Cheat Sheet: A Sneak Peek at the Novell CLE Study Guide
Articles and Tips: article
09 Dec 2004
Novell Press is the official book publishing imprint of Novell Inc. Below is a chapter from an upcoming book named Novell's CLE Study Guide by Rob Tracy. We at Novell Connection are excited to give you a sneak peek of this soon-to-be-released book. You're sure to find some of the tips that Rob gives useful in your Linux pursuit. We hope you find this sample chapter helpful and encourage you to visit www.novellpress.com to get the full text upon its release.
Introduction to the CLE Practical Exam
Congratulations on your choice to become a Certified Linux Engineer! By purchasing this book, you are on your way to earning one of the hottest new certifications around.
By gaining your CLE certification, you prove to your employer and your co-workers that you truly know your stuff with Novell services on Linux. That's because Novell's practical testing strategies ensure that anyone certified as a CLE really can do the job. No paper certifications allowed here! We'll go into more depth on the CLE in just a moment. For now, let's take a look at what will be covered in this book.
This chapter provides an overview of Novell's newest certification program?the Novell Certified Linux Engineer (CLE). The following topics will be covered:
Introduction to the CLE
Introduction to the CLE Test Environment
CLE Test-taking Strategies
Introduction to the CLE
For years, Novell certifications have represented the pinnacle of Information Technology industry training. Novell pioneered the certification industry with the Certified Novell Engineer (CNE) and Certified Novell Administrator (CNA) programs.
Novell continues this venerable tradition with the Certified Linux Engineer program. Why a whole new certification? The nature of the product on which CLE certifies you is dramatically different from prior Novell products. Let's take a look at the nature of the product you must know in order to become a CLE: Novell Nterprise Linux Services.
Novell Nterprise Linux Services
In 2003, Novell fused together two very powerful worlds. In one world, there is Linux, one of the most robust, stable and affordable network operating systems available today. These factors contribute to the popularity of Linux.
Each year Linux is finding its way into more and more organizations. According to IDC, an IT industry organization, "Linux servers have demonstrated six consecutive quarters of yearon- year revenue growth, proving that they are not a flash-in-thepan technology." (IDC Worldwide Quarterly Server Tracker, November 2003)
Residing in the other world are Novell's time-proven network services. Historically, these services were provided only on Novell's high-end NetWare server operating system. Although Novell did eventually port some of these services to the Windows Server platform, very few were made available on Linux.
In 2003, Novell changed all that with the introduction of Novell Nterprise Linux Services (NNLS). In this product, Novell ported its famous services such as iPrint, iFolder, NetStorage, Virtual Office and DirXML to run on the Linux platform. For the first time, these time-tested services are available on an operating system other than NetWare.
The benefits of this fusion are noteworthy for several reasons. System administrators can implement a reliable, inexpensive and fully supported opensource network operating system. Embracing Linux allows them to dramatically lower the all-important total cost of ownership (TCO) of the system.
Using eDirectory, administrators can configure the NNLS implementation as a standalone system or integrate it into an existing Novell eDirectory environment. eDirectory also provides administrators with a broad range of user identity management tools and options, depending on which networking platforms are present.
NNLS doesn't require a "rip and replace" approach to deployment. Using NNLS components, administrators can synchronize existing NetWare, Windows Domain or Active Directory user accounts with eDirectory on the NNLS system.
In addition, end users receive the benefits of Novell's productivity-enhancement services. These services provide users the tools they need to complete their daily tasks, whether they are in the office, at home or on the road.
For example, suppose a user is at home one evening and receives a call informing her that a report she has been working on is needed first thing in the morning. In the past, she would probably have to drive back to the office to complete the report, expending valuable time on travel.
With NNLS, however, she can use iFolder within a browser interface to access her files from her home computer. When she's finished with the report, all changes made at home are applied to her files on the Linux server at work. Because iFolder only synchronizes the changes she's made, her dial-up connection bandwidth can easily handle the task.
