Novell BorderManager Filter Configuration through iManager
Articles and Tips: article
Software Consultant
Novell, Inc.
USubbaraju@novell.com
Mrinal K Bhattacharjee
Software Engineer
Novell, Inc.
MKanti@novell.com
Thanks to Neil Cashell and Manisha Malla of Novell for their significant contributions to this AppNote.
01 Jun 2002
Novell BorderManager 3.7 comes with a Packet Filtering Configuration Task for configuring TCP/IP filters. This task and the Access Management role are automatically installed as Novell iManager plug-ins when BorderManager is installed in a NetWare 6 environment. This AppNote describes the filter configuration process and provides related management and troubleshooting tips.
- Introduction
- General Requirements
- Migrating Filters to eDirectory
- Configuring Packet Filters in iManager
- Troubleshooting Tips
- Future Scope
- Conclusion
|
Topics |
TCP/IP, packet filtering, network management |
|
Products |
Novell BorderManager 3.7, Novell iManager |
|
Audience |
network administrators, consultants, integrators |
|
Level |
intermediate |
|
Prerequisite Skills |
familiarity with TCP/IP, filtering, security |
|
Operating System |
NetWare 5.1, 6.0 |
|
Tools |
none |
|
Sample Code |
no |
Introduction
In Novell BorderManager (NBM) 3.7, filter configuration can be done from Novell iManager, a Web browser-based utility, as well as from the server console (FILTCFG). The configuration information is now stored in eDirectory. In BorderManager Enterprise Edition 3.6 and earlier, filter configuration was done through FILTCFG, a text-based utility that runs on the server. The configuration information was stored in files.
Filter configuration through iManager is role-based and can be done by the assigned users only. Figure 1 shows the location of the Role and Task associated with BorderManager filter configuration.
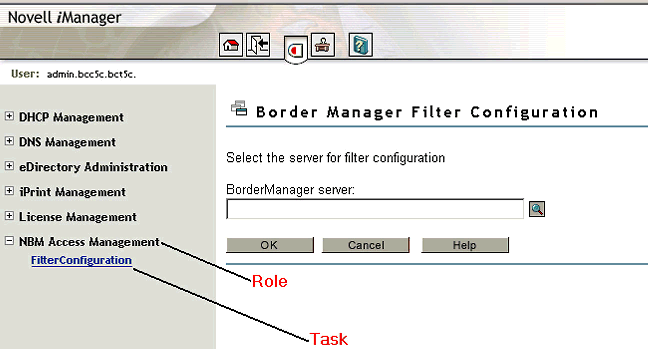
Location of the Role and Task for BorderManager filter configuration.
The iManager utility is user-friendly and streamlined to be much more intuitive than the FLTCFG utility. The packet filtering plug-in shares a common look and feel with other iManager plug-ins. So once you become familiar with plug-ins on iManager, it is relatively easy to navigate through NBM-related packet filtering. The filtering plug-in also comes with context-sensitive help to facilitate packet filtering operations.
This AppNote describes TCP/IP packet filter configuration through Novell iManager and provides relevant migration, management, and troubleshooting tips.
General Requirements
NetWare 6 ships with an iManager management framework; NetWare 5.1 does not. If you don't have any NetWare 6 servers in your tree, you will have to configure the filters through FILTCFG. If you do have a NetWare 6 server with NBM 3.7 in the same tree, you can use the iManager interface to select the NetWare 5.1 server in the "BorderManager server selection" screen and proceed with the configuration (as described later in this AppNote).
The files and directories on the NetWare 6 server that constitute the iManager plug-in for filter configuration are:
sys:\webapps\eMFrame\WEB-INF\install\bm\bm.xml
sys:\webapps\eMFrame\WEB-INF\plugins\bm\bmtasks.xml
sys:\webapps\eMFrame\WEB-INF\lib\bm.jar
sys:\webapps\eMFrame\WEB-INF\classes\templates\BMResources.properties
sys:\webapps\eMFrame\WEB-INF\templates\browser\bm
sys:\webapps\eMFrame\help\en\bm
The packet filtering functionality is handled by several NetWare Loadable Module (NLM) programs. FILTSRV.NLM reads the rules from eDirectory (or from the FILTERS.CFG file in the case of IPX and AppleTalk filters) and informs the IPFLT module. IPFLT.NLM checks the version of FILTERS.CFG and loads IPFLT31.NLM, which does the actual packet filtering.
Note: Even though NBM 3.7 reads the IP Filters from eDirectory, the product still has a dependency on the FILTERS.CFG file. Do not delete FILTERS.CFG or else filtering for NBM 3.7 will not work.
