Console Help Commands in NetWare 5.1: CDBE, Clear Station, CLS, and Config
Articles and Tips: article
Technical Editor
DeveloperNet University
mmckell@novell.com
12 Jul 2000
This section is one in a series that intends to descirbe each of the NetWare 5.1 console commands in alphabetical order and to tell when, why, and how to properly use them.
I have vivid memories as a child of spending many long, hot summer evenings exploring a small creek bed not far from home. Occasionally, I would overturn a large rock and discover strange water insects, scorpions, or other unexpected creatures. The best thing to do was to swiftly replace the disturbed object and be on my way. A similar thing happened in the course of preparing this article. As I began exploring the CDBE family of commands, I discovered something unexpected and swiftly went on my way to other commands.
CDBE Commands
CDBE EDIT, CDBE INFO, CDBE VALIDATE, and CDBE ERRLVL are all hidden commands that are visible from the console if you turn on the "Display Hidden Console Commands" option found in the configuration screen of the Portal utility. NetWare 5.0 and 5.1 use a registry to store SET parameter changes and other operating system configuration information. These settings are called "persistant" because they are stored and are therefore available without having to re-enter them each time you take the server down and back up again.
The explanation I received when I overturned this command was that CDBE (configuration database engine) is a cryptic registry editor that is used internally by Support at Novell. That's all I know, so let's be on our way to the next command.
Clear Station
In normal circumstances, the NetWare operating system's watchdog process tries to clear inactive workstation connections by sending a query packet to worksta- tions that the server hasn't heard from for a period of five minutes. If the watchdog does not hear anything from the workstation, it sends another query packet every minute for the next ten minutes to that workstation. If there is still no response, the server will clear that workstation's connection from the server Connection Table, thus making that connection license available for other users.
Disconnecting or clearing a connection on a server is also possible by using the CLEAR STATION command. This command is useful if a workstation has crashed and left files open on a server, or if you need to bring down the server and there are still unresolved connections to the server.
When CLEAR STATION is invoked, it closes the workstation files and erases the server's internal connection and other tables for that workstation, including drive mappings not saved in the login script. Thus, it effectively breaks the communication link between server and workstation.
The CLEAR STATION syntax includes the station number (N) or ALL as variables.
CLEAR STATION N or CLEAR STATION ALL
For example, at the console prompt I would first determine which connection I wanted to clear. This is done by loading the MONITOR utility and selecting Connections | Connection Information (or by using the NLIST command from a workstation's DOS prompt). Once I know the workstation's connection number, I would type: CLEAR STATION 12 <Enter> at the console prompt. (You can also perform this function through the NetWare 5.1 Portal utility--see "Beyond the Basics: Managing Connections through the NetWare Management Portal Utility" in Novell AppNotes June 2000.)
When using this command, be sure that you really want to clear the connection, because if the workstation is in the middle of a transaction or a file update, files might be saved with incomplete or corrupt data. This is especially important to remember if you're ever tempted to use the ALL variable, thereby disconnecting every workstation from the server.
CLS
When your screen is all a mess and you want some cleanliness, simply type CLS <Enter>. Rhyming aside, CLS is great way to clear your server's console screen (OFF also does the same thing). You're not actually erasing anything--you're merely telling the console to start displaying new information with the prompt at the top of the screen.
The syntax is simple, just type CLS or OFF and press <Enter>.
Config
Before you go installing any memory boards, network boards or host bus adapters, it's wise to first check the current hardware settings of current boards or adapters, and CONFIG is the easiest way to do it.
The syntax is yet again simple, without any variables or flags, just type CONFIG <Enter>. CONFIG can be used to display the following information (see Figure 1):
Figure 1: Information displayed by the CONFIG command.
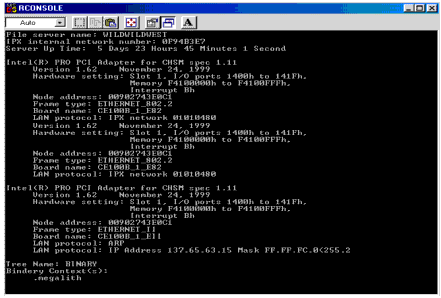
The file server name
The internal network number of the file server
The loaded LAN drivers
The hardware settings on all network boards
The node (station) addresses of the network boards
The communication protocol bound to the network board
The network number of the cabling scheme for a network board
The frame type assigned to the board
The board name assigned
The NDS tree name and context of the server
|
Console Command
|
Function
|
Example
|
|
CDBE commands (hidden) |
Cryptic registry editor used internally by Novell Support. |
N/A |
|
CLEAR STATION |
Allows you to disconnect or clear a workstation connection on a server without downing the server. |
CLEAR STATIONN or CLEAR STATION ALL |
|
CLS |
Allows you to clear your server's console screen. |
CLS |
|
CONFIG |
Allows you to display the file server name, the internal network number, the loaded LAN drivers, the hardware settings on all network boards and their node addresses, the communication protocol bound to the network board, and other information. |
CONFIG |
* Originally published in Novell AppNotes
Disclaimer
The origin of this information may be internal or external to Novell. While Novell makes all reasonable efforts to verify this information, Novell does not make explicit or implied claims to its validity.