Benefits of NDS
Articles and Tips: article
01 Aug 1999
Novell Directory Services (NDS) is the world's leading directory service. It is the unifying, cross-platform infrastructure for managing, securing, accessing, and developing to all major components of a network. NDS supports more application programming interfaces (APIs), tools, standards, and protocols than any other directory service. The advanced functionality in NDS offers a strong development foundation for delivering secure, manageable network applications. The market-proven and powerful structure of NDS streamlines administrative tasks to minimize management time and expense.
NDS scales to the largest network environments, including the Internet. It can manage new object types that provide additional directory-aware services such as software distribution, workstation management, NT Server management, and Internet access control.
NDS integrates various directories, open standards, platforms, resources, and people so that even the most widely dispersed, heterogeneous environment can be linked efficiently. And because it is based on the X.500 standard, NDS supports the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) and HTTP as well as the Java programming environment. It can bring a single point of management to intraNetWare/NT Server environments and is available for the most popular brands of UNIX. And, with Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA) encryption and a track record spanning nearly 5 years (and more than 30 million users), it is secure and reliable.
With NDS you can provide comprehensive and secure management of your network resources as well as seamless access for users. And as a directory for the entire network, NDS provides easy network access regardless of the user's physical location or the location of needed resources. Users will have the same network view and login procedure whether they log in from their local workstation or from a workstation in a different country.
NDS simplifies network administration by using objects to represent any network resource, including physical devices such as routers, switches, printers, and fax machines; software such as database and word processing applications; or volumes in the network file system. And with the authorization, authentication, and access control services of NDS you can manage the relationships and interactions between objects. Administrators can move individual objects, groups of objects, or entire branches of the NDS tree to different locations in the tree with one simple drag-and-drop operation.
Key benefits of NDS include the following:
Enjoy the most fully developed and powerful directory service available
Organize and secure Internet and intranet resources
Access all network resources with a single login
Lower the cost of network computing
Provide unequalled security
Provide unequalled manageability
Provide superior schema flexibility
Provide a single point of administration
Provide advanced directory management tools
Integrate multiplatform systems
Support open standards
Provide the tools needed for easy, fast application development
Increase efficiency through NDS replication
Scale to any size network
Ensure a seamless transition to the year 2000
Enjoy the Most Fully Developed and Powerful Directory Service Available
NDS has been in development for over a decade, during more than half of which people have repeatedly proven its value. By far the most widely developed directory service in the world, NDS is employed by more than 40 million users to access the services on their network. Many of the world's most successful companies from every business sector use it as the backbone of their networking operations.
Because NDS was designed to be partitioned and replicated, it is flexible, extensible, and powerful enough to be the directory for global networks. For example, Telcos like AT&T, Nippon Telephone and Telegraph, and Maritime Telegraph and Telephone are using NDS as the directory for the business intranet services they provide in the United States, Japan, and Canada respectively.
Organize and Secure Internet and Intranet Resources
Information, applications, and resources on your intranet and the Internet change constantly.With NDS you can organize and classify this information so that you can safely and effectively communicate with your users, vendors, customers, and salespeople. You can also control access to Internet and intranet resources just as you do on your private network.
Access All Network Resources with a Single Login
With NDS, users and network supervisors only have to log in once with one password to be authenticated to the entire network, instead of logging in to each file server and other network resources separately. Once authenticated, users have access to all the network resources to which they have rights, regardless of the size of the network and where the users or resources are physically located. And unlike other directories, NDS is cross-platform, supporting NetWare, Solaris, Windows NT, OS/390, and Linux.
Lower the Cost of Network Computing
A recent Gartner Group study revealed that 73 percent of the cost of owning a network results from administrative costs. NDS greatly simplifies network administration, thereby reducing the cost of networking.
With NDS, service management is centralized. You can distribute software, manage desktop settings, and provide remote management for workstations all from a single location and with one management utility.
Provide Unequalled Security
NDS offers superior security features. The standards-based infrastructure of NDS gives you easy, flexible control over your organization's security policies. NDS provides the best choice for your company's evolving and varied security needs by supporting flexible user authentication support with encrypted passwords and smart cards.
