NetWare 5 Overview, Part 2
Articles and Tips: article
Technical Writer
Documentation Development Group
01 Jan 1999
This article gives an overview of Novell's newest network operating system, NetWare 5. Covers NetWare 5 Security Services, Novell Licensing Services (NLS), Novell Storage Services (NSS), Novell Internet Access Server, Web Services, and Oracle8.
- Introduction
- Public Key Cryptography Basics
- The Need for Public Key Cryptography
- Secure Transmissions
- Establishing Trust
- Security Services in NetWare 5
- Auditing
- Licensing Services
- Benefits to Network Users
- Requirements for Using Licensing Services
- File Services
- Requirements for Using NetWare 5 File Services
- Storage Management Services
- Connectivity Services
- Web Services
- Scripting and Component Support in NetWare 5
- Database Services
- Oracle8 for NetWare
Introduction
This article is the second in a two-part series, designed to give you an overview of Novell's newest network operating system, NetWare 5. This article covers NetWare 5 security services, Novell Licensing Services (NLS), Novell Storage Services (NSS), Novell Internet Access Server, Web services, scripting and component support, and database services (including Oracle8 for NetWare).
Please refer to the first article in this series, "NetWare 5 Overview, Part 1" in the September 1998 issue for information on the new Java-based installation utility, NetWare 5's pure IP solution, Novell Directory Services (NDS), ZENworks, and Novell Distributed Print Services (NDPS).
NetWare 5 security services include the following:
NetWare Auditing to help you collect and examine records of network transactions to ensure that your server's resources are adequately protected.
Public key cryptography services for protecting confidential data transmissions over public communications channels such as the Internet.
NDS-based tools for managing these public key cryptography services.
The cryptographic services in NetWare 5 are part of Novell's International Cryptographic Infrastructure, NICI, which is a set of network services designed to support strong cryptography on a region-by-region basis, while complying with the diverse national policies on the shipment and use of cryptography. Cryptography-enabled applications, such as those mentioned in this section, will not function if cryptography services are not fully installed.
The next section contains information regarding basic public key cryptography mechanisms. This background information is necessary to understand NetWare 5 cryptography services. If you are already familiar with these concepts, you might want to skip the section. The following table will help you decide where to go from here.
|
If you want to
|
Go to
|
|
Learn the basic concepts of public key cryptography |
"Public Key Cryptography Basics" |
|
Read about the public key cryptography features and services in NetWare 5 |
"Public Key Cryptography in NetWare"5" |
|
Read about NetWare Auditing |
"Auditing" |
Public Key Cryptography Basics
Public key cryptography mechanisms are not familiar to many network administrators. For this reason we have provided this section.
The Need for Public Key Cryptography
The content of most Internet communications, such as Web page browsing or public chat forums, can be monitored by anyone equipped to do so. The content of other data transmissions, such as the exchange of credit card information for online purchases, needs to be kept private.
Public key cryptography is a widely used method for keeping data transmissions private and secure on the Internet.
Secure Transmissions
Data transmissions can be private and secure when at least two things happen:
Authentication. The data sender verifies that the data receiver is exactly who or what it claims to be.
Encryption. The data sent is encrypted so that it can be read only by the intended receiver.
Key Pairs
Authentication and encryption are both provided through the use of mathematically related pairs of digital codes or "keys." One key in each pair is publicly distributed; the other is kept strictly private.
Each data transmitter, whether a person, a software program, or some other entity such as a bank or business, is issued a key pair by a public key cryptography system similar to that included in NetWare 5.
The basic principles and functions of each key in the key pair are summarized in the following illustration.
Figure 1: Basic principles and functions of each key in the key pair.

Key Pairs and Authentication
Authentication means the data sender verifies that the data receiver is exactly who or what it claims to be.
Suppose that you want to authorize your bank to transfer funds from your account to another account. The bank needs proof that the message came from you, and that it has not been altered during transit. The following illustrates the process your online transaction would follow using public key cryptography.
Figure 2: Process of online transaction using public key cryptography.
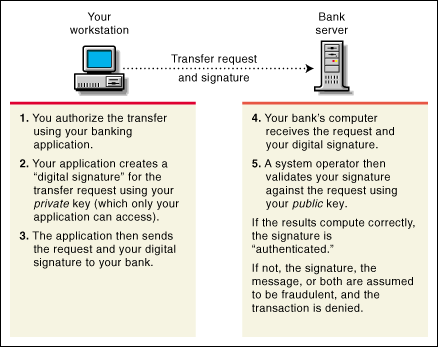
Digital signatures and their verification are further explained beginning with "More About Digital Signatures."
