Convergence of Technology: Integrating CollabraSpace Collaboration Server with Novell exteNd
Articles and Tips: article
Product Developer
CollabraSpace, Inc.
john.madden@collabraspace.com
Gary Daigle
Director of Business Development
CollabraSpace, Inc.
gary.daigle@collabraspace.com
01 Dec 2002
This AppNote explains how to integrate CollabraSpace's CollabraSuite software components into Novell's portal framework using the Novell exteNd Web application development products.
- Introduction
- Server Files
- Configuration Files
- Deploying the EAR Files
- Starting the Collaboration Server
- Developing a Portal Component
- Conclusion
|
Topics |
developer tools, portal applications, third-party product integration, Web application development |
|
Products |
Novell exteNd 3.7, CollabraSpace CollabraSuite 2.2.6 |
|
Audience |
developers, integrators |
|
Level |
intermediate |
|
Prerequisite Skills |
familiarity with Web application development |
|
Operating System |
n/a |
|
Tools |
none |
|
Sample Code |
yes |
Introduction
Portal products continue to be at the center of technology convergence. Integrated application frameworks assembled portal components and Web services that offer off-the-shelf integration are now a standard feature in the portal product mix. Recognizing that seamless integration of collaborative functionality is crucial to today's information management systems prompted CollabraSpace to assemble a suite of graphical real-time collaboration components that allows its users to build customized collaborative environments made up of the following components:
Campuses, which are the virtual grounds that buildings are housed on
Buildings, which are virtual structures that house operations and reside within the campus
Floors, which are the divisions of buildings, much like a physical structure
Rooms, which support individual or specific activities and can be configured as offices, conference rooms, and so on
CollabraSpace's CollabraSuite software is developed completely in Java utilizing the Java 2 Enterprise Edition (J2EE) application model, making it deployable to multiple J2EE servers, existing applications, or system frameworks such as portals or other suite products as a complementary technology It adds a layer of collaboration services that deliver target functionality like: content management, knowledge exchange, information organization and retrieval, and expertise location and management. This core functionality offers client interaction presented through the use of applets within dynamically-generated Web pages or from within standalone applications. Coupled with an environment that supports information persistence, rigid security, scalability, and platform independence, CollabraSuite makes it possible for an organization to choose those tools that best match its needs to meet today's real-time business requirements.
This AppNote presents an overview with illustrations of how to integrate and deploy CollabraSuite software components into Novell's portal framework using the Novell exteNd Web application development products.
Server Files
There are five files associated with CollabraSpace's Collaboration Server:
cservice.ear contains all of the code necessary to run the CollabraSpace Collaboration Server from within the Novell eXtend application server.
suiteletfactory.ear contains the HTTP based API for building a Web application (or portlet) using CollabraSpace components.
appServerDeploy.properties contains the various configuration items the Collaboration Server needs to function properly.
ss_cservice_ear.xml is the SilverStream-specific deployment descriptor for the cservice.ear file.
ss_suitelet_ear.xml is the SilverStream-specific deployment descriptor for the suiteletfactory.ear file.
Configuration Files
In order for the Collaboration Server to work, several configuration modifications to the appServerDeploy.properties file are required. These changes are needed so that the server can interact with the network configuration at any given site. Also inside the file are several other configuration items that will most likely need to be changed.
The following table describes each item that might need to be altered.