It protects access to the network by requiring users to authenticate to it when they log in. NDS uses an authentication service based on the public-key/private-key encryption technology developed by RSA Data Security, Inc., which relies on a private key and digital signature to verify the user's identity. Once the user is authenticated to the network, further authentication (which is required when a user makes a request to a different server) is handled in the background and is transparent to the user.
NDS also protects access to network resources once users are logged in to the network. Network supervisors control access to all network resources by assigning rights to objects that represent network resources, user groups, and individual users.
With NDS you can secure your network against data loss and downtime by replicating partitions to strategic locations on the network. This protects your network from problems caused by a single point of failure, such as a server going down or the temporary loss of a communication link. If a primary partition is lost, the network automatically reconfigures itself to use another copy, or replica, of the partition. In addition, you can restore a partition that has been lost from one server by using a replica on a different server.
Novell has tested NDS replication with millions of objects replicated over multiple servers. NDS uses a proven replication model that powers the world's largest companies, including Telcos, Internet service providers (ISPs), banks, governments, and global enterprises.
Companies looking to extend their directory infrastructure to the Internet, bring all their customers and employees online, and participate in e-business require a directory with a robust and flexible replication model. NDS allows organizations to implement a highly distributed directory model where replicas of partitions are distributed to servers throughout the organization, or to store a large copy of the directory on a single server and replicate the entire database to a select number of servers.
Because of NDS' massive scalability and proven replication model, companies have the flexibility to deploy their enterprise directory without interruption and build the necessary infrastructure required for distributed or highly centralized directory applications, such as those required for electric commerce.
Provide Unequalled Manageability
The hierarchical structure of NDS simplifies network administration by enabling network supervisors to arrange network resources in the directory tree according to the way they are used. With resources placed near the users who access them, network supervisors can grant access rights to entire branches of the tree at one time. They can give rights to complete groups of users and then deal with exceptions on an individual basis.
Provide Superior Schema Flexibility
NDS offers a flexible schema, a rules system that defines how the NDS tree is structured: what objects are defined, what attributes can be associated with objects, and what positions objects occupy in the directory tree.
NDS includes a robust default schema; nevertheless, you can extend the default schema to customize the database to fit your needs. For example, you can extend a user object by adding new attributes such as a Social Security number or an emergency contact name and telephone number. Independent software vendors (ISVs) can also integrate new services into the network by extending the NDS schema and creating new objects. For example, ISVs have added fax server functionality to the network by adding a fax server object to the directory tree.
Provide a Single Point of Administration
Because NDS supports multiple platforms and open standards such as LDAP, it provides a single, global directory that can contain information for all network applications. NDS maintains information about every resource on the network including users, groups, printers, volumes, network devices, and any other customizable object in a hierarchical tree structure, and provides a single point of administration for the entire network.
Because NDS is a global directory, network supervisors can eliminate a number of redundant tasks. For example, to give a user access rights to all servers on the network, a network supervisor would normally have to give that user rights to each server individually. With NDS, however, you only need to create one user object. The one object gives the user the same user ID for every server on the network.
With NDS, organizations can choose whether to centralize management and administration services that cross departmental boundaries or to delegate administration to the department or workgroup level.
In addition, using one directory for all applications means that there will never need to be multiple copies of information. This saves system resources, and users and network supervisors can get the information they need from a single location and a single set of integrated tools, all of which use the same interface.
Provide Advanced Directory Management Tools
With NDS management tools you have the flexibility to design and manage a directory infrastructure that suits your organization's needs. With the NDS Manager utility, for example, you can partition the directory tree into branches and replicate the branches on multiple servers in your network. You can also perform manual data synchronization, repair synchronization problems, and monitor the overall health of your network. No other directory has such comprehensive and easy-to-use tools.
Integrate Multiplatform Systems
NDS is access-protocol and platform independent so that you can build networks or intranets with different hardware and operating systems. You can choose the hardware, server operating systems, and client operating systems that best suit your needs, and still enjoy all the cost savings, ease of management, and other benefits of NDS.