Key Pairs and Encryption
Encryption means that the data can be decrypted and read only by the intended receiver.
Suppose you want to order a book from an Internet vendor and to use your credit card to pay for it. You will want to ensure your credit card number can't be read by anyone other than the intended recipient.
The encryption process in the following illustration provides the mechanisms through which your credit card number can be safely transmitted.
Figure 3: The encryption process.
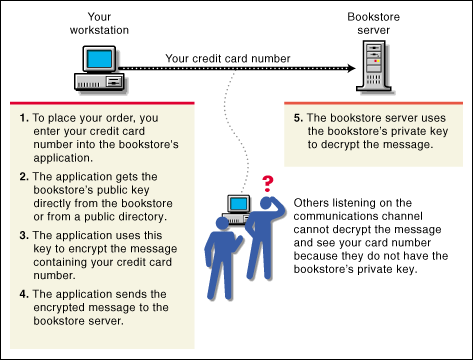
Establishing Trust
If a sender and receiver know and trust each other, they can simply exchange public keys and establish secure data transmission, including authentication and data encryption as just described. To do this they would use each other's public keys and their own private keys.
Under normal circumstances, however, parties needing secure data transmissions have no foundation for trusting the identity of each other. Each needs a third party, whom they both trust, to provide proof of their identity.
Certificate Authorities
A party needing to prove its identity in a public key cryptography environment enlists the services of a trusted third party known as a Certificate Authority (CA).
The CA's primary purpose is to verify that a party is who or what it claims to be and then to issue a public key certificate for that party to use.
Figure 4: CA verifies the identity of the party requesting certificate.
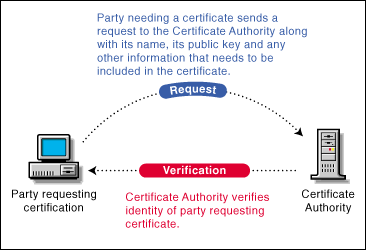
Once the identity of the requesting party has been established to the satisfaction of the CA, the CA issues an electronic "certificate" and applies its digital signature (as shown in the next section).
More About Digital Signatures
Just as a personal signature applied to a paper document indicates the authenticity of the document, a digital signature indicates the authenticity of electronic data.
To create a digital signature, the software used to create the signature links the data being signed with the private key of the signer. The following illustration shows the process that a CA follows to create its digital signature for a public key certificate.
Figure 5: CA creates its digital signature for a public key certificate.
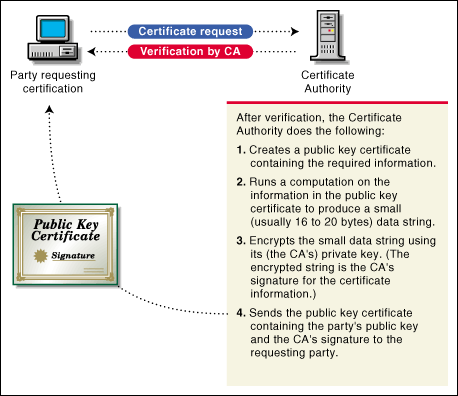
A digital signature is uniquely linked to the signer. No one else can duplicate the signature because no one else has the signer's private key. In addition, the signer cannot deny having signed the data and is therefore obligated to preform any actions prescribed. This is known as non-repudiation.
When a Certificate Authority signs a public key certificate, it guarantees that it has verified the identity of the public key owner according to the CA's established and published policies also known as a certification practice statement.
After signed data (signed by a public key certificate) is received, software verifies data authenticity by applying the same computation to the data that the signing software used originally. If the data is unaltered, both computations will produce identical results. Then both the sending and receiving parties safely assume that neither the data nor the signature was modified in transit.
Security Services in NetWare 5
Product Components
The security services components in NetWare 5 include
The Novell International Cryptographic Infrastructure or NICI the underlying cryptographic infrastructure on which NetWare 5 cryptography services are built.
Using NetWare Administrator, you request that key pairs be generated for cryptography-enabled applications. NICI fills these requests.
Novell Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) Services NetWare Administrator tools for managing the mechanisms and components that provide public key services in NetWare 5.
After installing Novell PKI Services, you can use NetWare Administrator to:
Create an NDS tree CA for your organization.
Request server-based public key certificates from the tree CA or from an external CA.
Create Key Material objects for cryptography-enabled applications. (Key Material objects are NDS objects that store an application's public key certificate and encrypted private key.)
Novell Secure Authentication Services (SAS), which includes support for the Secure Socket Layer (SSL) protocol.
SSL is a protocol that establishes and maintains secure communications between SSL-enabled servers and clients across the Internet. Novell SAS and SSL are an integral part of LDAP Services for NDS, a cryptography-enabled application included in NetWare 5.
