Preserving WAN Bandwidth
Articles and Tips:
01 Aug 1997
As you expand your company's network to include more servers, workstations,and WAN links, network performance can become a problem. To ensure thatyou are not wasting bandwidth, you should examine the type of communicationsthat are being sent across the network. For example, if your company's networkincludes a dial-on-demand WAN link, such as an Integrated Services DigitalNetwork (ISDN) line between two offices, you need to eliminate unnecessarycommunications that initiate this WAN link.
Because IntranetWare and NetWare devices perform several processes tomaintain connectivity, these devices may be sending unnecessary communicationsover your company's WAN link. This article examines how processes such asNetWare serialization, NetWare Core Protocol (NCP) watchdog, SPX keep-alive,and queue sampling affect a WAN link. This article then explains how toprevent these processes from creating network traffic across a WAN link.
NETWARE SERIALIZATION
Like many products, IntranetWare, NetWare 4, and NetWare 3 use a serializationprocess to detect copyright violations. Approximately every 66 seconds,each IntranetWare or NetWare server sends five serialization packets toother IntranetWare or NetWare servers on the network. These serializationpackets are IPX packets that are addressed to serialization socket 0x0457and contain the serial number of the transmitting server. (See Figure 1.) Although serialization packets provide onlycopy-protection information, they can consume bandwidth on your WAN link.If your company has a dial-on-demand WAN link, serialization packets caneven establish this link between two servers.
Figure 1: IntranetWare and NetWare serialization occurs approximately every 66 seconds.
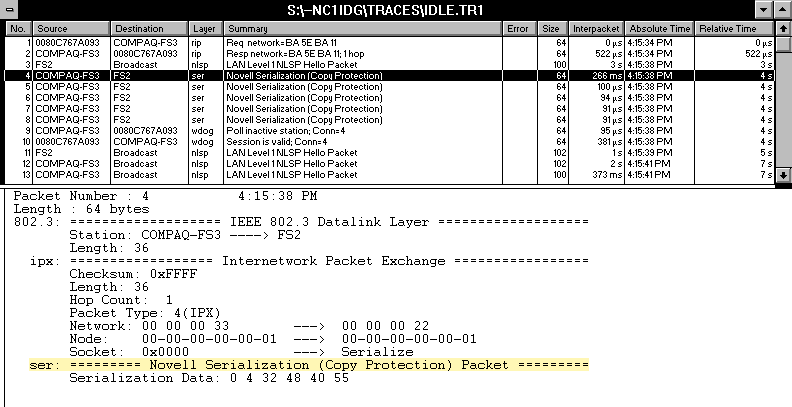
Despite what you may have heard, you can use routers on each side ofthe WAN link to filter out serialization packets without affecting the wayIntranetWare and NetWare servers communicate. In fact, many routers, suchas Novell's NetWare MultiProtocol Router (MPR) 3.1, filter out serializationpackets across a dial-on-demand WAN link by default.
NCP WATCHDOG
When you log in to an IntranetWare or NetWare server, the server beginsto monitor your workstation's connection for activity. If you log out ofa server, the Novell client on your workstation sends a Destroy ConnectionNCP request to the server, which clears your workstation's connection IDnumber. If you simply turn off your workstation without logging out of thenetwork, however, the Novell client on your workstation cannot send a DestroyConnection NCP request to the server. As a result, the server does not clearyour workstation's connection ID number.
IntranetWare and NetWare use the NCP watchdog process to identify andterminate invalid connections. If you log in to a server and do not communicatewith this server within a specified amount of time, the server sends yourworkstation an NCP watchdog request to determine if your workstation's connectionis still valid. (See Figure 2.)
Figure 2: An IntranetWare or NetWare server sends NCP watchdog packets to identify valid connections.
