Enabling FTP Services for intraNetWare
Articles and Tips:
01 Jul 1998
Have you ever sat at home, wishing you could somehow access a file on your company's intraNetWare network? Have you ever worked from a non-NetWare client and needed a file from an intraNetWare volume? UNIX systems solve these types of problems for UNIX users with File Transfer Protocol (FTP), and FTP Services for intraNetWare can solve these types of problems for intraNetWare users.
FTP is a TCP/IP service that enables you to copy a file from any Internet host to any other Internet host, regardless of the host's platform. (If you are not familiar with FTP, see "What Is File Transfer Protocol?".) Need a file from the office? With an FTP server running on your company's network, you can get that file by dialing in to the Internet and downloading the file using the FTP client software on your home computer.
Need a file from another file system on your company's network? If you are using a workstation that has FTP client software installed, you can download the file from the other file system's FTP server.
FTP client software exists for almost every platform, and nearly every World-Wide Web browser provides FTP capabilities. Also, FTP server software exists for most network operating systems--including intraNetWare.
FTP Services for intraNetWare is included with intraNetWare. By installing FTP Services for intraNetWare on one server, you can enable users to access files from any intraNetWare server on your company's network--not just the server running FTP Services for intraNetWare. As part of FTP, you can require users to authenticate to your company's network before accessing any files. And of course, through Novell Directory Services (NDS), you can control each user's ability to access files on a file-by-file basis, regardless of how users choose to access these files.
This article explains how to install, enable, and access FTP Services for intraNetWare. This article also explains how to configure and monitor FTP Services for intraNetWare.
INSTALLING AND ENABLING FTP SERVICES FOR INTRANETWARE
You use the INSTALL NetWare Loadable Module (NLM) to install FTP Services for intraNetWare, which is located on the FTP Services for intraNetWare CD-ROM that ships with intraNetWare. Before you install FTP Services for intraNetWare, your company's network must meet the following requirements:
The server must be running NetWare 4.1 or above.
The server must have at least 12 MB of RAM.
The server must have 5 MB of available hard drive space.
DOS must be resident on the server. (You cannot install FTP Services for intraNetWare if you have entered the REMOVE DOS command at the server console.)
TCP/IP must be loaded and configured on the network, which must be using the Ethernet_II frame type.
To install FTP Services for intraNetWare, you must be able to log in to the server as the ADMIN user or as another user with the following rights:
All rights except Supervisor and Access Control to the SYS:SYSTEM and SYS:ETC directories on the intraNetWare server
Supervisor rights to the Organization or Organizational Unit (OU) object in which the installation program must create new NDS objects
If your company's network meets these requirements, you complete the following steps to install and enable FTP Services for intraNetWare:
At the server console, enter the following command:LOAD INSTALL
Select the Product option from the Installation Options menu.
Select the Install a Product Not Listed option from the Other Installations Options menu. The installation program prompts you to insert the first installation diskette for the product you want to install. (By default, the installation program looks in the server's A drive.)
Insert the FTP Services for intraNetWare CD-ROM into the server's CD-ROM drive.
Press the F3 key, and enter the path to the NWUXPS directory on the FTP Services for intraNetWare CD-ROM. For example, you might enter D:\NWUXPS for a server that is configured to read the CD-ROM through the D drive. After entering the correct directory path, press the Enter key.
A message appears, explaining that the installation program found a README file on the CD-ROM. Press the Escape key to continue.
A message appears, asking if you want to read the README file. Select No, and press the Enter key.
The installation program begins installing the FTP Services for intraNetWare files and prompts you to enter the directory path to the server's SERVER.EXE file. (On many servers, the directory path is C:\NWSERVER.) Enter the correct directory path, and press the Enter key.
A message appears, asking if you want to install the documentation. Select Yes or No, and press the Enter key.
If a message appears warning you that the HOSTS.DB file does not exist, press any key to clear the message. If you were going to run Domain Naming System (DNS) on this server, you would need to provide a HOSTS.DB file, but you do not need this file to run FTP Services for intraNetWare.