An Example of Public Key Cryptography in NetWare 5
The Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) is an Internet communications protocol that allows client applications (such as a Web browser) to access information, such as telephone numbers and E-mail addresses, stored in LDAP-compliant directories.
NetWare 5 includes LDAP Services for NDS, a server application that allows LDAP clients (such as a Web browser) to access information stored in NDS. Using this application, you can selectively publish information in your NDS tree to Web browsers or other LDAP clients.
LDAP Services for NDS is integrated with Novell SAS, establish a secure connection via Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), to provide secure data transmission between an LDAP client and LDAP Services for NDS running on a NetWare 5 server.
The following illustration shows the SSL authentication process involved when an LDAP client establishes a data transmission session with LDAP Services for NDS running on a NetWare 5 server.
Figure 6: SSL authentication process.
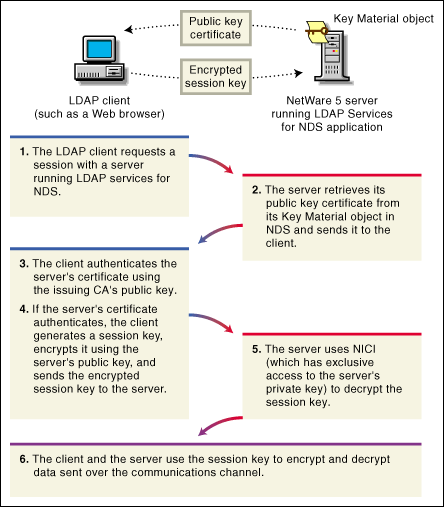
Benefits to You and Your Organization
Deploying security presents unique challenges to you as a network administrator. NetWare 5 helps you meet these challenges as shown in the following table.
|
Management Needs
|
How NetWare 5 Helps
|
|
Provide public key cryptography services on your network. |
You can create an organizational-specific NDS tree CA within your NDS tree, use the services of an external CA, or use a combination of both as your Certificate Authority needs dictate. You can manage all components using the power of NDS. |
|
Control the costs associated with obtaining key pairs and managing public key server certificates. |
NetWare 5 lets you create a tree CA, generate unlimited key pairs, and issue unlimited public key server certificates through the NDS tree CA at no charge. |
|
Allow public keys and public key certificates to be openly available while also protecting them against tampering. |
Key pairs are stored in NDS and can therefore leverage NDS replication and access control features. |
|
Allow private keys to be accessible to only the software routines that use them for signing and decrypting operations. |
Private keys are encrypted by NICI and made available only to the software routines using them for signing and decrypting operations. |
|
Securely back up private keys. |
Private keys are encrypted by NICI, stored in NDS and backed up using standard NDS backup utilities. |
|
Developers do not need to include cryptographic code in their products, and therefore can ship one version of an application worldwide. |
Cryptographic services will be made available for both server and client use through a standardized Novell Software Developer Kit (SDK). Application developers will be able to use the SDK to build world-class security products based on Novell's cryptographic infrastructure. Applications written to the NICI APIs need to go through a one-time and usually expedited export approval process because Novell has already received export approval for NICI. |
|
Multi-national corporations can use the same application (based on NICI) worldwide because NICI will control the encryption policy and usage instead of the application. |
Restrictions on the use of cryptography are transparent to the applications. For example, if your application has been written to NICI APIs, you can install your application wherever you want around the world and NICI will manage the encryption level. You buy one package and use that application worldwide. Cost of ownership is reduced because you don't have to manage or categorize different software versions--you have only one. |
|
National governments can limit the cryptographic algorithms which can be present in NICI rather than on the entire application because the engines within NICI that implement cryptographic algorithms are replaceable. |
Government restrictions do not affect Novell's and third party application developers' inherent ability to offer a variety of network security services. |
|
New cryptographic algorithms can be dynamically added to NICI through the installation and loading of additional cryptographic engines through NICI's extensible infrastructure. |
Third parties can develop a variety of cryptographic algorithms to offer value-added functionality or to meet the specific needs of national governments. The NetWare 5 server does not need to be restarted to add new algorithm support. Other supporting modules, such as cryptographic libraries and policy management modules can also be dynamically added without the need to restart the server in order for the new modules to be used. |
|
NICI modules are manufactured with strong digital signatures based on public key infrastructure using an in-house high-assurance root certificate authority. |
NICI offers a controlled infrastructure and ensures module integrity through the NetWare 5 operating system loader. The signature keys are generated and stored on a high assurance platform that conforms to the Trusted Computer System Evaluation Criteria (TCSEC) B3 rating. When a NICI module is loaded, the NetWare 5 operating system validates and verifies the signature on the module. Only after the module is verified does the operating system allow the services provided in the module to be used or accessed via standard interfaces. |
Requirements for Using NetWare 5 Security Services
You must install the following on all servers in the NDS tree that run applications integrated with NetWare 5 cryptography services:
Novell Secure Authentication Services (SAS) including SSL
Novell PKI Services (PKIS)
NICI Cryptographic Modules appropriate to your locale
After the service components are installed, we recommend you use 32-bit NetWare Administrator (nwadmn32.exe) to set up a tree CA.