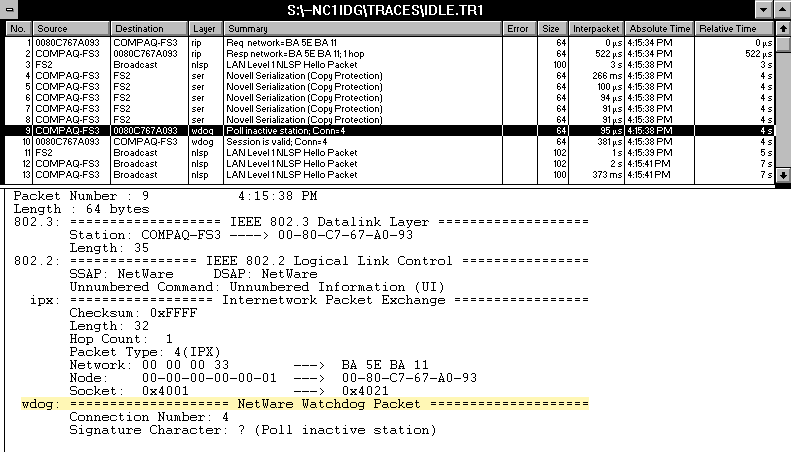
If the Novell client is loaded on your workstation, this client sendsan NCP watchdog reply to ensure that the server does not clear your workstation'sconnection. If the Novell client on your workstation does not send an NCPwatchdog reply (because you shut off your workstation, for example), theserver sends another NCP watchdog request. The server repeats this processthe number of times specified by the Number of Watchdog Packets SET parameter.After reaching this number, the server assumes that the workstation's connectionis invalid and clears the connection.
By default, an IntranetWare or NetWare server sends an NCP watchdog requestafter your workstation's connection has been inactive for five minutes.If your company has a dial-on-demand WAN link and no user is accessing thislink, you certainly don't want the NCP watchdog process to establish thislink because the connection has been idle five minutes.
To avoid establishing a WAN link for the sole purpose of sending andreceiving NCP watchdog packets, some routers perform NCP watchdog spoofing:If the server and your workstation are separated by a dial-on-demand WANlink, the local router replies to the NCP watchdog request on behalf ofyour workstation. As a result, a WAN link is not established. NetWare MPR3.1 provides an NCP watchdog spoofing option, and Cisco's IOS software includesan IPX watchdog spoofing command that performs the same function.
Because these routers perform NCP watchdog spoofing, your workstation'sconnection remains intact unless you log out of the network. If you wantto periodically clear connections on your server, you can have this serverforce every workstation to log out at a predetermined time, such as 9 p.m.In this way, all connections are available the next day.
If you do not have a router that performs NCP watchdog spoofing, youcan reduce the traffic sent across the WAN link by increasing the valuesfor three SET parameters:
Delay Before First Watchdog Packet (default: five minutes)
Delay Between Watchdog Packets (default: one minute)
Number of Watchdog Packets (default: 10 watchdog packets)
The default values apply to IntranetWare, NetWare 4, and NetWare 3. Youcan use the SET utility to change these parameters on your server. For IntranetWareand NetWare 4, you can also use the SERVMAN utility.
SPX KEEP-ALIVE
Because SPX applications are connection oriented, each SPX applicationperforms an SPX"handshake"with its partner before transferringdata. Each side of an SPX connection is called a partner. For example, ifyou were to use Novell's RCONSOLE utility, this utility would instruct theNovell client on your workstation to initiate a connection with the serverthat supports the RSPX and REMOTE NetWare Loadable Modules (NLMs). The SPXpartners in this case are the Novell client (acting on behalf of the SPXapplication) and the server.
Because an SPX application sends an acknowledgment request with the databeing transmitted, the SPX partner sends an acknowledgment packet afterreceiving this data. The following are common SPX applications:
NetWare for SAA Gateway
Btrieve
Print server applications such as Novell's PSERVER utility and Hewlett-Packard's JetDirect
Backup applications such as Cheyenne's ARCserve and Seagate's Backup Exec for NetWare
SPX applications such as the ones listed above use a keep-alive, or watchdog,process that is similar to the NCP watchdog process: By default, the SPXpartners send watchdog packets to each other after their connection hasbeen idle six seconds. For example, Figure 3 shows SPX watchdog traffic from an idle RCONSOLE session.
Figure 3: An idle RCONSOLE session initiates the SPX watchdog process.