With iPrint, she can securely print the document from home to a color laser printer at the office so it is ready as soon as she arrives in the morning. Using NetMail, she can reserve a conference room and send out an appointment?from home?for a morning meeting with co-workers to review the report before turning it in.
We at Novell Connection are excited to give you a sneak peak of this soon-to-be-released book. You're sure to find some of the tips that Rob gives useful in your Linux pursuit.
Why CLE?
As you can probably see, implementing and managing NNLS require that system administrators really know their stuff with both Linux and Novell services. In accordance with the CLE, certification is very difficult to achieve for two reasons.
First, you have to know the Linux operating system and the technology behind Novell's NNLS services in depth. You need to know the following:
How to manage a SUSE LINUX Enterprise Server 8 system, including managing users, groups, permissions, ownership, processes and services
How to install NNLS
How to manage eDirectory on Linux
How to configure and manage eGuide
How to manage Linux user accounts in eDirectory with Linux User Management (LUM)How to implement DirXML (no small task, I assure you)
How to manage iFolder and NetStorage
How to deploy iPrint
How to implement NetMail
How to configure Virtual Office to pull all these services together into a single interface
Second, Novell has implemented a practical exam, discussed in detail later, to ensure you really have the skills required. You have to be able to deploy an NNLS system, not just fill in a bubble sheet with a No. 2 pencil.
When researching the need for a new certification, Novell discovered that there are many administrators with strong Linux skills and, likewise, many administrators with strong Novell skills. However, there are relatively few administrators in the industry with both Novell and Linux skill sets.
In light of this, Novell designed and implemented the CLE certification program. The CLE program is composed of two elements:
NNLS Courseware?This Study Guide or Novell's Course 3015 provides you with the skills and knowledge you need to pass the CLE exam.
CLE Practicum?Instead of a written exam, the CLE uses a hands-on, live exam that certifies you are sufficiently skilled in both the Linux and Novell realms.
I can't emphasize enough the importance of thorough preparation for the Practicum. With a multiple-choice test, many network administrators have discovered over the years that you can get away without studying. After all, you have a one in four chance of getting the right answer without any knowledge at all. With a little bit of networking background, many candidates can discern the correct response.
Not so with the Practicum. You must be able to "walk the walk and talk the talk," or you will fail miserably. And a large number of candidates have done just that.
With that, let's discuss the target audience of the CLE certification.
Who is the CLE For?
When designing the CLE, Novell encountered a quandary of sorts. Should the CLE be aimed at existing Novell system administrators who need Linux training, or should it be aimed at existing Linux administrators who need to learn how to use Novell services?
After a great deal of debate, Novell decided to proceed with both candidates in mind. The question then becomes one of where to start. Do you teach Linux and eDirectory in depth, or do you assume a certain level of proficiency on the part of the student? Novell opted for the latter option.
Therefore, the CLE exam and courseware (including this Study Guide) assume that you already have a pretty good grasp of basic Linux concepts and commands. Novell recommends that you complete LPI (Linux Professional Institute) Level I certification (or have an equivalent level of experience) before completing course materials or taking the CLE exam.
With this said, Novell also realizes that not all CLE candidates have the prerequisite Linux knowledge. Novell also realizes that many candidates may have Linux skills that are out of date.
To accommodate students in these categories, the first portion of the CLE objectives covers very basic Linux skills and tasks. These skills represent about 10 percent of the CLE exam.
The Novell staff reviewed the various tasks required to implement and manage NNLS services to determine which Linux skills to include in the CLE objectives. From these, it identified the basic Linux skills required and added those to the objectives list for the certification.
In accordance, the first portion of this Study Guide will present a brief introduction to Linux. Be aware, however, that this will not be an exhaustive review. If you have little or no Linux experience, you should spend some time getting to know the product before completing this Study Guide or taking the CLE exam. To do this, you should purchase or borrow three items:
An Easy-To-Read Linux Study Guide Unfortunately, many of the Linux guides on the market today are not well written and tend to assume a lot more knowledge than the average new user has. Look for a title that is geared toward the newuser audience.
