Developing NDS-Enabled Applications
Articles and Tips: article
NDS Market Development Manager
Developer Alliance Division
01 Dec 1997
Discusses the following questions: What is a directory service and, specifically what is NDS? Why build an NDS-enabled application? What are the directory opportunities for directory services applications?
- Introduction
- Why Build an NDS-Enabled Application?
- NDS: A True Directory Service
- NDS Features and Benefits
- Platform Independence
- Getting Started
Introduction
Until recently, the value of a directory service was linked almost exclusively to centralized file and print service management. But developers and other IT professionals are discovering the power of directory services for user access, system management and application development.
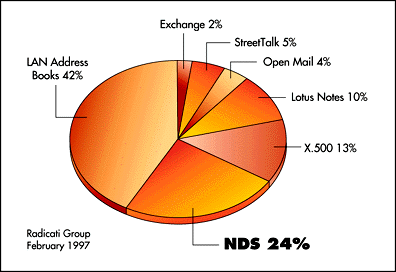
NDS (Novell Directory Services) provides solutions that let developers build instantly discoverable, directory-enabled applications rapidly--applications that require much less effort and lower overhead than ever before. NDS provides a wide range of developer interfaces that let developers choose the best, most familiar tools for the job, including Java, ActiveX controls, JavaBeans, C/C++, and Scripting. And NDS lets developers focus on the core application components that bring their original ideas to light, while leaving fundamental aspects of application development such as administration, data storage, security, and authentication to Novell. What's more, NDS enhances an application's market appeal because its robustness enhances any application, and its widespread name recognition adds credibility. According to the Radicati Group, NDS is the overwhelming leader in the directory services category with more than 20 million users and a 24 percent share of the market (see Figure 1). That's more than twice the market share of its nearest competitor.
NDS provides a single point of administration, storing all information in one central location for any application. It offers single sign-on, meaning an application can verify that a user object has authenticated to NDS and leverage this authentication instead of presenting a dialog of its own. It provides network-wide security; instead of having the user-profile information located on the client machine or a closed database, for example, user- profile information can be stored in NDS, so it's centrally located and controlled.
Novell Application Launcher (NAL) utilizes NDS to distribute and manage applications, thus lowering the cost of administration and making resources readily available.
NDS is open based on X.500 and international standards. Therefore, it simplifies access and navigation for users and integrates various directories, platforms, resources and people. NDS is a major intra-organizational tool while being a window to the outside world.
It's accessible from all of the emerging open Internet standard interfaces. And, clearly, it makes network usage and administration far less complicated, thus enhancing productivity while lowering the cost of ownership. Since NDS is available on all the most popular UNIX platforms, Windows NT and IntranetWare, it is the only true platform-independent directory technology that can take care of your application, no matter where it needs to go on the network.
A wide variety of applications can gain value by being NDS-enabled. These include:
line of business
database
groupware
electronic commerce
E-mail
management
telephony
system administration
utilities/tools
router
Developers designing these types of applications can pick and choose the NDS solutions they want to leverage, including single sign-on, authentication, administration, management and object repository.
Figure 1: The directory services market.
Why Build an NDS-Enabled Application?
By building applications that consume functionality provided by NDS, you create software with features that are far more flexible and robust than they would otherwise be. Moreover, you don't have to build and promote your own access and administration methods. As a result, you can speed up your product cycle and concentrate on your own areas of development and marketing expertise and let Novell build and market the directory component of your application.
NDS is valuable for developers because of its support of emerging Internet standards, its stability, and its ever-increasing interoperability with platforms from a wide array of vendors. NDS is technology with a long track record that includes nearly a decade in development and more than four years on the market. Novell recognizes that developers want to preserve their investment or "sweat equity" in their code, and they want options. NDS is a stable, mature, widely used directory service that lets you choose the development environment that's right for you (Java, ActiveX controls, Java Beans, Scripting, C/C++, etc.).
NDS supports several open standards and emerging Internet protocols and languages. For example, LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol), JNDI (Java Naming and Directory Interface), CORBA (Common Object Request Broker) and RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) let you approach any directory-enabling project with confidence and a wide range of choices. NDS is also being integrated into UNIX systems, Windows NT Server and other operating systems.
NDS offers technology that acts as a repository of information for the network, and it makes it possible to keep tabs on network resources while enhancing the availability and security of business-critical resources. NDS is also distributed, fully replicated and fault-tolerant. Because of replication, users can log in once and access services and the most current information from any server on the network. In addition, in the event of a server failure, NDS automatically reroutes user requests to the closest replicated server without users taking any action.