You must create and manage a Key Material object in the NDS tree for applications whose secure transmissions you want to manage using Novell PKI Services.
Auditing
NetWare 5 includes auditing services that allow you or your organization to collect and examine records of specific network transactions to ensure that your server's resources are being adequately protected.
Businesses and other organizations such as government agencies often contract with independent parties to audit network transactions. These auditors review various events as requested. Generally, auditors are granted rights only to track events and activities, but they cannot open or modify network files (other than audit files).
You enable auditing using the AUDITCON utility. After auditing is enabled, audit data and history files are automatically created for the volumes and containers you specify. Audit files continue to accept records until auditing is disabled or the file becomes full.
Licensing Services
Novell Licensing Services (NLS) help you manage and monitor the use of licensed software in your NDS network.
NLS includes Novell's implementation of the LSAPI standard. NLS is designed to help network administrators ensure compliance with software licensing agreements.
Novell Licensing Services is tightly integrated with NDS to facilitate:
The interaction between software and the licenses that allow it to run.
Your ability to manage that interaction and monitor licensed software usage on your network.
NetWare 5 includes two tools you can use to install software licenses and monitor and manage license usage:
NLS Manager a stand-alone tool that lets you monitor and manage all aspects of configuring your licensing services, including generating reports on license usage.
NLS snap-in a NetWare Administrator snap-in that lets you do everything NLS Manager does except generate reports on license usage.
Note: NetWare 5 connection licenses are managed through NLS. You can increase your NetWare 5 connections by purchasing additional licenses and installing them using NLS Manager or NetWare Administrator. For more information, contact your Novell Authorized Reseller representative.
Understanding NLS
You can think of NLS in terms of three basic components: NLS clients, License Service Providers (LSPs), and License container objects in NDS.
NLS Clients
Ensuring compliance with license agreements requires confirmation of an available license before software is used.
In NLS this compliance is accomplished by the software making a request for a license before the software runs. Any software that makes a license request is referred to as an "NLS client."
If software is license-enabled, NLS client functionality is built in, and the software can request a license, receive a response to the request, and execute only if a license is available.
If an application is not license-enabled, you can configure ZENworks to act as an NLS client on behalf of the application.
License Service Providers (LSP)
The NLS client locates a license by contacting a License Service Provider and asking it to check whether a license is available.
A License Service Provider is simply an NLM called NLSLSP that runs on a NetWare 4.11 or later server.
To use NLS, you must have one or more LSPs in your NDS tree. The LSP receiving the request searches the NDS tree for a license appropriate to the software.
First it locates an NDS object called a License container object that corresponds to the software. Then it asks the License container object whether it has any available licenses for the software.
If the License container object has no available licenses, the LSP continues its search until it has either found a license or contacted all License container objects in the tree.
License Container Objects
The License object contains NDS leaf objects called License Certificate objects, which represent software licenses. Each License object contains License Certificates for only one piece of software.
Stored with the License container object in NDS is information such as how many licenses the License object contains, what kind of licenses they are (single-use, multiple-use, etc.), and how many licenses are currently in use.
NLS Graphical Summary
NLS component functionality is illustrated by the following:
Figure 7: NLS component functionality.
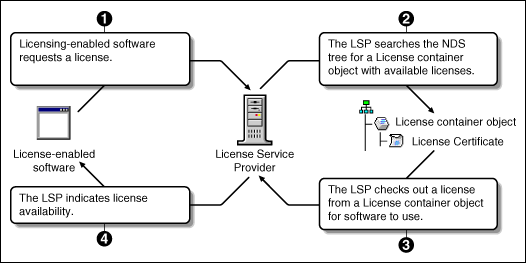
Benefits to Network Users
NLS will help your network users be certain they are using only licensed software.
Benefits to You and Your Organization
NLS allows you to manage and monitor the use of licensed software as shown in the following illustration.
Figure 8: NLS allows you to manage and monitor licensed software.