To learn of changes made through iManager, FILTSRV.NLM registers with eDirectory for Event Notification. Whenever a change is made in eDirectory, eDirectory notifies FILTSRV, which reads the latest list of filters from eDirectory and informs the IPFLT module. (This may cause a delay of up to 30 seconds from the time the change is made and when the filtering actually goes into effect.)
Note: If for some reason eDirectory is not available, FILTSRV.NLM tries to read filters from eDirectory every 30 seconds until it reads the information successfully. Until such time, temporary "Deny All" filters are added to protect all public interfaces on the system.
Storing the filter information in eDirectory poses a major new requirement: the NBM server must have a Read/Write replica of the partition where the Server object resides in eDirectory. You need eDirectory version 8.0.9 for NetWare 5.1 SP4 and version 8.6.2 for NetWare 6.0 SP1.
Several new eDirectory objects for filter configuration are created by the NBM 3.7 installation program:
An NBMRuleContainer object is created at the same level as the NCP Server object of the BorderManager server.
Role, Module and Task objects are created under Role Based Service objects for iManager management tasks.
In addition, the eDirectory schema is extended by attaching the fwsAuxFiltServer auxiliary class to the NCP Server object with the fwsAction and fwsStatus attributes initialized to zero.
The recommended browser for filter configuration using iManager is Internet Explorer 5.5 and above. It is possible to browse iManager pages using the Netscape browser, but currently NBM filter configuration through Netscape is not supported.
Migrating Filters to eDirectory
If you are upgrading from BorderManager 3.5 or BorderManager Enterprise Edition 3.6 to Novell BorderManager 3.7 and you currently have existing filters on your BorderManager server, you can migrate them from the FILTERS.CFG file to eDirectory. To do this, follow these steps.
After installing NBM 3.7, restart the server.
If FILTSRV is already loaded, unload it.
Load FILTSRV with the migrate option by typing "FILTSRV MIGRATE <Enter>" at the server console.
After the migration is complete, unload FILTSRV and reload it in normal mode by typing "FILTSRV <Enter>".
All existing filters will now be stored in eDirectory. Migration does not remove existing filters; it only adds filters from FILTERS.CFG. You can perform this migration at any time you want to move filters from FILTERS.CFG to eDirectory.
If you forget to load FILTSRV MIGRATE, the configured filters will not be displayed with the FILTCFG menu and the SYS:\ETC\FILTERS.CFG file will be empty. To work around this, recopy a backed-up version of FILTERS.CFG to the server. If no backup is available, run BRDCFG to get the BorderManager 3.6 default filters back in place, unload FILTSRV, and then follow the steps above to migrate the filters to eDirectory.
Configuring Packet Filters in iManager
To configure the NBM packet filters from within Novell iManager, first log in to the utility as follows:
Set your browser to https://<ip_address>:2200/eMFrame/iManager.html or use https://<DNS_name>:2200/eMFrame/iManager.html where <ip_address> is the IP address of a NetWare 6 server that has BorderManager installed, and <DNS_name> is the DNS name of a NetWare 6 server with BorderManager installed.
On the login page, log in to iManager with the same user name as the user who installed NBM 3.7 on the server, or as the user who has been assigned the NBM Access Management role.
Specify the eDirectory tree which has the NBM server on which you want to configure filters.
Once you have logged in to iManager, you can see the NBM Access Management role on the left panel. Click on "NBM Access Management" to see the Filter Configuration task.
Click the Filter Configuration task to see the Novell BorderManager Server Selection option.
Select the BorderManager 3.7 server where you want to configure filters.
When you log in to iManager, you are authenticated to an eDirectory tree but are not logged in to any server. Because a tree can have more than one server, you can select the server on which you want to configure the filters. The object selector next to the server input field allows you to browse the tree and select any server you want (provided it has NBM 3.7 installed on it).
You can configure filters on a NetWare 5.1 server with NBM 3.7 using iManager provided you have a NetWare 6 server with NBM 3.7 in the same tree. Simply select the NetWare 5.1 server in the BorderManager server selection screen and proceed with the configuration.
Note: To ensure that the configured filters are active, make sure you have enabled filter support using INETCFG.
After you have reached the filter configuration task, you will see the following seven types of configuration:
Configure Packet Forwarding Filter
Configure Service Type
Configure Incoming RIP Filter
Configure Outgoing RIP Filter
Configure Incoming EGP Filter
Configure Outgoing EGP Filter
Configure OSPF Filter
You cannot configure filters on BMEE 3.6 servers using the NBM 3.7 iManager plug-in. Also, the functionality of toggling the interface status between private and public is not provided in iManager; it must be done using FILTCFG.NLM.