After installing the FTP Services for intraNetWare files, the installation program loads the UNICON utility, which prompts you to log in to the NDS tree. All of the files the server needs to run FTP Services for intraNetWare now reside on this server, but you must use the UNICON utility to enable these services.
The UNICON utility displays the Available Name Service Options menu, which includes options to install DNS and Network Information Services (NIS). To run FTP Services for intraNetWare, the server does not need either DNS or NIS, so select the No DNS and Remote NIS option. (The FTP Services for intraNetWare CD-ROM also includes software for UNIX file and print connectivity, which requires DNS and NIS.)
The UNICON utility displays a message about DNS and NIS. Press the Enter key to continue.
The Setup (No DNS and Remote NIS) Name Service dialog box appears. Accept the default values, and press the Escape key to continue.
A message appears, asking if you want to continue installing name services. Select Yes, and press the Enter key.
Another message appears, asking if you want to initialize the NIS database. Select No, and press the Enter key.
The Product Initialization Status screen appears. When the initialization process is completed, press the Escape key to continue.
The Running Services screen, which is empty, appears. Press the Insert key.
Select the FTP Server option, and press the Enter key.
Press the Escape key five times to close all of the installation screens, and press the Enter key to unload both the installation program and the UNICON utility.
After you enable FTP Services for intraNetWare, the FTP Services NLMs remain unloaded until a user requests an FTP session. The first time a server running FTP Services for intraNetWare receives an FTP login request, the server loads the FTP Services NLMs. By loading these NLMs only when they are needed, the server saves memory and other system resources. If no users request an FTP session for the period of time that you specify in the Idle Time Before FTP Server Unloads parameter, the server automatically unloads the NLMs. (See "Changing Parameters.")
ACCESSING FTP SERVICES FOR INTRANETWARE
At this point, you have installed and enabled FTP Services for intraNetWare. If you want to allow all users to access your company's network through FTP, you don't need to make any configuration changes. By default, FTP Services for intraNetWare enables all NDS users to access your company's network through FTP. (If you want to control FTP access to your company's network, see the "Restricting FTP Access" section.)
However, FTP Services for intraNetWare does enforces all of the intraNetWare file system access controls you have established. For example, suppose that user Jane did not have rights to access the SYS volume on a particular server. If Jane tried to access the SYS volume from a workstation running intraNetWare client software, FTP Services for intraNetWare would prevent Jane from accessing this volume through FTP. Also, by default, FTP Services for intraNetWare does not allow anonymous users to use FTP to retrieve files from your company's network.
After you enable FTP Services for intraNetWare, users can access your company's network through FTP client software such as the FTP client software available in Netscape Navigator and Microsoft Internet Explorer. For example, if user Sean wanted to access files in the HOME/SEAN directory on a particular SYS volume, he would enter a URL similar to the following in his web browser:
ftp://sean:password@www.ftpserver.com/SYS/HOME/SEAN
You should notify users that FTP Services for intraNetWare supports only DOS and Network File System (NFS) name spaces. By default, FTP Services for intraNetWare presents all directory lists from the DOS name space. As a result, users will be unable to view the complete names of files stored in LONG name spaces. All of the files users transfer will have a shortened DOS name.
CONFIGURING AND MONITORING FTP SERVICES FOR INTRANETWARE
FTP Services for intraNetWare allows you to control certain aspects of FTP sessions, such as the maximum length of each session. You can also monitor active FTP sessions, manually disconnect users from the server running FTP Services for intraNetWare, and restrict users' FTP access.
To configure and monitor FTP Services for intraNetWare, you use the UNICON utility. The next sections explain how you can configure FTP Services for intraNetWare. (You load the UNICON utility by typing LOAD UNICON at the server console.)
Changing Parameters
If you want to impose more controls on FTP sessions, you must change the FTP Services for intraNetWare parameters. To change these parameters, you complete the following steps:
Select the Manage Services option from the UNICON utility's main menu.
Select the FTP Server option, and then select the Set Parameters option.
The FTP Server Parameters screen appears. (See Figure 1.) To change a parameter, you highlight the value you want to change, type the new value, and press the Enter key.