A Copy of SUSE LINUX Enterprise Server (SLES) 8 You can download an evaluation copy from www.novell.com. That's the good news. The bad news is that SLES 8 comes on four CDs. Each CD download is almost 650MB in size. Unless you have a really fast Internet connection, you will probably need to purchase a copy from your local computer store or from www.suse.com. You may be asking, "Why can't I use Red Hat or some other Linux distribution?" The CLE objectives are written to SLES 8. This is the distribution you will be expected to use in the CLE exam and the distribution we will be using in this Study Guide.
A Pentium II or later PC to use as a lab machine Although it is possible to make Linux and Windows coexist on the same PC hardware using the grub or lilo bootloaders, it's a good idea for you, as a new learner, to use dedicated hardware until you have developed a degree of experience with the operating system.
With these items in hand, go through the Linux study guide and familiarize yourself with the operating system. You will then be prepared to complete this Study Guide and the CLE exam.
Novell also assumes you have a certain degree of experience with eDirectory. You need to know concepts such as trees, objects, attributes, rights, containers, leafs and inheritance. If these terms leave you bewildered, you will need additional training.
Chapter 5, "NNLS Installation and Administration," presents a detailed, yet concise, overview of eDirectory concepts. Try using the content of this chapter first. If it still isn't enough to bring you up to speed, Novell offers an eDirectory fundamentals course (Course 3017) that you may want to consider.
In addition to Linux and eDirectory, you should also have a solid background in computer networking before attempting to complete this Study Guide. The CLE certification assumes that you already have your Network+ certification from CompTIA or have equivalent experience.
If you can answer the question, "What's the default subnet mask for a Class B IP address?" without hesitation, you are probably prepared to begin study for the CLE. If not, you should probably purchase Network+ study materials and review them before completing this Study Guide.
CLE Objectives
With this information in mind, we're ready to move on to a review of the CLE objectives. Be aware that you will be expected to know the concepts and do the tasks specified in each objective.
With many certifications, it's possible to pass the associated exam even if you lack proficiency with a few objectives, as long as you have a good understanding of the other remaining objectives.
With the CLE, however, you must have a strong working knowledge of all the objectives. To be blunt, the CLE Practicum is an unforgiving pass/fail exam. More candidates fail it than pass it. This is due to the way Novell structured the CLE exam, which will be covered in more depth later in this chapter.
Novell's CLE exam incorporates multiple objectives into a given testing scenario. If you lack proficiency with one of the objectives, you could potentially fail the entire scenario, thus failing the exam.
For a list of the CLE objectives, see CLE Certification Objectives.
Using this Study Guide
To pass the CLE exam, you must have both the theoretical knowledge and the technical skills reflected in the objectives. This Study Guide is designed to provide you with both of these elements.
First, each chapter in this Study Guide presents conceptual information related to each CLE objective. For chapters that are heavy with conceptual information, you will find a "Check for Understanding" exercise at the end that you can use to verify that you have mastered the information presented.
It is critical that you take time to complete these activities. Use the results to identify information you may need to review. Doing so will greatly increase the likelihood that you will pass the CLE exam.
Second, each chapter in this study guide, with the exception of this one, includes one or more hands-on exercises to help you gain the Linux and NNLS skills required to pass the CLE exam. As you progress through this guide, you will build a complete NNLS implementation, piece by piece from the ground up.
Again, it is absolutely critical that you complete these exercises. The CLE exam requires that you be able to complete these tasks in a live NNLS environment.
This is a departure from most certification exams in the IT industry today. They generally require you to complete an exam that tests your mastery of only the conceptual subject matter. The CLE, on the other hand, tests your ability to do the tasks specified in the objectives.