|
Property
|
Description
|
Required
|
|
AppServer.campus.name |
The name of the Collaboration Campus - a business or organization name, for example. A server will have one campus but potentially many buildings (departments or regional branches, for example). |
yes |
|
AppServer.campus.description |
A description for the Campus |
yes |
|
AppServer.campus.dir |
The directory where the Campus data is stored |
yes |
|
AppServer.building.name |
The name of the Collaboration Building |
yes |
|
AppServer.building.description |
A description for the Building |
yes |
|
AppServer.building.dir |
The directory where the Building data is stored. In the metaphorical sense, this is a department, division, or regional area of an organization. |
yes |
|
AppServer.licenseKey |
The license key provided by CollabraSpace |
yes |
|
AppServer.useSSL |
Turns on secure communication between the clients and the server |
yes |
|
AppServer.adminAccount |
The account used to administer the Campus and Building |
yes |
|
AppServer.adminPassword |
The password for the account used to administer the Campus and Building |
yes |
|
AppServer.clientRegistryHost |
Specifies the CampusDirectory host for client applets to connect. If not set, it will default to AppServer.localHost. This is only necessary when the server is on a NAT network and the clients are not on the same network. In this case, set the property to the external IP address. |
no |
|
AppServer.clientRegistryPort |
Specifies the CampusDirectory port for client applets to connect. If not set, it will default to AppServer.localPort. This is only necessary when there is a firewall performing port forwarding. In this case, set the property to the external port. |
no |
|
AppServer.localHost |
Specifies the host the server will listen on for incoming client connections. If not set, it will default to all network interfaces on the machine. This is only necessary for machines that have multiple network interfaces. |
no |
|
AppServer.localPort |
Specifies the port the server will listen on for incoming client connections. If not set, it will use port 2000. |
no |
|
AppServer.useHttpsFor Sensitive |
Enables the use of HTTPS for any sensitive Web trans- actions such as account creation and login. This requires the Web container to be configured for HTTPS. |
yes |
|
AppServer.httpsPort |
The HTTPS port used by the Web container |
yes |
|
AppServer.httpPort |
The HTTP port used by the Web container |
yes |
Deploying the EAR Files
Both the suiteletfactory.ear and the cservice.ear files must be deployed within the eXtend application server. Perform the following steps on both enterprise archive files to complete the deployment process.
-
Create a temporary directory.
-
Move the enterprise archive file (for example, Suiteletfactory.ear) to this temporary directory.
-
Extract the Web archive file (.war file) from the enterprise archive file by using the jar command (for example, "jar xf cservice.ear cservice.war").
-
Extract the web.xml deployment descriptor from within the Web archive file by using the jar command (for example, "jar xf cservice.war WEB-INF/web.xml").
-
Properly configure the servlet by editing the web.xml file to adjust the deployProperties parameter to include the correct path to the appServerDeploy.properties file (for example, set the value of the init-param named deployProperties to "file:///c:/appServerDeploy.properties").
-
Update the Web archive file with the modified web.xml file Type ("jar uf cservice.war WEB-INF/web.xml"). This will put the web.xml file back into the WAR file in the correct location inside the EAR.
-
Update the enterpise archive file with the newly-updated Web archive file (for example, "jar uf cservice.ear cservice.war").
Perform the same set of steps for the suiteletfactory.ear file (substituting "suiteletfactory" wherever "cservice" is used in the above steps).
After finishing the changes to the web.xml files, the two EAR files are ready to be deployed. The cservice.ear file should be deployed first, followed by the suiteletfactory.ear file.
Starting the Collaboration Server
The Collaboration Server and SuiteletFactory should be started automatically when the EAR files are deployed into the application server.
To manually check that the Collaboration Server was properly deployed, direct your Web browser to:
http://<servername>/<databasename>/cservice/intro.jsp
To manually check successful deployment of the SuiteletFactory, direct your Web browser to:
http://<servername>/<databasename>/CollabraSuite/intro.jsp
Developing a Portal Component
CollabraSpace components, referred to as suitelets, can be deployed using a flexible HTTP-style interface. An HTTP request is made to the "suitelet factory" and the suitelet factory then returns the HTML needed to generate the requested suitelet.
The steps below walk you through a typical scenario of creating a portal component that contains a CollabraSpace suitelet. The example illustrates how to add the CollabraSuite Dashboard component into a portal component.
This example assumes that a Director EAR has already been created and that the portal component will be added to the resource set called "ResourceSet" (the default resource set).