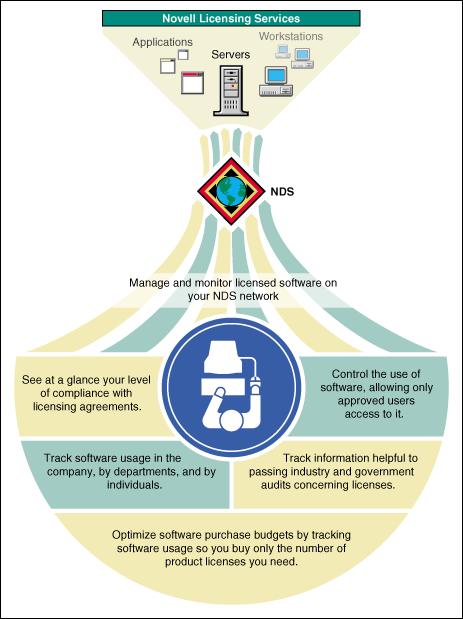
Requirements for Using Licensing Services
To use Novell Licensing Services you must
Ensure NLS is installed on your network. (By default, when you install a NetWare 5 server or upgrade from NetWare 3 or NetWare 4, NLS is installed on that server.)
Install or create License Certificates in the appropriate NDS context.
For each NDS partition, ensure that at least one server with a master or secondary replica is functioning as a License Service Provider (nlslsp.nlm is running on the server).
Configure ZENworks to function as the NLS client for non-license-enabled applications you want to manage.
File Services
NetWare 5 offers two choices of mutually compatible file services: Novell Storage Services (NSS) and the traditional NetWare File System. Both kinds of file services let you store, organize, manage, access, and retrieve data on the network.
With either service, NetWare stores directories and files in logical containers known as volumes.
Users, groups of users, and other NDS objects are granted access rights to volumes, directories, and files as required. Your network's data security depends on specifying which objects can access which files, and whether they can merely read a file or modify it.
This section introduces the main features of NSS.
Novell Storage Services
NSS is a powerful new modular storage service that runs on NetWare 5 and is fully compatible with the traditional NetWare File System.
NSS gathers all unpartitioned free space that exists on all the hard drives connected to your server, together with any unused space in NetWare volumes, and places it into a storage pool. You create NSS volumes from this storage pool during server installation or later through NWCONFIG.
The following table provides a quick overview of the tremendous storage capacity and astonishing response times NSS delivers.
|
Feature
|
NSS Capability
|
|
Number of files per server |
8 trillion |
|
Maximum file size |
8 terabytes |
|
Maximum simultaneously open files |
1 million per server |
|
Time to open files |
Independent of file size all files open immediately |
|
Maximum volume size |
8 terabytes |
|
Maximum number of volumes on a single server |
255 mounted |
|
Volume segments |
Unlimited |
|
Directory tree depth |
As limited by client |
|
Volume mount time |
Dependent on volume size generally less than one minute |
|
RAM required |
4 MB minimum; add RAM as needed for cache performance |
NSS Benefits to Network Users
If your network users are accustomed to the industry-leading file services of a Novell network, they will get even better service from NSS.
If the network is being upgraded from a non-Novell network, network users will notice substantial improvements in storage services. If they are using very large files, such as large databases, the service improvements are dramatic.
NSS Benefits to You and Your Organization
You can rely on NSS to exceed any network user file size or file service performance demands. Including NSS volumes on your network will give you the following benefits.
You can access CD-ROM and other storage devices attached to the server from within the NSS space without loading additional device drivers.
You can leverage traditional NetWare features such as NetWare drive mappings, search drive mappings, and NDS Map objects to provide direct access to working areas and applications for your network users.
You can maintain volumes with far less downtime because of NSS fast volume mounting.
You can use NSS flexible RAM requirements to better tune your server to your needs.
Requirements for Using NetWare 5 File Services
The traditional NetWare File System requires specific amounts of RAM, depending on the total disk space supported by your server. NSS requires at least 4 MB of free RAM and unpartitioned free space on the disk.
You can upgrade traditional NetWare volumes to NSS at any time. Keep in mind that not all features of the traditional NetWare File System are currently supported in NSS.
Storage Management Services
Novell Storage Management Services (SMS) lets you back up, restore, and verify data stored on the network and on network clients.
SMS is an extensive architecture for platform independent utilities. Many third parties have built backup solutions based on Novell SMS technology.
You will want to ensure that all data on your network (including the NDS database) is protected against corruption and loss by backing up data at regular intervals. For this reason, Novell has included Enhanced SBACKUP with SMS in NetWare 5.
Enhanced SBACKUP lets you back up and restore:
Your NDS database
Bindery data
GroupWise data
The file systems on your NetWare server (including NSS and DOS partitions) and on attached Novell Client workstations.