Aside from the obvious benefits of single sign-on and single point of administration (and the enhanced security inherent in those features), NDS is the source for additional security, scalability, and user/administrator productivity. For example, Novell developer teams exploited the power and flexibility of NDS in ManageWise to enable administrators to monitor and manage mixed IntranetWare and Windows NT environments to reduce network failures more than ever before. Also through NDS, ManageWise can provide an application inventory across the network to tell administrators which application versions are located on each workstation.
Novell also used NDS functionality to develop NAL, which enables administrators to easily manage applications at the network level instead of machine by machine. NAL can also update Internet/intranet documents and content from one location. For example, phone numbers, contact names, titles, photos and other information created within an application and stored in NDS can be automatically updated on Web pages and across the intranet with NAL.
NDS: A True Directory Service
Unlike other products with limited functionality that are called directories or directory services, NDS is a true directory service because it lists and provides access to every resource on your network. NDS provides administrators with a single, logical, and concise view of all network resources and services.
It offers single sign-on access through a secure login and organizes network resources (users, printers, workgroups, applications, volumes, file servers, database servers, routers, objects, etc.) hierarchically in a directory tree. It also provides security by keeping the criminals and the curious from logging on. The bottom line is that NDS simplifies, automates and protects information and information technology.
No definition of NDS would be complete without mentioning its platform- independent capabilities. NDS is the only directory service that supports the leading UNIX implementations, Windows NT Server, and Novell's own widely deployed networking software products, including IntranetWare, GroupWise, and ManageWise.
Major Novell OEM partners such as IBM, Hewlett-Packard, Sun, and SCO support NDS, and many third-party applications leverage NDS, including products from Cheyenne Software, Motorola, CallWare Technologies, and Oracle Corporation.
NDS Features and Benefits
NDS also adds value to your applications in other ways:
Single sign-on
NDS allows users to access applications through a single sign-on, meaning that one-password access to any authorized resource on the network is possible. Your application can verify that a user object has authenticated to NDS and leverage this authentication. For example, a user can log on to the network with a single password and user ID and access an Oracle database securely without having to go through a different login/authentication process again. With NDS, one authentication process is enough.
Single point of administration
In Fortune 1000 companies today, a user is likely to be registered in no fewer than 14 different proprietary directories. So, it's no wonder that, according to a recent Gartner Group study, approximately 79 percent of the total cost of owning a network is incurred in administration costs alone. NDS lowers cost of ownership and dramatically reduces administration tasks by storing and replicating information across servers. NDS is accessible at a single point anywhere on the map, and personal user information can be updated across applications with a single entry. In addition, with NDS, network administrators no longer have to spend hours visiting each user's workstation to install or upgrade applications.
With NDS and NAL, network administrators can deploy directory-enabled applications or upgrade existing applications across the network without ever leaving their desks. Many network administrators will purchase your software for that reason alone. And, aside from being able to log in to the network with a single password and user ID, end users will appreciate easy access to resources on servers as well as the automated delivery of applications and documents to their desktops.
Security
Network security is an issue of critical importance these days. By developing your application to integrate with NDS, you can leverage the integrity and security of the directory itself. Instead of having the user profile information located on the client machine, it can be stored in NDS. That way, the profile information is centrally located for fault-tolerance and management, and access is tightly controlled.
To give users access to network services, NDS uses an authentication service based on the RSA public-key/private-key encryption/decryption algorithms. This authentication mechanism uses a private key attribute and a digital signature to verify a user's identity. Authentication is session-oriented and the client's signature is only valid for the duration of the current session.
However, the client doesn't have to be re-authenticated every time the user asks for additional services or applications, as re-authentication takes place automatically in the background. Thus, the integrity of directory-enabled applications is protected and secure, and the user can access resources globally easily.
NDS provides powerful Access Control Mechanisms (ACLs) that allow developers to ensure that only the data they want to expose ever reaches the light of day. For example, your product might require that a Social Security attribute be added to the user object. NDS, through its ACLs, provides the capacity to restrict access to an individual attribute so that only authorized personnel in Human Resources can read this or any other kind of confidential information.
NDS brings to the network the security it needs. Authentication to NDS enables the network to verify who's gaining access or which resources are located where, and the only one who can alter the network's and the directory's configurations is the administrator. In addition, with Novell BorderManager using the power of NDS, enterprises can enhance back- end security and manage internet access in the following ways:
Control outbound access from intranets to the Internet
Control worldwide inbound access from the Internet to intranets, such as access to internal Web servers, with appropriate security controls in place
Through the power of NDS, Novell BorderManager allows organizations to connect their intranets to the Internet in an integrated, flexible and secure manner, while boosting performance. BorderManager also allows organizations to take advantage of the broad reach and low cost of the Internet to link sites through worldwide Virtual Private Networks (VPNs). VPNs combine sites into sub- networks that run on top of their existing enterprise networks. In turn, VPNs combine the intranet and the Internet and allow organizations to serve multiple constituencies internal workers, customers, vendors, etc. over the same network.