To complete these exercises, you will need the following equipment:
A Lab PC This computer must meet the following specifications:
CPU Pentium III 800MHz or later
MEMORY 512MB minimum
HARD DISK 4GB or more
PERIPHERALS Printer, monitor, mouse and keyboard
A Copy of NNLS 1.0 An evaluation copy of NNLS is available from Novell at the product site
A Copy of SLES 8 An evaluation copy of SLES 8 is available from Novell at the product site. NNLS will run on other Linux distributions. However, the only supported distributions are SUSE LINUX Enterprise Server 8 and Red Hat Enterprise Server 2.1. Because SLES 8 is specified in the CLE objectives, this is the distribution used in this Study Guide. If you choose to use a different distribution, some of the steps in the hands-on exercises may not work.
Introduction to the CLE Test Environment
Let's discuss the CLE exam in a little more detail. As mentioned earlier, the CLE exam is called a "practical" exam, and you may hear it referred to as "The CLE Practicum." They mean the same thing.
Why Practical Exams Are Used
Traditional certification exams in the IT industry usually provide the student with a series of multiple-choice, fill-in-the-blank and matching questions, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Identity federation based on the Liberty Alliance specifications requires that users give their consent before identity data is shared.
The strength of these types of exams is the fact that they are very effective at evaluating your mastery of theoretical concepts. They are also easier to create and deliver.
Their weakness is the fact that they don't test your ability to actually perform the tasks specified in the objectives. In other words, they tend to evaluate what you know instead of what you can do. You may have heard the term paper certified before. This term refers to network administrators who have passed the multiple-choice exam for their certification, but who can't actually perform on the job. Novell wanted to make sure this situation didn't happen with the CLE certification.
Novell has been a pioneer in the field of practical testing since its Certified Directory Engineer (CDE) certification was introduced in 1999. Novell has implemented exams that present you with a scenario and then require you, without guidance, to determine the proper resolution and to implement that resolution correctly.
The strength of this strategy is that it truly verifies whether you have mastered the skills specified in the objectives.
Students who pass a practical test are much more likely to be able to perform better on the job than those who pass traditional exams only. To a job applicant, this is of high value. It gives you bargaining power with an employer, allowing you to provide a higher degree of verification of your skill set.
Unfortunately, "certified" IT job applicants have burned many employers over the years. Because their skills were only verified at the conceptual level, their ability to actually do the job was sometimes less than what was necessary.
Practical certification testing helps employers filter out less qualified job applicants. When you apply for a job, employers can have a higher degree of confidence in your abilities if you have successfully completed a practical exam.
You should, however, be aware that the pass rate on practical exams tends to be much lower than traditional exams. To pass the CLE practical exam, you will probably have to spend twice as much time preparing as you would for a traditional certification exam. Interestingly, Novell reports that even though the pass rate on the CLE exam is lower than a traditional exam, most candidates feel the test was a fair one?even those that fail. Some exam-preparation tips are presented later in this chapter.
How the CLE Practicum Works
The CLE Practicum is composed of the components shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Identity federation based on the Liberty Alliance specifications requires that users give their consent before identity data is shared.
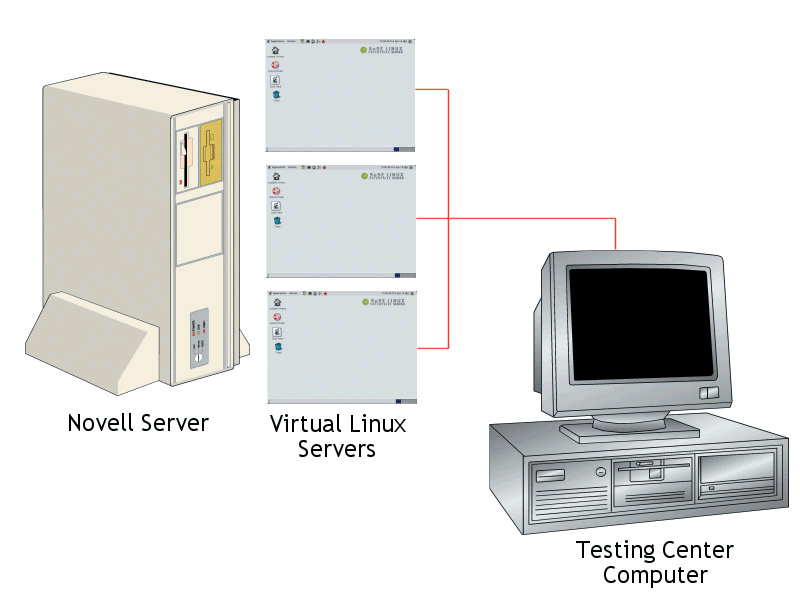
The role of each of these components is as follows.