-
Create a class that implements com.sssw.portal.api.EbiPortalComponent. This is the portal component class. An example is given below.
package com.collabraspace.webapps.ssportlet; // potential useful imports import com.sssw.portal.api.*; import com.sssw.fw.api.*; import com.sssw.fw.exception.*; import java.util.Properties; /** DashboardPortlet */ public class DashboardPortlet implements com.sssw.portal.api.EbiPortalComponent, CollabraSpaceConstants { // code deleted for example } -
In the getComponentData method, create the needed HTTP request for the Collaboration component (and any other HTML needed for the portal component). Here is an example.
package com.collabraspace.webapps.ssportlet; // potential useful imports import com.sssw.portal.api.*; import com.sssw.fw.api.*; import com.sssw.fw.exception.*; import java.util.Properties; /** DashboardPortlet */ public class DashboardPortlet implements com.sssw.portal.api.EbiPortalComponent, CollabraSpaceConstants { // anInstance of a log for error/trace reporting private com.sssw.fw.api.EbiLog log; private static final int APPLET_HEIGHT = 105; private static final int APPLET_WIDTH = 500; private static final String SUITELET_SPEC = "suitelet=com.collabraspace.comps.dash.DashboardSuitelet," + "gridx=0,gridy=0;" + "suitelet=com.collabraspace.comps.location.RoomLocation Suitelet," + "gridx=0,gridy=1,weightx=1,fill=HORIZONTAL, titleborder=Location;" + "suitelet=com.collabraspace.comps.alert.AlertSuitelet," + "gridx=0,gridy=2,fill=HORIZONTAL;"; /** * Initializes an Component object * * @param context a wrapper around the request and response * @param params an map that contains parameters. */ public void initialize( com.sssw.portal.api.EbiPortalContext context, java.util.Map params ) throws com.sssw.fw.exception. EboUnrecoverableSystemException { // obtain the log from the factory, it is maintained as a singleton. log = com.sssw.fw.log.EboLogFactory.getLog( "COMPONENT" ); // only log items if the log level indicates we should if ( log.isTrace() ) { log.trace("DashboardPortlet in initialize method" ); } } /** * Gets the component data (in HTML or XML format) at run-time. * * @param context a wrapper around the request and response * @param params an map that contains parameters. */ public void getComponentData( com.sssw.portal.api. EbiPortalContext context, java.util.Map params ) throws com.sssw.fw.exception.EboUnrecoverableSystemException { // only log items if the log level indicates we should if ( log.isTrace() ) { log.trace( "DashboardPortlet in getComponentData method" ); } String suiteletString = CollabraSpaceHelper.getSuitelet( context, SUITELET_SPEC, APPLET_WIDTH, APPLET_HEIGHT); Properties defaultValues = context.getComponentInfo().getComponentDefaultValues(); String htmlString = generateHtml( defaultValues.getProperty(COLLABORATION_URL_PARAM), /* defaultValues.getProperty(CLASSIFICATION_IMG_PARAM), defaultValues.getProperty(CLASSIFICATION_ALT_PARAM), */ suiteletString); context.setContentType(EbiComponentConstants.MIME_TYPE_HTML); context.setComponentContent(htmlString); CollabraSpaceHelper.adjustResponse(context) ; if ( log.isTrace() ) { log.trace( "DashboardPortlet returned component content => " + context.getComponentContent() ); } } private String generateHtml( String collaborationUrl, /* String classificationImgUrl, String classificationAltText, */ String suiteletString) { StringBuffer html = new StringBuffer(); html.append("<table cellpadding=5>\n") ; html.append(" <tr><td align='center'>\n"); html.append(" <table bgcolor='white' border=0 cellspacing=0\n") ; html.append(" cellpadding=0 >\n") ; html.append(" <tr><td colspan=2 align=' center' >\n" ); html.append( suiteletString).append("\n"); html.append(" </td></tr>\n") ; html.append(" </table>\n") ; html.append(" </td></tr>\n") ; html.append("</table>\n") ; return html.toString() ; } /** * Process request. * * @param context a wrapper around the request and response * @param params an map that contains parameters. */ public void processRequest(com.sssw.portal.api. EbiPortalContext context, java.util.Map params ) throws com.sssw.fw.exception.EboUnrecoverableSystemException { // only log items if the log level indicates we should if ( log.isTrace() ) { log.trace( "DashboardPortlet in processRequest method" ); } //process incoming items on the request object //String parm = context.getRequest().getParameter ("parm-name");| } }For an example of building the HTTP request for a suitelet, review the CollabraSpaceHelper.getSuitelet method. The suitelet factory must be deployed prior to using this portal component; otherwise, the request to the suitelet factory will fail and the portal component will not function properly.