Each constituency sees only the VPN it is authorized to use, and it's all made possible with NDS. As workgroups and enterprises continue the trend toward geographically dispersed, global IS infrastructures, VPNs and other Internet-based solutions will become commonplace, and so will the need for NDS. As a fully authenticated global directory with built-in RSA encryption and C2-level certification, NDS will safeguard data within any directory- enabled, internetworking application or service.
Scalability
Since your application is designed to work in a variety of settings, you would hope that a company's network is equally dynamic. NDS is scaleable to any size and type of network. Because of its flexible partitioning and replication, NDS makes all the parts fit, from the organizational unit right down to individual applications, objects and nodes on the network. Its schema is extensible and customizable like nothing else on the market today. For example, a user object can be extended to include a social security number or an emergency contact number. Application objects can also be extended to include any number of attributes.
NDS is designed to accommodate growth, and new resources can be added to the network with a simple point and click of the mouse. It is also appropriate for small networks the kind of single-server installations with fewer than 25 users. For them, NDS helps organize the operation internally while establishing links to the Internet and to other network platforms used by suppliers and customers.
Shared Object Store Database
Object store databases have become extremely important with the growing popularity of objects and components in the developer environment and across the Internet and intranets. By leveraging NDS, you simplify your workload while enabling your application to take advantage of object- and component- based computing.
Service Location
The traditional way of making a service viable on a network is to use a SAP (Service Advertising Protocol) to announce its existence. Generally, the SAP is broadcast every 60 seconds by default through every segment of the network, or to specific network segments using a NetBIOS name server. NDS is essentially a tool for locating and using network resources and by making services objects on the directory, it obviates the need for SAPs, thus reducing network traffic and making the developer's job a lot easier.
On the client side, the end user or network administrator can browse the directory and determine if there is a particular kind of service object that suits them. Moreover, it will be a secure object--one that has been registered and authenticated to the network.
Platform Independence
NDS offers platform independence: it has been licensed to Hewlett-Packard to be bundled in its HP-UX servers and is also bundled with SCO UnixWare and will soon run on Sun Solaris and IBM RS/6000 and S/390 systems; and Novell is porting it to Windows NT Server for release in late 1997, with more operating systems coming soon thereafter.
In addition, NDS already provides standard IP support that's accessible through a standard Web browser, LDAP or HTTP. And, it will soon provide access and management for Netscape SuiteSpot services, thanks to the recent collaboration of Novell and Netscape that has resulted in a new company called Novonyx. (http://www.novonyx.com)
With the evolution of the NOS and the globalization of network computing, directories have risen in stature and importance. Novell is working with IT industry leaders to provide NDS functionality to numerous operating system platforms. Novell is also bringing directory capabilities to the physical network layer so that leading hardware vendors (Ascend, U.S. Robotics, Cisco, Bay Networks, 3Com, etc.) can provide directory services functionality with their dial-in products.
At the Internet/intranet level, NDS is the "carrier-grade" directory service. Novell is extending NDS's reach globally via telecommunications companies which include AT&T, Deutsche Telekom and Nippon Telephone and Telegraph. AT&T WorldNet Intranet Connect Services, for example, is an NDS-enabled network that brings the secure authentication and access of NDS to AT&T's customers and partners.
WorldNet Intranet Connect Services enables users to make interconnections with literally thousands of networks yet still maintain security, reliability and, most importantly, the ability to find and manage things in the networked world all without building and maintaining WAN links or investing in soon-to-be outdated hardware. Novell, unlike any other company, is influencing networking at every level with a focused directory services stratagy that extends all the way from routers to operating systems.
Because of NDS's compatibility with LDAP and ODBC, it can serve as a directory for resources stored on the Internet and legacy databases. Plus, NDS can interoperate with any other operating system, application, or object that supports these standards. NDS can serve as the link between disparate (and distant) workstations, servers, hubs, routers, databases, operating systems, network environments, individual users, workgroups, organizations and your application.
Getting Started
With a multitude of development options and many new services to come, Novell and DeveloperNet are supporting developers in every way with the goal of providing a common network-services engine and support framework for developing to all major operating systems. Check out all of Novell's development options at the DeveloperNet Web site (http://developer.novell.com) or call DeveloperNet at 1-800-REDWORD.
* Originally published in Novell AppNotes
Disclaimer
The origin of this information may be internal or external to Novell. While Novell makes all reasonable efforts to verify this information, Novell does not make explicit or implied claims to its validity.