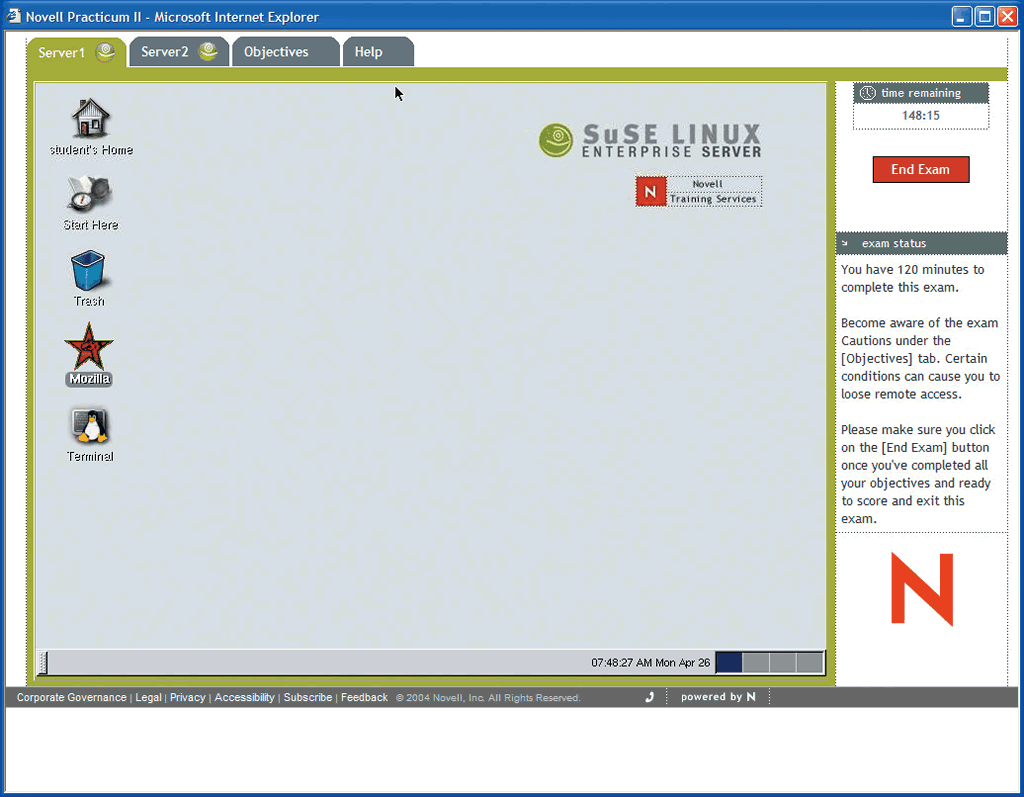
The Testing Center Computer The first component in the CLE Practicum is the testing center computer. In order to complete the Practicum, you must schedule a test with a Novell education partner center. This can be done by visiting the testing center web site. At the testing center, you will use a Web browser on the testing center computer to access the virtual servers running on the Novell server. The CLE exam interface is shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3: Identity federation based on the Liberty Alliance specifications requires that users give their consent before identity data is shared.
The Novell Server The second component in the Practicum is the Novell server. This server is maintained at Novell's Provo campus and is used to run VMWare, a product that allows multiple operating systems to be run simultaneously on a single computer. More information about VMWare can be found at www.vmware.com.