Figure 1: You can use the UNICON utility to configure FTP Services for intraNetWare.
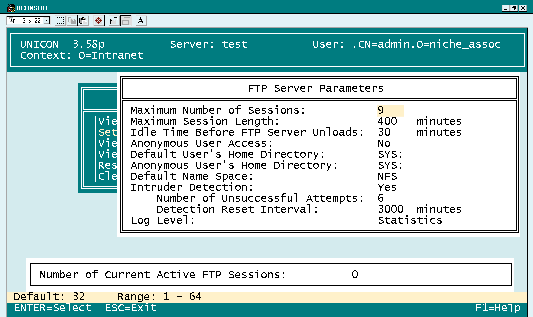
From the FTP Server Parameters screen in the UNICON utility, you can configure the following parameters:
Maximum Number of Sessions. This parameter determines the maximum number of users that can concurrently connect to the network through FTP Services for intraNetWare.
Maximum Session Length. This parameter determines the maximum number of minutes a user can remain connected to the network before the server automatically disconnects this user's FTP session.
Idle Time Before FTP Server Unloads. This parameter determines the number of minutes without any FTP activity that the server should wait before unloading FTP Services NLMs to conserve system resources.
Anonymous User Access. This parameter indicates whether or not you allow anonymous users to connect to the network through FTP.
Default User's Home Directory. This parameter specifies the default directory path for a user who does not have a home directory on the server.
Anonymous User's Home Directory. This parameter specifies the default directory path for anonymous users.
Default Name Space. This parameter specifies the name space used to present directory information to users. You can select DOS or NSF.
Intruder Detection. This parameter indicates whether or not the server prevents a user from connecting to the network after several unsuccessful login attempts.
Number of Unsuccessful Attempts. This parameter specifies the number of unsuccessful login attempts the server accepts from a user before preventing that user from accessing the network.
Detection Reset Interval. This parameter specifies the number of minutes the server locks out a user who has triggered intruder detection.
Log Level. This parameter determines what information is recorded in the FTP log file. If you enter NONE, the server does not log FTP sessions. If you enter LOGINS, the server records user logins. If you enter STATISTICS, the server records logins and the number of files users transfer to and from the network. If you enter FILE, the server records user logins, statistics, and details about every FTP transaction made during a user's FTP session.
Viewing FTP Session Statistics
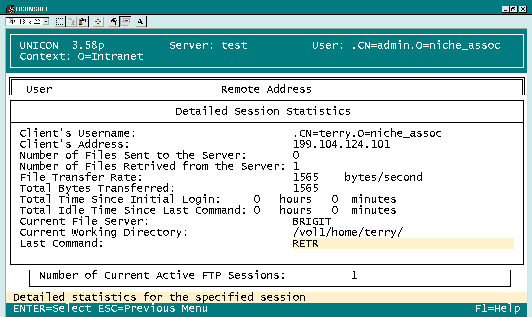
You can view detailed FTP session statistics about each user connected to your company's network via FTP Services for intraNetWare. (See Figure 2.) To view these statistics, you complete the following steps:
Figure 2: With the UNICON utility, you can monitor a user's FTP session, viewing information such as the user's name and IP address.
Select the Manage Services options from the UNICON utility's main menu.
Select the FTP Server option, and then select the View Current FTP Statistics option.
A list of all active FTP sessions appears. To view detailed statistics about a particular FTP session, highlight that session, and press the Enter key.
The Detailed Session Statistics screen appears. (See Figure 2.) You can view the user's name (including NDS context), the user's IP address, the number of files the user has sent and received, the speed of the last file transfer, the total number of bytes transferred in this session, how long the user has been connected to the server, the user's current server and directory, and the last FTP command the user issued to the FTP server.
Deleting an Active FTP Session
Just as you can disconnect an intraNetWare client's connection to a server, you can disconnect an FTP client's connection to FTP Services for intraNetWare. To disconnect an FTP client's connection to FTP Services for intraNetWare, you complete the following steps:
Select the Manage Services option from the UNICON utility's main menu.
Select the FTP Server option, and then select the View Current FTP Statistics option.
