traffic through the BorderManager proxy cache, you block all web requests except those requests made from the BorderManager server's IP address. To block certain web requests, you perform three tasks:
Enable packet filtering.
Create a packet filter that blocks all web traffic from your company's Internet connection.
Create an exception to the packet filter that allows only the BorderManager proxy cache to use your company's Internet connection.
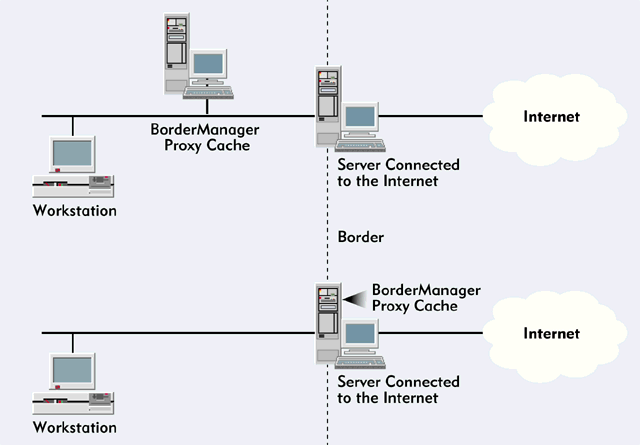
This solution assumes that you have configured a server to connect your company's network to the Internet. (See Figure 1.) If you have configured a router to connect your company's network to the Internet, you can use the router's management software to create the same packet filters.
Figure 1: Whether the BorderManager proxy cache is on the border or behind the border, you can force users to access the Internet through the BorderManager proxy cache.
ENABLING PACKET FILTERING
To enable packet filtering, you complete the following steps:
At the console of the server that provides your company's Internet connection, enter the following command:LOAD INETCFG
Select the Protocols option from the Internetworking Configuration menu, and then select the TCP/IP option from the Protocol Configuration menu. The TCP/IP Protocol Configuration menu appears.
Set the Filter Support option to Enabled, and press the Escape key.
When you are prompted to update the TCP/IP configuration, select Yes.
Press the Escape key twice, and then press the Enter key to close the Internetworking Configuration utility.
CREATING A PACKET FILTER TO BLOCK ALL WEB TRAFFIC
To create the packet filter to block all web traffic from your company's Internet connection, you complete the following steps:
At the console of the server that provides your company's Internet connection, enter the following command:LOAD FILTCFG
Select the Configure TCP/IP Filters option from the Filter Configuration Available Options menu, and then select the Packet Forwarding Filters option from the TCP/IP menu. The Packet Forwarding Filters menu appears.
Set the Status option to Enabled, and then set the Action option to Deny Packets in Filter List.
Highlight the List of Denied Packets option, and press the Enter key.
Press the Insert key to create a packet filter, and set the Destination Interface option to the interface that provides your company's Internet connection.
Set the Packet Type option to www-http.
Press the Escape key and the Enter key to save the packet filter.
CREATING AN EXCEPTION TO THE PACKET FILTER
At this point, you have created the packet filter that blocks all web traffic from getting to the Internet. You should see a screen similar to the screen shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2: You first create a packet filter to block all web traffic, and you then create an exception to allow only BorderManager to send and receive web traffic.

You must now create an exception to this packet filter that enables the BorderManager proxy cache to send web traffic to the Internet. To create an exception, you complete the following steps:
Press the Escape key to return to the Packet Forwarding Filters menu.
Highlight the List of Packets Always Permitted option, and press the Enter key.
Press the Insert key to create an exception, and set the Destination Interface option to the interface that provides your company's Internet connection.
Set the Source Address Type option to Host.
In the Source TCP/IP Address field, enter the TCP/IP address of the server that runs the BorderManager proxy cache.
Press the Escape key and the Enter key to save the exception.
Press the Escape key four times, and then press the Enter key to close the Filter Configuration utility.
At the server console, enter the following command to enable the packet filters:REINITIALIZE SYSTEM
CONCLUSION
After you implement the packet filter, users who attempt to bypass the BorderManager proxy cache will not receive a response to their web requests because the packet filter blocks these requests. Eventually, users' web browsers will display an error message telling these users that the server on the Internet did not respond. To access web pages, users must configure their web browsers to use the BorderManager proxy cache.
For more information about BorderManager, visit Novell's web site (http://www.novell.com/bordermanager). You can also read the followingNetWare Connectionarticles:
"Virtual Private Networks: Making a Public Network Private,"NetWare Connection, Feb. 1998, pp. 6-21.
"BorderManager Caches in on the Web,"NetWare Connection, Aug. 1997, pp. 22-31.
"Novell's Border Services,"NetWare Connection, May 1997, pp. 25-36.
Terry L. Jeffress works for Niche Associates, an agency that specializes in technical writing and editing.
NetWare Connection,May 1998, pp.42-43
* Originally published in Novell Connection Magazine
Disclaimer
The origin of this information may be internal or external to Novell. While Novell makes all reasonable efforts to verify this information, Novell does not make explicit or implied claims to its validity.