Virtual Servers The final Practicum component is the group of virtual server sessions running on the Novell server. Each session represents a SUSE LINUX server. These servers have been preconfigured using a specific scenario.
Depending on what scenario you are required to complete, you may find that these servers have been deliberately configured incorrectly. To pass the exam, you must correct any errors and implement the requirements of the scenario in these virtual servers.
CLE Practicum Tips and Strategies
When you are in the testing center taking your CLE Practicum, you should keep the following tips in mind. They will save you a lot of trouble!
Follow all the instructions to the letter! When you begin your exam, you will bepresented with detailed instructions on how to complete the exam. Don't skip reading these.
You are accessing the virtual servers using a TCP/IP connection. Never change the IP address, subnet mask, router address or DNS server address of your virtual servers. Doing so will disrupt your ability to access them.reading these.
You will be automatically logged in to the virtual server as a non-root user. If you need root-level access, you should open a terminal session and use the sucommand. Under no circumstances should you log out. You won't be able to log back in.
Remember that the virtual Linux server has several key processes running on it that provide you with remote access at the testing center. Don't kill a running process unless you are absolutely sure you know what it is first. If you accidentally kill a process that provides remote access, your session will be closed.
You should never exit the X Windows System. If you need access to a shell prompt, open a terminal session.
If you need to restart your server, use the reboot command. Never use the halt or logout commands.
On occasion, your mouse cursor may disappear when using Mozilla within the virtual server desktop. It may or may not come back. (Sometimes wiggling the mouse quickly will cause it to reappear.) If you can't get your cursor back, you must exit Mozilla by pressing Ctrl+Q and then restart it.
It can take some time to load iManager on your server for the first time. Be patient. After it is loaded into memory on your virtual server, it should run at a reasonable speed.
Remember that you are completing the exam on a virtual server being accessed through a remote-access Web connection. It's going to run much slower than a real server. Exercise patience and don't get "click happy."
As mentioned previously, passing the CLE Practicum will require considerably more effort than traditional certification exams. Before you start studying the CLE objectives, we need to spend some time in this chapter discussing some test-taking strategies that will help you be successful in your Practicum experience.
Read the Scenario
Remember that the CLE Practicum is scenario based. Novell has a number of different CLE scenarios. Each one is slightly different from the others. When you sign on at the testing center, you will be randomly assigned one of these scenarios to complete.
When you receive your scenario, keep the following points in mind:
Read the scenario thoroughly. Due to the time constraints imposed on the Practicum, your first impulse will be to get working right away on your virtual Linux server. Avoid this impulse at all costs. It is imperative that you read through your scenario line by line. The time spent will be well invested.
As you read, carefully analyze the details of your scenario. Your testing center should provide you with scratch paper or a whiteboard for making notes. Use these materials to record the following information:
What is the problem or error condition identified in the scenario?
Are there any special or unusual conditions identified in the scenario?
What criteria must be met in order for the scenario to be considered resolved? (It is critical that you list each item!)
What tests can you run to verify that each success criteria has been met?
Don't assume that your server has been configured properly as you read the scenario. Depending on your scenario, you may have to isolate and resolve various misconfigured parameters.
After you have read through and analyzed your scenario, read it again! Chances are you will find one or more items that you missed. Add these to your scenario analysis.
Plan Your Strategy
After you have thoroughly read and analyzed your scenario, you will be, once again, tempted to immediately dive in and start working on your virtual server. Avoid this impulse at all costs!
Before working on your server, it is imperative that you use your scenario analysis to create a plan of action. Again, using your testing center scratch paper or whiteboard, identify each of the tasks you must complete in order to resolve the condition in the scenario. List them in the order that they must be completed.
Implement Your Plan
When you have thoroughly analyzed your scenario and have planned your strategy, you can now give in to your impulse and actually start working on your virtual server. If you've organized yourself properly, you should be able to complete the scenario quickly and methodically.