The URL to access the suitelet factory is dependent on how it was deployed, but should look something like this:
http://<servername>/<databasename>/suiteletfactory
-
Create the XML portal component descriptor for the new portal component. An example is given below.
<portal-component> <class-name>com.collabraspace.webapps.ssportlet.Dashboard Portlet</class-name> <display-name>CollabraSpace Dashboard</display-name> <description>CollabraSpace Dashboard Portlet</description> <lifetime>true</lifetime> <enable-title-bar>true</enable-title-bar> <personalizable>false</personalizable> <personalize-uri/> <component-styles/> <categories/> <default-style/> <defaults> <default> <name>collaborationServerUrl</name> <!--<value>http://www.collabraspace.com/crm/</value>--> <value>http://localhost:80/suitelet/suiteletfactory/</value> </default> <default> <name>collaborationGroup</name> <value>All DemoCampus Users</value> </default> <default> <name>buildingName</name> <value>Maryland</value> </default> <default> <name>floorName</name> <value>Public</value> </default> <default> <name>roomName</name> <value>Conference Room</value> </default> </defaults> </portal-component> -
Create any needed utility classes. Below are examples of two utility classes:
UrlHelper.java
UrlConnectInfo.java
UrlHelper.java package com.collabraspace.webapps.ssportlet; import java.util.Map; import java.util.HashMap; import java.net.URL; import java.util.Set; import java.util.Iterator; import java.io.Reader; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.StringWriter; import java.io.PrintWriter; import java.net.URLConnection; public class UrlHelper { public static UrlConnectInfo getUrl(String urlString, Map requestHeader) { StringBuffer content = new StringBuffer(); UrlConnectInfo connectInfo = new UrlConnectInfo(); Map headerResponses = new HashMap() ; try { URL url = new URL(urlString); // Initialize the connection (doesn't actually make the request) URLConnection connection = url.openConnection(); Set names = requestHeader.keySet(); for (Iterator iter = names.iterator(); iter.hasNext();) { String key = (String)iter.next(); if (key.toLowerCase().startsWith("accept") || key.toLowerCase().startsWith("user-agent")) { String value = (String)requestHeader.get(key) ; connection.setRequestProperty(key, value) ; } } // Make the request connection.connect() ; // Retrieve the content Reader raw = new InputStreamReader(connection.getInputStream()); BufferedReader buffer = new BufferedReader( raw ); String line; while((line = buffer.readLine()) != null) { content.append( line + "\n" ); } buffer.close() ; /* // Retrieve the response headers String headerKey; for ( int i=0; null != (headerKey = connection.getHeaderFieldKey(i)); i++) { headerResponses.put( headerKey, connection.getHeaderField(headerKey)) ; } */ } catch(Exception e) { StringWriter sw = new StringWriter(); PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(sw); e.printStackTrace(pw) ; pw.close() ; content.append( "ERROR:" + sw.getBuffer() + "\n" ); } connectInfo.setContent(content.toString()) ; connectInfo.setResponseHeader(headerResponses) ; return connectInfo; } }UrlConnectInfo.java package com.collabraspace.webapps.ssportlet; import java.util.Map; /** * A data object which packages information resulting from some http request */ public class UrlConnectInfo { private String content; private Map responseHeader; /** Getter for property content. * ©return Value of property content. */ public String getContent() { return content; } /** Setter for property content. * @param content New value of property content. */ public void setContent(String content) { this.content = content; } /** Getter for property responseHeader. * ©return Value of property responseHeader. */ public Map getResponseHeader() { return responseHeader; } /** Setter for property responseHeader. * ©param responseHeader New value of property responseHeader. */ public void setResponseHeader(Map responseHeader) { this.responseHeader = responseHeader; } } -
Using eXtend Workbench, open up the portal project that CollabraSpace components will be integrated into and place all of the code for the portal component into the resource set (see Figure 1).