The Enhanced SBACKUP utility runs on a host server, a Windows 95 client, or a Windows NT client and includes the following improvements over previous releases:
Queue-based backup/restore job definition/control
Scheduling and automatic rerun
A graphical interface for administration of 32-bit client backup/restore sessions
Improved SMS performance
Pure IP support (automatically available to third-party SMS-compliant solutions)
Auto loader support
To back up information, Enhanced SBACKUP reads the information on the target device and copies it onto the storage medium you specify. The restore process works in reverse.
Figure 9: Back up and restore process using Enhanced SBACKUP.
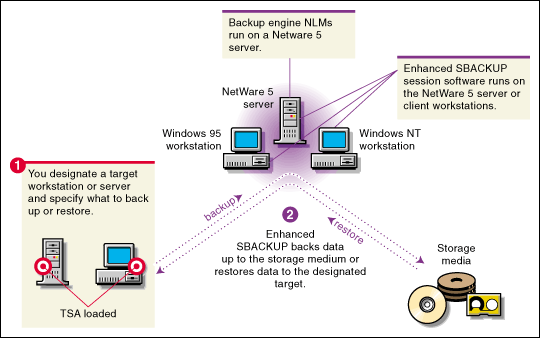
Benefits to Network Users
Most of your network users will probably never think about protecting their data until they need something they have lost. Enhanced SBACKUP will ensure that you can help them recover what they need quickly.
Benefits to You and Your Organization
Enhanced SBACKUP is simple to understand and easy to use.
You will be able to concentrate better on your other network management tasks if you know all the data on your network is protected by Enhanced SBACKUP.
Requirements for Using Enhanced SBACKUP
To use Enhanced SBACKUP you need:
The backup engine NLM programs running on a NetWare 5 server.
The Enhanced SBACKUP session software sbcon.nlm or nwback32.exe running on a NetWare 5 server or on a Windows 95 or Windows NT Novell Client, respectively.
The appropriate Target Software Agent (TSA) loaded on each server or workstation to be backed up.
Enhanced SBACKUP features three types of backup sessions:
Full backs up the entire file system and clears the modify bit on all files.
Differential backs up data that has the modify bit set, but does not clear the modify bit on backed-up files.
Incremental backs up data that has the modify bit set and clears the modify bit on backed-up files.
You need to plan which combination of session types to use as part of your backup strategy.
Note: Differential and Incremental backup sessions must not be used in combination with each other.
Connectivity Services
NetWare 5 offers you the option of installing one of Novell's award-winning connectivity products Novell Internet Access Server 4.1 on your NetWare 5 server.
Novell Internet Access Server 4.1 provides the following services:
Routing between local and remote LANs running a variety of protocols to create a cohesive network.
Remote access to all company network resources (including E-mail and Internet access) through a modem or other connection.
Remote service management of all connectivity services and servers from your workstation.
The following figure illustrates connectivity services provided by Novell Internet Access Server 4.1.
Figure 10: Novell Internet Access Server 4.1.
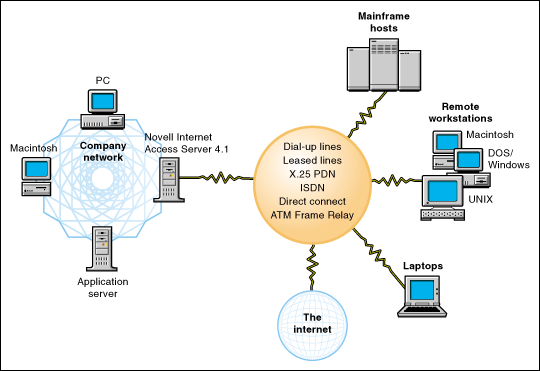
Routing
Novell Internet Access Server routing software supports the following:
IPX the original network-layer protocol used by NetWare.
TCP/IP a suite of networking protocols widely used to enable dissimilar nodes to communicate in a heterogeneous environment.
AppleTalk the native protocol for communication between AppleTalk nodes.
Source Route Bridging Novell's software solution for linking token ring networks.
NetWare Link/PPP Novell's implementation of the Point-to-Point Protocol, which enables point-to-point high-speed transmission of data over leased lines or asynchronous / synchronous switched transmission facilities.
NetWare Link/ATM Novell's connectivity solution to ATM networks, which provide a unified communications infrastructure capable of supporting voice, video, and data communications worldwide.
NetWare Link/X.25 Novell's connectivity solution to X.25 backbones.
NetWare Link/Frame Relay Novell's connectivity solution to Frame Relay, a streamlined, connection-oriented frame mode data service optimized for modern, reliable digital and fiber-optic transmission networks.
