Console Help Commands in NetWare 5.1: CPUCHECK, CSET, DISABLE TTS, and DISABLE LOGIN
Articles and Tips: article
Technical Editor
DeveloperNet University
mmckell@novell.com
01 Aug 2000
This section is one in a series that intends to descirbe each of the NetWare 5.1 console commands in alphabetical order and to tell when, why, and how to properly use them.
Check CPU
The CHECKCPU command in NetWare 5.1 allows you to display information at the server console about your server's processor or processors. The command reveals the following processor information (see Figure 1):
Processor number
Processor clock speed (MHz)
Processor ID
Processor version and sub-version
Amount of L1 and L2 cache memory
Current revision number
Figure 1: Information displayed by the CPUCHECK command
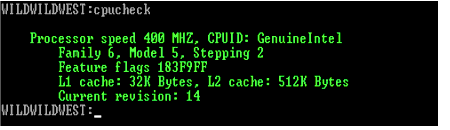
The syntax is straightforward. Type CPUCHECK [N] and press <Enter>. The N is an option you can add to only display CPU information for a specific processor number.
Set Parameters by Category
Choosing the Server Parameters option within the MONITOR utility offers fifteen settable parameter categories. You can also set or view these same categories from the server console using the CSET or the SET command. CSET is a simplified version of the SET command, for it allows you to modify the setting without having to type in the entire parameter as well. The following table lists the fifteen parameter categories by name and function.
|
entrymeter Category
|
Function
|
|
Communications |
Communication parameters control the packet receive buffers. |
|
Directory Caching |
Directory Caching parameters control directory cache buffers, which hold entries from the directory table. As directory cache buffers increase, file cache buffers decrease. In tuning the server for performance, directory caching and file caching need to be balanced. |
|
Directory Services |
Directory services parameters control various NDS processes, the NDS trace file, and the specification of bindery contexts. |
|
Disk |
Disk parameters control aspects of disk geometry, elevator height, mirroring and synchronization. |
|
Error Handling |
Error handling parameters control the size or error log files and specify what happens to error log files after they reach a specified size. |
|
File Caching |
File cache parameters control file cache buffers and must be balanced with directory cache buffers. File cache buffers hold files in memory for faster access. |
|
File System |
File system parameters control file purging, warnings about volumes that are almost full, and reuse of turbo FAT. |
|
Locks |
Lock parameters control how many open files and record locks each client is allowed to have, and how many total open files and total record locks the operating system is allowed to handle. |
|
Memory |
Memory parameters control the memory recovery process ("garbage collection") as well as memory above and below 16 MB. |
|
Miscellaneous |
Miscellaneous parameters control encrypted passwords, alerts, and server processes. |
|
Multiprocessor |
Multiprocessor parameters control system threshold (load balancing) and Auto Start Processors. |
|
NCP |
NetWare Core Protocol (NCP) parameters control NCP packets and boundary checking. |
|
Service Location Protocol (SLP) |
SLP parameters control SLP Retry count, multicasting, unicasting, DA discovery, Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) size, and broadcasts. |
|
Time |
Time parameters control time synchronization, the timesync.cfg file, and time zone settings. |
|
Transaction Tracking |
These parameters control the Transaction Tracking System (TTS). Most of these parameters should not be changed. We recommend that you retain the defaults. |
The syntax for calling the CSET command is as follows:CSET category name
For example, to view or set the parameters for miscellaneous settings, you would typeCSET miscellaneous and see information similar to Figure 2 at the console screen.
Figure 2: Information displayed by the CSET miscellaneous command
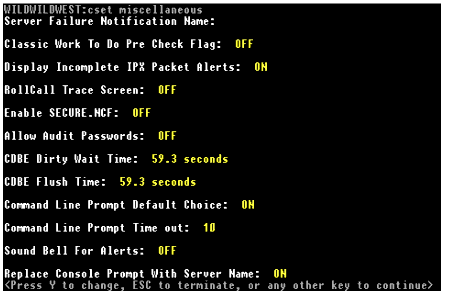
The parameters in the category selected are displayed one by one, allowing you to view, change, or skip each parameter. By pressing Y, you can modify the setting for the selected parameter, or you can press any key and go on to the next parameter. CSET will then display the new setting and drop you at the console prompt. To quickly view or set one of hundreds of set parameters by category, the CSET command is a fine alternative to the SET command(which makes you type out the entire SET parameter along with change you want to make) or to the MONITOR utility.
Disabling TTS
Beginning with NetWare 3.12, NetWare Transaction Tracking System (TTS) became an integral part of the NetWare operating system. TTS protects database applications from corruption by backing out incomplete transactions that result from a failure in a network component. Backing out means that data and index information in the database are returned to the state they were in before the transaction began.
Disabling TTS turns off the TTS system of being able to back out of incomplete transactions of database applications. Enabling or Disabling TTS are primarily functions that application developers would employ while testing their applications on the server. It is recommended that you leave TTS enabled for normal server functionality.
The syntax is DISABLE TTS without any flags or options.
TTS is an integral part of NetWare v3.12; it is not an optional feature as in earlier versions. However, it can be turned on and off.
Disabling Login
You can use the DISABLE LOGIN command to prevent future users from being able to log in to a server without having to bring the server down, thereby affecting current users' connections, or causing any other interruption or damage. This command is useful when you are making repairs, backing up files, or loading software. Users already logged in aren't affected. However, a user who logs out won't be able to log in again until you execute the ENABLE LOGIN command.
The syntax is simply DISABLE LOGIN.
|
Console Command
|
Function
|
Example
|
|
CPUCHECK |
Allows you to display information at the server console about the server's processor or processors. |
CPUCHECK or CPUCHECK [N] |
|
CSET |
Allows you to set or view the settable server parameters by category. |
CSET category name |
|
DISABLE TTS |
Allows you to disable TTS, the system of being able to back out of incomplete transactions of database applications. |
DISABLE TTS |
|
DISABLE LOGIN |
Allows you to prevent future users from being able to log in to a server without bringing the server down, affecting current users' connections, or causing any other interruption or damage. |
DISABLE LOGIN |
* Originally published in Novell AppNotes
Disclaimer
The origin of this information may be internal or external to Novell. While Novell makes all reasonable efforts to verify this information, Novell does not make explicit or implied claims to its validity.