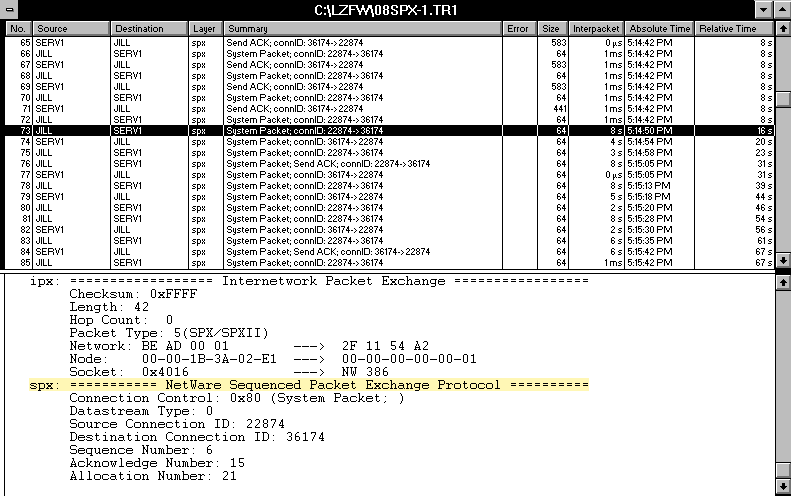
You can decrease SPX watchdog traffic in the following ways:
Increase the time before the SPX watchdog process begins, and increase the interval between the SPX watchdog packets.
Disable the SPX watchdog process at the workstation to stop the Novell client from sending SPX watchdog requests to the server. (However, the client will still answer SPX watchdog requests from the server.)
Purchase a router that can perform SPX watchdog spoofing.
Increase Time Before the SPX Process Begins
To decrease the number of SPX watchdog packets sent over a WAN link,you can change the following SPX parameters.
SPX Watchdog Verify Timeout. This parameter specifies the time in ticks that an SPX partner waits before requesting a watchdog packet from its SPX partner. (A tick is approximately 1/18 of a second. Default: 108 ticks.)
SPX Ack Wait Timeout. This parameter specifies the time in ticks that an SPX partner waits for an acknowledgment packet before resending an SPX watchdog packet. (Default: 54 ticks.)
SPX Watchdog Abort Timeout. This parameter specifies the time in ticks that the SPX partner waits without receiving an acknowledgment packet from its partner before concluding that the connection is no longer valid. (Default: 540 ticks.)
For example, to make the server wait a longer time before sending anSPX watchdog query, you would increase the SPX Watchdog Verify Timeout parameterand the SPX Ack Wait Timeout parameter. You could increase the SPX WatchdogVerify Timeout parameter to 14 seconds, and you could increase the SPX AckWait Timeout parameter to three minutes.
On an IntranetWare or NetWare 4 server, you can use the INETCFG utilityto change the SPX parameters. (You must load the INETCFG utility at theIntranetWare or NetWare 4 server console.)
You can also change the SPX parameters at the workstation level. If youare using Novell's NETX shell or Virtual Loadable Module (VLM) client, youcan change SPX watchdog parameters in the NET.CFG file. If you are usingNovell's IntranetWare client or NetWare Client 32, you can change the SPXparameters by accessing your Windows 95 Control Panel. Then you select Network,IPX 32-bit Protocol for Novell NetWare Client 32, and SPX.
Changing these parameters can significantly reduce the overhead on aWAN link. If you have a dial-on-demand WAN link, however, you should disablethe SPX watchdog process or purchase a router that performs SPX spoofing.
Disable the SPX Watchdog Process
You can also prevent an SPX application on your workstation from usingthe SPX watchdog process to periodically validate SPX connections. If youare using Novell's NETX shell or VLM client, you can disable the SPX watchdogprocess by entering SPX WATCHDOGS = OFF under the PROTOCOL IPX heading inthe NET.CFG file.
Of course, the Off setting specifies that the workstation cannot usethe watchdog process. However, using the Off setting does not disable theSPX watchdog process at the server. If the server sends an SPX watchdogrequest to your workstation, the Novell client still answers this request.