Remote Access Connection Types
Remote workstations can use two types of connections:
Remote Node. The remote workstation functions as if it were a workstation directly connected to the LAN. All data required for a session (file data and application packets) is transferred over the communications link. Data processing occurs on the remote workstation.
Remote Control. The remote workstation controls a dedicated workstation on the LAN. Only keystrokes and screen updates are transferred over the communications link. Data processing occurs on the dedicated workstation on the LAN.
Note: Macintosh remote node connections are made through Apple Remote Client and the AppleTalk Remote Access Service (ARAS) server.
Remote Service Management Using ConnectView 2.x
ConnectView 2.x is the management utility associated with Novell Internet Access Server 4.1 connectivity services. This utility allows you to:
View and manage Novell Internet Access Server 4.1 servers, including their ports and connections.
Manage current remote connections and current sessions as part of your system.
Create and run an accounting system for monitoring and charging remote users.
Print and store network event histories and remote access usage records.
Benefits to Network Users
Network users can access the Internet from their regular workstations as well as from remote connections.
They can also access the company network when they are teleworking and do everything they could if they were sitting at their dedicated office workstation.
If they need to use their personal workstation, they can connect to it using a Remote Control connection.
Benefits to You and Your Organization
You might already provide your network users with access to the Internet and some forms of remote access to your network. Novell Internet Access Server 4.1 will greatly expand and enhance your connectivity options and the power and quality of service you provide.
Requirements for Using Novell Internet Access Server 4.1
To support Novell Internet Access Server, you need:
NetWare 4.11 or a later version running on the server.
Novell Client software provided with NetWare 5.
Approximately 60 MB of free disk space, with an additional 40 MB on the SYS volume (needed only during installation).
Approximately 48 MB of free RAM on the server.
Web Services
The NetWare 5 product package includes:
The Netscape FastTrack Server for NetWare, a powerful Web server you can install on a NetWare 5 server.
Support for the major Web scripting languages so you can leverage your scripting expertise in creating customized server-side applications.
Netscape FastTrack Server for NetWare
Your NetWare 5 server can function as an extremely fast and efficient intranet and/or Web server.
Figure 11: Netscape FastTrack Server.
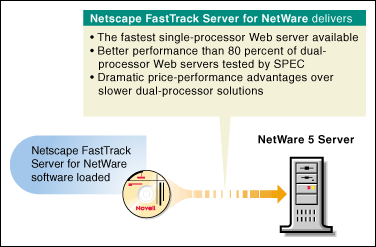
Note: The performance statistics listed in this graphic are based on recent benchmark tests conducted by the Standard Performance Evaluation Corporation (SPEC).
Benefits to You and Your Organization
With no additional investment in hardware or software, you can install a Web server to benefit network users and your company. For example:
You can create a company intranet to provide network users with easy access to company news, department information, company policies and procedures, and other information they need in order to be more efficient and productive.
You can create a Web server to publish company information on the Internet.
Requirements for Using Netscape FastTrack Server for NetWare
To install the Netscape FastTrack Server from the CD included in the NetWare 5 product package, you must have the following system resources:
A Windows 95 or Windows NT 4.0 client machine that:
Is running the appropriate Novell 32-bit Client.
Is running a Netscape 3 or later browser.
Has a CD-ROM drive.
Has 100 MB free disk space (for use only during the install process).
A target NetWare server that:
Is running NetWare 4.11 or a later version.
Has at least 32 MB of free RAM (64 MB is recommended).
Has at least 100 MB free disk space on the SYS volume.
Scripting and Component Support in NetWare 5
NetWare 5 supports the major scripting languages available, including:
Perl 5
NetBasic 6.0
NetBasic 7.0 (a VB Script-compatible language)
JavaScript
Java programmers can write servlets using the LCGI servlet Gateway running alongside the Netscape FastTrack Server for NetWare. In addition, pre-built NetBasic 7.0 components, Java Beans, and ActiveX controls make it easy to assemble powerful and effective network applications.
Using the development environment of choice, Web scripters and RAD developers can quickly and easily embed network services into Web pages and construct server-side applications that leverage the security and power of NetWare.
Benefits to Network Users
Scripting languages and reusable components afford server and Web developers the power, versatility, and compatibility to respond to the needs of network users.
Developers can incorporate NDS, login and authentication, file management, printing, Oracle and Btrieve database management, and other NetWare services into network solutions tailored to the specific needs of the enterprise. Timely and targeted network solutions allow both the end user and network developer the ability to be more productive.
Benefits to You and Your Organization
NetWare 5 scripting and component services offer you choice, compatibility, and speed.