A list of all active FTP sessions appears. To disconnect a session, highlight that session, and press the Delete key.
A message appears, asking you to verify that you want to delete the session. Select Yes, and press the Enter key.
The UNICON utility does not immediately update the list of active FTP sessions. However, the number of active FTP sessions displayed at the bottom of the screen is reduced by one. To refresh the FTP session list, repeat step 1.
Restricting FTP Access
You can grant and deny FTP access to your company's network by editing the RESTRICT.FTP file. In this file, you can specify User, Group, or container objects and the level of access you want to grant these objects.
To edit the RESTRICT.FTP file, you complete the following steps:
Select the Manage Services option from the UNICON utility's main menu.
Select the FTP Server option, and then select the Restrict FTP Access option.
Edit the RESTRICT.FTP file as needed, and press the Escape key.
A message appears, asking if you want to save the changes you have made. Select Yes.
You can grant or deny FTP access to individual users and to groups of users. For example, you could deny FTP access to all users in the ACME container object while granting the ADMIN user access to establish an FTP connection. To do so, you would type the following lines in the RESTRICT.FTP file:
.ADMIN.O=ACME ACCESS=ALLOW *.O=ACMEACCESS=DENY
You can also allow users to access only files on the server running FTP Services for intraNetWare, preventing users from accessing files on other intraNetWare servers. You can also grant access only if users request an FTP session from a workstation with a particular Internet host name or IP address. In addition, you can allow users to read files while restricting these users from writing files to your company's network. To learn how to format such FTP commands, you can read the instructions at the beginning of the RESTRICT.FTP file, or you can read theAdministrator's Guidein the online documentation.
CONCLUSION
By installing and enabling FTP Services for intraNetWare, you provide users with another way to access files on your company's network. FTP Services for intraNetWare can be especially useful for users who work from home or travel frequently and need to upload files to or download files from the network. Because FTP Services for intraNetWare provides FTP services regardless of the server's or the client's platform, you can grant anyone with FTP client software access to files stored on an intraNetWare server.
Terry L Jeffress works for Niche Associates, an agency based in Salt Lake City.
NetWare Connection,July 1998, pp. 25-31
What Is File Transfer Protocol?
If you have downloaded files from the Internet, you have probably used File Transfer Protocol (FTP). FTP is a TCP/IP service that enables you to transfer a file from any Internet host to any other Internet host. It doesn't matter where the two computers are located, how they are connected, or even whether or not these computers are using the same operating system.
FTP follows a client-server model: You use FTP client software to connect to an FTP server. When you begin an FTP session, the FTP server responds with a request for your username and password. After the FTP server authenticates you, you can enter FTP commands. For example, you could enter an FTP command requesting a particular file from the FTP server. The FTP server would respond to this request by sending the file.
Many companies use FTP to allow Internet users to access demonstration software and other files stored on the companies' networks. In most cases, these companies allow any Internet user to access the files without providing a username and password. Internet users that can access files through FTP without providing a username and password are called anonymous users.
When you use FTP from a UNIX workstation or through a Telnet session, you usually have to enter FTP commands through a command-line interface. However, if your operating system supports a GUI, the FTP client software you are using probably displays a simple interface and enters all of the FTP commands for you. For example, most Windows-based FTP client software displays a list of the FTP server's files in a window that looks similar to the Windows Explorer interface, enabling you to transfer files from this server as easily as you copy files from one directory to another.
Using FTP to access files is, in many ways, similar to using intraNetWare to access files. Both FTP and intraNetWare use the client-server model. To access files on an intraNetWare server, a user runs intraNetWare client software, which contacts the server. This server then authenticates the user and grants this user access only to the files to which he or she has rights.
An FTP server, like an intraNetWare server, enforces all of the file system access controls you have established on the FTP server. As a result, an FTP server does not allow you to view, modify, or delete files to which you have not been granted the necessary rights.
NetWare Connection, July 1998, p. 29
* Originally published in Novell Connection Magazine
Disclaimer
The origin of this information may be internal or external to Novell. While Novell makes all reasonable efforts to verify this information, Novell does not make explicit or implied claims to its validity.