Figure 1: Placing the portal code into the resource set.
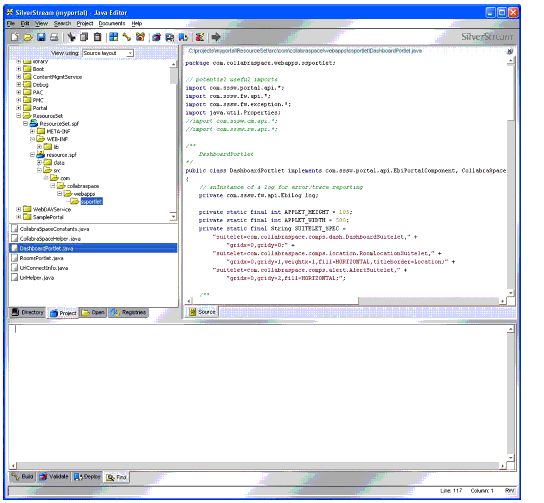
-
Again, using eXtend Workbench, place the portal component descriptor in the resource set (see Figure 2).
Figure 2: Placing the portal component descriptor in the resource set.
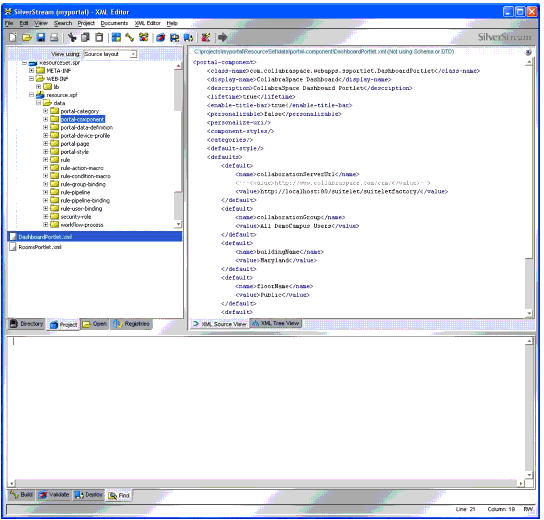
At this point, the Director EAR should be rebuilt and deployed. The new portal component should be available for placement on a user's page.
Figure 3 shows the CollabraSuite Dashboard as an example of what a new component would look like in a finished portal.
Figure 3: The CollabraSuite Dashboard in a finished portal.
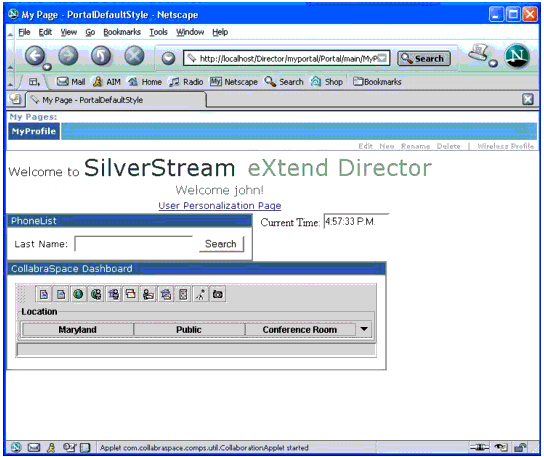
Conclusion
This AppNote provided an overview on how to integrate CollabraSpace's CollabraSuite software components into Novell's portal framework using exteNd Web application development products. Leveraging the J2EE application model offers off-the-shelf integration as a standard portal product offering.
Additional Resources
For more information about the CollabraSpace software offerings, refer to these resources:
The CollabraSpace Web site at http://www.collabraspace.com.
A list of the CollabraSuite collaboration components can be found at http://www.collabraspace.com/docs/novell/director/3.0/cs_helper.html.
* Originally published in Novell AppNotes
Disclaimer
The origin of this information may be internal or external to Novell. While Novell makes all reasonable efforts to verify this information, Novell does not make explicit or implied claims to its validity.