You can choose the best scripting option to run on the fastest network and Web server. The Netscape FastTrack Server for NetWare running on NetWare 5 delivers twice the performance of its closest competitor. And by using the scripting and component technology that fits you best, you not only leverage your current network and scripting investment, you also leverage your existing development expertise.
Requirements for Using Scripting Services
Requirements depend on your scripting choice.
Support for NetBasic 6.0 and Perl 5 scripting is available on the NetWare 5 CD.
JavaScript components are installed with the Netscape FastTrack Server for NetWare (included in the NetWare 5 product package).
NetBasic 7.0, and the LCGI servlet Gateway for Java are available on the Novell developer Web site.
To obtain these, go to http://developer.novell.com and follow the appropriate links to the kits and download area. Download the Web Services pack.
You will need to subscribe to DeveloperNet and obtain a password. There is no charge for an electronic DeveloperNet subscription.
Database Services
NetWare 5 is the ideal platform for high performance databases and database applications because it delivers:
Database server and application manageability through NDS.
Lightning-fast, highest-capacity storage services through NSS.
Outstanding scalability through enhanced native support for multiprocessor hardware.
Memory protection features that bolster the reliability of the NetWare platform.
The NetWare 5 product package includes the world's leading database software, Oracle8, as well as the ever-popular key-indexed file management system, Btrieve.
Oracle8 for NetWare
The 5-user version of Oracle8 for NetWare in NetWare 5 includes:
An intuitive installation for getting a pre-tuned and pre-configured Oracle8 database up and running.
Wizards to help you:
Create databases
Migrate Oracle7 Server databases to Oracle 8
Create HTML Web pages based on data retrieved from Oracle8 (no knowledge of SQL or HTML syntax is required)
The Oracle Migration Assistant for Microsoft Access for complete and easy migration from your Microsoft Access database to Oracle8 for NetWare.
Figure 12: Oracle 8 for NetWare.
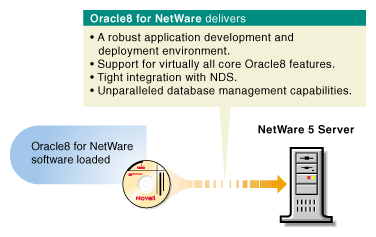
Oracle8 for NetWare was created to meet the needs of the most demanding and complex database applications.
Oracle8 for NetWare
Takes full advantage of NetWare 5 multitasking and I/O capabilities.
Provides much higher scalability than earlier versions of Oracle, supporting thousands of users and extremely high-volume transaction work loads.
Provides exceptional scalability on Symmetric Multiprocessing (SMP) machines.
Handles the most demanding online transaction processing (OLTP) and data warehousing applications. (Novell Storage Services supports database files up to 8 terabytes.)
Benefits to Network Users
Network users will experience exceptional performance from database applications that are built on Oracle8 for NetWare. And because of the product's NDS integration, they need remember only their network password to sign on and authenticate to any Oracle Server on the network.
Benefits to You and Your Organization
You can use Oracle8 for NetWare to:
Deliver premier database services across your network that will reduce cost-of-ownership and streamline business processes.
Oracle8 for NetWare includes all the necessary tools developers need to build business-critical applications that comprehensively and easily manage corporate data.
Manage all your Oracle8 servers and associated applications using tools that leverage the power of NDS.
The NDS-enabled Oracle Enterprise Manager allows administrators at any experience level to perform complex management tasks with point-and-click ease.
Build enhanced network computing applications that execute on Novell's JVM and offer database access via Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) by leveraging Novell's Open Systems Architecture and Oracle's Network Computing Architecture.
Build distributed network applications by leveraging the Oracle Java Class libraries for NetWare.
Requirements for Using Oracle8
Oracle8 for NetWare requires a NetWare 4.1x or NetWare 5 server with the following resources:
48 MB free RAM (minimum)
16 MB additional free RAM for the Advanced Replication option
200 MB free disk space (minimum)
Oracle8 client software requires:
A 486 or higher processor
Windows 95, Windows NT Workstation version 4, or Windows NT Server version 4 operating system
16 MB free RAM
25 MB free disk space (minimum)
The Oracle Enterprise Manager running on an Oracle8 client requires:
32 MB free RAM
25 MB free disk space for the manager
Btrieve Installation and Operation
The Btrieve key-indexed record management system included with NetWare 5 is designed for high-performance data handling and improved programming productivity. Btrieve allows an application to retrieve, insert, update, or delete records either by key value, or by sequential or random access methods.
* Originally published in Novell AppNotes
Disclaimer
The origin of this information may be internal or external to Novell. While Novell makes all reasonable efforts to verify this information, Novell does not make explicit or implied claims to its validity.