NDS is currently available on NetWare 5, NetWare 4, NT 4.0, NT 3.51, Solaris, and OS/390. In addition, Novell continues to work with Microsoft, Sun Microsystems, Red Hat, Caldera, IBM, and several ISVs and partners to promote integration with NDS.
Support Open Standards
NDS is based on the X.500 international standard as defined by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Telecommunications Union (ITU). This standard was adopted to enable the creation of an interoperable, distributed, worldwide directory service. NDS provides functionality beyond the X.500 specification, offering a complete networking infrastructure that links users to network services, applications, and data.
NDS supports many Internet protocols and de facto standards, including Bindery, DHCP, DNS, LDAPv3, NDAP, PKCS10, PKI, RADIUS, SMB, SSLv3, and X.509
Novell co-authored the Lightweight Directory Update Protocol (LDUP) over a year ago, and the draft is up for comment in the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). Novell representatives worked with other leading vendors on the LDUP specification to help define a standard for server-to-server replication for LDAP. Novell believes that companies must embrace open standards, like LDAP and LDUP, rather than invent proprietary methods and interfaces.
To ensure compatibility with other standards-based directories, Novell natively supports the LDAPv3 specification. And, Novell is working directly with the IETF to propose "mission-critical" standards for replication and scalability functions.
Provide the Tools Needed for Easy, Fast Application Development
NDS is a great foundation for simple, fast development of powerful, network-enabled applications. Without NDS, application developers would have to create their own methods for tracking users, user rights, and any other information necessary to administer their application. This means they would either have to create their own application-specific database or use a server-specific application such as NetWare bindery. Application development without NDS is difficult, time consuming, and expensive.
In addition, developers can eliminate or greatly simplify the task of creating a directory for their network-enabled applications. By using NDS as the directory for their applications, developers can save a great deal of time years, in some cases.
Third parties have developed more than 400 applications that leverage NDS. In fact, the number of developers signing up for Novell's DeveloperNet program has almost tripled in the last year, and over 70 percent of them are developing applications that use NDS. There are more development tools for NDS than for all other directory services combined. Some of the most popular development interfaces used to develop these applications include ADSI, JavaBeans, JNDI, LDAP, NDS SDK, NetBasic, OCX, ODBC, Oracle NCA, REXX, and VisualBasic.
For a listing of Novell partners, applications they have developed that leverage NDS, NDS development tools and APIs, and developer-related documentation, visithttp://developer.novell.com/nds.
Increase Efficiency through NDS Replication
With the database replication features in NDS you can ensure optimum network performance. You can divide the database into partitions and then distribute replicas of these partitions to distant servers, placing resources closer to users who need them. Because users will not have to go to a central database location each time they log in to the network, authentication to the network and access to data is almost immediate.
A replicated directory increases your network's reliability and enables you to construct a system where server failure, maintenance, or a temporary loss of a communication link will not affect your users.
NDS is very predictable in replica placement when new children partitions are created: it will place the master replica of the child partition on the same server that holds the parent's master replica, and it also does the same with the read/write replicas. By exploiting this design, "layer one" levels of the NDS tree can be partitioned and replicated to necessary servers quickly and easily. Any new partitions created below "layer one" are guaranteed to have the master and read/write replicas on the correct servers.
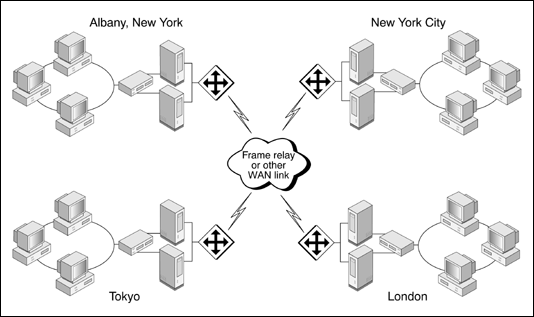
To illustrate the benefits of directory replication and distribution, consider the following two figures. Figure 1 shows the physical layout of a portion of Computer Software, Inc.'s global enterprise network. Computer Software, Inc., has offices in Albany, New York City, London, and Tokyo. Each office has two servers and several workstations. Wide area network (WAN) links using frame relay or other WAN technology connect the offices.
