Console Help Commands in NetWare 5.1: Memory, Memory Map, Mirror Status, MM and Modules
Articles and Tips: article
Senior Editor
DeveloperNet University
eliebing@novell.com
01 Apr 2001
This section is one in a series that intends to describe each of the NetWare 5.1 console commands (both normal and hidden) in alphabetical order and to tell when, why, and how to use them properly. To see a list of the commands that you can perform at the server console, type HELP <Enter> at the server console prompt. To use the commands described here, simply type the command at the server console prompt followed by the <Enter> key.
MEMORY and MEMORY MAP
The MEMORY and MEMORY MAP commands both allow you to display the total amount of server RAM (random access memory) that the operating system can address, only their presentation of this information is different. The syntax for MEMORY is:
MEMORY <Enter>
Depending on how much available server memory there is, this command gives you a response similar to the following:
THE-MATRIX: memory Total server memory: 130,686 Kilobytes
The syntax for MEMORY MAP is:
MEMORY MAP <Enter>
This command gives you a reply similar to the following:
THE-MATRIX: memory map
System memory map:
0 - 12288 (DOS)
12288 - 63824 (DOS)
63824 - 653312 (Server)
1048576 - 134217728 (Server)
While the two numbers look different, the number for the MEMORY comand is in Kilobytes, while the number for MEMORY MAP is displayed in bytes.
Note: On PCI bus computers, NetWare 5.x can address up to 4 GB of memory.
MIRROR STATUS
The MIRROR STATUS or MIRROR STATUS [partition number] command displays the status of NetWare mirrored partitions. You can use the MIRROR STATUS command to view how mirroring on a partition is progressing.
To view a list of all logical disk partitions with their present mirroring status, simply type
MIRROR STATUS <Enter>
To view a particular partition's mirrored status and the devices that make up the members of the mirror group, add the partition number after the command, such as:
MIRROR STATUS 0 <Enter>
There are a number of status messages that you might see--especially if the status process is happening at this time. The following table describes the possible status messages that you can see:
|
Status
|
Explanation
|
|
Being remirrored |
Remirroring is in progress; the percent completed is displayed. |
|
Fully synchronized |
The mirrored partitions have the same data. Remirroring is complete. |
|
Not mirrored |
Disk mirroring was not set up for this partition. It has no mirrored partner. |
|
Orphaned state |
A partition has been removed from a mirrored group, and the volumes on the partition have not been renamed. These volumes cannot be mounted unless they are renamed or remirrored. However, you can restore the orphaned partition to its mirrored partner with NWCONFIG. |
|
Out of synchronization |
The partition is out of synchronization with its mirrored partners and for some reason cannot be resynchronized. |
MM
The MM commands are marked as Hidden and used in conjunction with Novell's clustering solution. These commands are used by the person who sets up clustering, putting together these specific commands in script form. Then once the clustering commands are in script form, they are automatically performed whenever there is a clustering problem and the server reboots for some reason.
Since these commands are mostly related to clustering solution, it would not be a good idea to talk about them outside their context, which is to be used in a clustering script. Failure to use these commands properly can result in the NetWare operating system not being able to find partitions on servers even though the partitions exist according to the Media Manager.
There is one MM command that can assist you in identifying mirrored partitions. Suppose you wanted to label your mirrored partition "Partition Mirror of SYS." To do this, you would type the following:
mm assign partition owner label = Partition Mirror of SYS (128 bytes max)
However, if you are working in a clustering environment, this command can disassociate a partition from a server designation. So unless you know the dynamics of clustering script commands, only perform the given command on non-clustered servers.
MODULES
The MODULES or MODULES [module name] shows you which NetWare Loadable Modules (NLMs) and other drivers are running on the server. To display all of the modules that are running on the server, simply type
MODULES or M <Enter>
You can also see all of the modules and drivers that begin with a certain character or set of characters by including the * wild card in the command. For instance, if you wanted to see all of the modules and drivers that begin with the letters MA, you would type:
MODULES MA* <Enter>
You can also specify a single module to see its version number and shipped date. For instance, if you needed to know which version of the DS.NLM (Novell Directory Services) you are running, you would type:
M DS <Enter>
You will see a screen similar to the following:
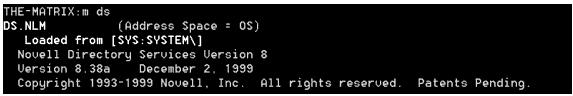
When you run the MODULES command, you will see modules and drivers displayed in different colors. These colors also apply as modules and drivers are being loaded. The color meaning is as follows:
Blue.
These modules and drivers are loaded from a hard-coded internal list that is called when SERVER.EXE executes. You can see this list by typing LIST STAGE <Enter> at the server console prompt.
Red.
These modules and drivers are also bound in to the SERVER.EXE, but are loaded from the startup partition found in the C:\NWSERVER directory (or one of its subdirectories). For instance, DSLOADER.NLM is always colored Red because it needs to load from the C: drive.
Purple.
These NLMs and drivers are autoloaded by another NLM as the server initially comes up. For example, LONG.NLM, CLIB, STREAMS, are colored Purple when they initially load, but they are then colored Red when you see them listed using the Modules command.
White.
These NLMs and drivers are loaded from a Novell configuration file, from any .NCF files (such as AUTOEXEC.NCF or STARTUP.NCF), or from the server console prompt.
Yellow.
Informational messages that refer to symbol information about the modules that are being loaded.
Green.
Information messages on the modules themselves that are loading.
|
Console Command
|
Function
|
Example
|
|
MEMORY |
Allows you to display the total amount of installed memory that the operating system can address. |
MEMORY |
|
MEMORY MAP |
Displays memory as it is allocated to DOS and to the server operating system |
MEMORY MAP |
|
MIRROR STATUS |
Displays the status of NetWare mirrored partitions. You can also specify a particular partition. |
MIRROR STATUS or MIRROR STATUS 0 |
|
MM |
Hidden commands that are to be used in Novell clustering scripts. Know what you are doing before using these commands. |
MM |
|
MODULES or M |
Lists the NetWare Loadable Modules (NLMs) and other device drivers that are loaded on the server. |
MODULES MODULES <name> MODULES D* |
* Originally published in Novell AppNotes
Disclaimer
The origin of this information may be internal or external to Novell. While Novell makes all reasonable efforts to verify this information, Novell does not make explicit or implied claims to its validity.