If you are using the IntranetWare client or the NetWare Client 32, youcan disable the SPX watchdog process by accessing your Windows 95 ControlPanel. Then select Network, IPX 32-bit Protocol for Novell NetWare Client32, and SPX. You must then deselect the Allow Connection Watchdogging option.
If you want to disable the SPX watchdog process at the server, you canuse the SPXWDOG NLM. You can download this NLM from the Novell Support ConnectionWorld-Wide Web (WWW) site at http://support.novell.com. (Use the search engine to find the STRTL5.EXE file.)
Purchase a Router That Performs SPX Watchdog Spoofing
To eliminate SPX watchdog traffic across a WAN link, you can use a routerthat performs SPX watchdog spoofing. For example, Cisco's IOS Software 11.1includes an IPX/SPX spoofing parameter that enables the router to respondto SPX watchdog packets on behalf of your workstation. (For more informationabout Cisco's IOS Software 11.1, see http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/732/Releases.)
QUEUE SAMPLING
Your printer configuration can also generate unnecessary traffic if youassign a print server to a remote printer that is located on the other sideof a WAN link. When a printer is idle, the print server assigned to thatprinter queries its print queue at regular intervals. This process is calledqueue sampling, orqueue polling.
IntranetWare and NetWare 4 have a default queue sampling interval offive seconds; NetWare 3 and NetWare 2 have a default queue sampling intervalof 15 seconds. (Thequeue sampling intervalis the number of secondsbetween each query.) Unless you have changed the default setting, the printserver looks for jobs in the print queue every five to 15 seconds, dependingon which version of the operating system you are running. This queue samplingis a nightmare for WAN links.
You can solve this problem in one of two ways:
Do not configure a print server to service print queues that are located on the other side of a WAN link.
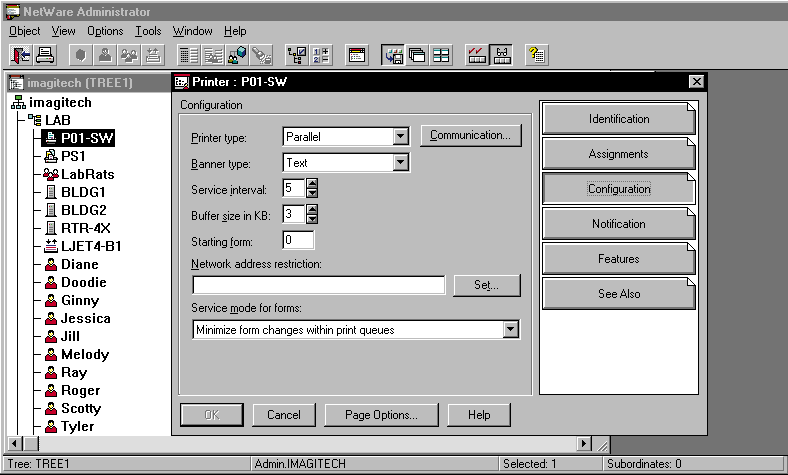
Use Novell's NetWare Administrator (NWADMIN) utility or Novell's PCONSOLE utility to increase the queue sampling interval to the maximum setting, which is 255 seconds. (See Figure 4.)
Figure 4: You can use the NWADMIN utility to configure a higher queue sampling interval.
CONCLUSION
Analyzing the communications sent across your company's network is essential--whatyou don't know can hurt you. If network devices are sending serializationpackets, NCP watchdog packets, SPX watchdog packets, and queue samplingpackets across a WAN link, you should prevent these packets from crossingthe WAN link or reduce the number of packets being sent. Taking these stepswill improve performance and even reduce costs if your company has a dial-on-demandWAN link and pays for this link on a per-packet basis.
Laura Chappell researches, writes, and lectures on NetWare protocolperformance, troubleshooting, and optimization. She speaks at NetWare Conferencesand presents customized training courses on network analysis. You can reachLaura at lchappell@imagitech.com, and you can view her trace files and presentation notes at www.imagitech.com.
NetWare Connection, August 1997, pp.32-37
* Originally published in Novell Connection Magazine
Disclaimer
The origin of this information may be internal or external to Novell. While Novell makes all reasonable efforts to verify this information, Novell does not make explicit or implied claims to its validity.