Figure 1: Physical layout of Computer Software, Inc's global enterprise network, connected through frame relay or other WAN link.
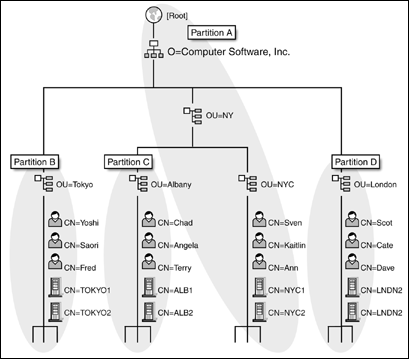
Figure 2 shows the NDS tree for Computer Software, Inc. (This is for demonstration only; any tree might contain many more objects). To provide the best performance, you can partition the NDS tree so that the servers in each location contain a copy of the partition in which they reside. As a result, Sven will be able to authenticate to the server in his local office, rather than to one across town or around the world. Although Sven can be granted a complete view of the global network and allowed to access any resource on any part of the network at any time, the local servers will handle the majority of the requests from his workstation.
Figure 2: NDS tree for Computer Software, Inc., illustrating how you can partition the NDS tree so that servers in each location contain a copy of the partition on which they reside.
To further illustrate the benefits of directory replication and distribution, suppose that 2,500 employees in the New York City office of Computer Software, Inc., need to authenticate to the network, but that only 30 of these employees need to access network resources located in other offices. If all New York City users had to authenticate to a server at the company's headquarters in Tokyo, they would have to do so across WAN links. This would mean the company would have to purchase enough WAN link bandwidth to accommodate (at least) 2,500 users an expensive proposition.
With NDS, however, network supervisors can make a partition of the New York City office portion of the tree and place a replica of that partition on the servers physically located in the New York City office. All 2,500 users in the New York City office would then authenticate locally providing optimum performance and minimizing the company's WAN link costs. Rather than buying enough WAN bandwidth to accommodate 2,500 users, the company would buy only the bandwidth necessary to accommodate the 30 employees who need access to network resources located in other offices.
Scale to Any Size Network
In March, 1999, Novell demonstrated NDS with a billion users in the directory tree, setting a new bar for directory scalability. Even more impressive, Novell demonstrated NDS performing LDAP searches with subsecond speed. Therein lies the power of NDS: even at large capacities, it performs amazingly fast. Organizations that deploy NDS can be confident the infrastructure will support growth with consistent performance.
With virtually unlimited capacity, NDS allows you to extend your directory infrastructure to the Internet, bringing your customers, partners, and suppliers online. In fact, NDS can manage more than five times the number of users as there are on the Internet today. This unlimited scalability is invaluable to ISPs and Internet customers that are constantly capturing and managing enormous amounts of data in a central location. NDS helps enterprise customers build the infrastructure required for e-commerce.
Ensure a Seamless Transition to the Year 2000
With NDS you can plan confidently for trouble-free operation as the year 2000 approaches. You will experience a smooth transition from the year 1999 to the year 2000 without any changes in your system's functionality, data content, or user interface. With NDS you can keep your productivity high throughout the transition to the new millennium. See http://www.novell.com/year2000for more information.
Hardware and Software Requirements
NDS is bundled with NetWare 4.2 and above. For system requirements refer to the NetWare documentation specific to your operating system.
Ordering Information
You can order NDS from any Novell Authorized, Gold, or Platinum Partner. For more information contact your local Novell office or call the Novell Customer Response Center at 1-801-228-4CRC (1-801-228-4272). In the United States and Canada call toll free 1-888-321-4CRC (1-888-321-4272). You may also visit the NDS page on Novell's World Wide Web site at http://www.novell.com/products/nds.
* Originally published in Novell AppNotes
Disclaimer
The origin of this information may be internal or external to Novell. While Novell makes all reasonable efforts to verify this information, Novell does not make explicit or implied claims to its validity.