As you do, it is important that you keep your eyes open for hidden issues that may not have been overtly described in the scenario. Be prepared to reevaluate your plan at any time.
Test the Resolution
As a part of your overall plan, you should have identified how you would test your resolution to ensure that you have completed each criterion in the scenario. (It's interesting to note that many CLE candidates fail to complete this simple task.)
When you have completed each task in your plan, implement your evaluation plan and verify that the scenario has been truly completed.
There's a better-than-average chance that you will find one or more problems remain unresolved. Identify each of these and, again, develop a plan for how you will work them out.
If you study the materials in this book, practice with the lab exercises, follow the exam instructions, plan your strategy and test your implementation, you will greatly increase your chances of passing the CLE practicum. Let's review what you learned in this chapter.
CLE Certification Objectives:
Describe the characteristics of Linux.
Use the Linux command-line interface.
Manage the Linux file system.
Manage Linux applications.
Manage Linux network interfaces.
Describe Novell Nterprise Linux Services (NNLS).
Perform an NNLS installation.
Manage NNLS with Red Carpet.
Describe the purpose of eDirectory.
Describe how eDirectory works.
Perform eDirectory administration tasks.
Manage user objects with iManager.
View user information with eGuide.
Access a Linux server with Linux User Management (LUM).
Describe the purpose of DirXML.
Describe how DirXML works.
Install the DirXML Starter Pack on Linux.
Implement the Delimited Text driver for DirXML.
Implement the eDirectory driver for DirXML.
Describe the purpose and architecture of iFolder.
Install and configure iFolder.
Describe the purpose and architecture of Samba.
Install and configure Samba.
Describe the role and function of NetStorage.
Install and configure NetStorage.
Identify the benefits of iPrint.
Describe how iPrint works.
Install and configure iPrint.
Print with iPrint.
Identify NetMail features.
Describe NetMail components.
Describe how NetMail works.
Install NetMail.
Configure and use NetMail.
Describe Virtual Office.
Install Virtual Office.
Configure Virtual Office.
Novell Press Titles (www.novellpress.com)
Titles Now Available
Novell NetWare 6.5 Administrators Handbook
ISBN: 0-7897-2984-9, 800 pages, $49.99
Novell ZENworks For Desktops 4 Administrator's Handbook
ISBN: 0-7897-2985-7, 500 pages, $39.99
Novell ZENworks For Servers 3 Administrator's Handbook
ISBN: 0-7897-2986-5, 512 pages, $39.99
Novell GroupWise 6.5 Administrator's Guide
ISBN: 0-7897-2982-2, 800 pages, $59.99
CNA Study Guide For NetWare 6
ISBN: 0-7897-2980-6, 650 pages, $74.99
Novell GroupWise 6.5 User's Handbook
ISBN: 0-7897-2983-0, 320 pages, $29.99
Novell's CNE Update To NetWare 6 Study Guide
ISBN: 0-7897-2979-2, 576 pages, $69.99
Titles Coming Soon
CNE Study Guide For NetWare 6
ISBN: 0-7897-2988-1, $99.99
CLE Study Guide
Novell's Guide To Troubleshooting eDirectory
ISBN: 0-7897-3146-0, $59.99
Novell ZENworks 6.5 Administrator's Guide
ISBN: 0-7897-3204-1, $59.99
Summary
In this chapter, you were introduced to the CLE certification from Novell. You learned about its purpose, its audience and how it is delivered.
You then learned about the nature of the CLE practical testing environment. You learned about the various components that comprise the practical exam.
Finally, you were presented with some test-taking tips and strategies for increasing your chances of passing the CLE practical exam.
In the next two chapters, you will learn the basics of Linux. After that, we will dig into the various components of NNLS as we progress through the rest of the book.
* Originally published in Novell Connection Magazine
Disclaimer
The origin of this information may be internal or external to Novell. While Novell makes all reasonable efforts to verify this information, Novell does not make explicit or implied claims to its validity.