For further details on these configuration options, refer to the online manual at http://www.novell.com/documentation/lg/bmee37/index.html. You'll find the relevant information by clicking on Administration Guide > Filters > Packet Filtering based on Novell iManager, and then selecting the option you are interested in.
Assigning the NBM Access Management Role
If you install BorderManager as user Admin, the NBM Access Management role is automatically assigned to the administrator. If you install BorderManager as any other user, the user should have Admin-equivalent rights and the role will be assigned to that particular user.
If you want to assign the NBM Access Management role to another user in the same tree, go to the iManager and click on the Configure button in the top right-hand portion of the screen. Select Role Management > Modify Role > and click the Members button for the NBM Access Management role. Add the user, as shown in Figure 2. Make sure that this user has rights to modify the NCP Server object and NBMRuleContainer object.
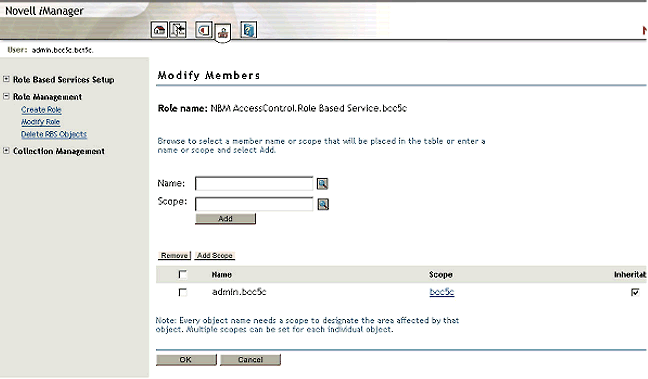
Assigning a member to the NBM Access Management role.
Filter Synchronization
Filters in eDirectory and the FILTERS.CFG file are not fully synchronized. When you configure filters using the FILTCFG utility, FILTERS.CFG is updated with the latest information from eDirectory. But when you use iManager to configure filters, the filters will not be reflected in FILTERS.CFG until the next time you use FILTCFG.
Making Filter Configuration Changes Immediate
As mentioned earlier, due to the event notification method that FILTSRV uses to become informed of configuration changes, there may be a maximum delay of 30 seconds between the time you make a change and the time it goes into effect. If you want to force FILTSRV to read the latest information from eDirectory immediately, enter the following command at the server console prompt:
REINITIALIZE SYSTEM
Backing Up and Restoring Filters
In NBM 3.7, all the filters you create are stored in a container object in eDirectory called the NBMRuleContainer. This container is created at the same level as the NCP Server object of the server on which NBM 3.7 is installed.
To back up IP filters in eDirectory, type the following command at the server console prompt:
FILTSRV_BACKUP_FILTERS <filename>
This will back up the filters to the specified file in the SYS:/ETC folder. If you do not specify the file name, the filters will be backed up in a file named FILTERS.BAK in the SYS:/ETC folder. The FILTERS.BAK file is essentially in the same format as the FILTERS.CFG file.
To restore IP filters to eDirectory, copy the backup file (FILTERS.BAK by default) to the SYS:/ETC folder on the server where you want to restore filters, and rename the file to FILTERS.CFG. Then type the following command at the console prompt (if FILTSRV is already loaded, unload it first and then type the command):
FILTSRV MIGRATE
Troubleshooting Tips
Unable to See iManager-Configured Filters in FILTCFG
If you have configured filters through iManager but are not able to see the filters in FILTCFG, it is probably because FILTCFG.NLM was already loaded on the server. Unload and reload FILTCFG.NLM.
Troubleshooting Nonfunctional Filters
If you have configured filters using iManager orFILTCFG.NLM, but the filters are not functional, follow these steps to find out why:
Check to see if filter support is enabled in INETCFG.NLM by selecting Protocols >TCP/IP > Filter Support. Make sure filter support is enabled. Configured filters will not be active until this is done.
Verify that the IPFLT31 module is loaded. You can do this by typing the"M IPFLT <Enter>" command at the server console prompt.
Verify that the FILTERS.CFG file exists in the SYS:ETC folder.
Check the actual filters in place to see that there is no rule allowing or blocking access to a service that is not behaving as it should.
A good document on troubleshooting packet filtering issues can be found at http://support.novell.com/cgi-bin/search/searchtid.cgi?/10018659.htm.
Manually Extending the Schema for Filtering
Normally, the eDirectory schema is extended for filtering during NBM 3.7 installation. If you need to manually extend the schema, run SCHEXT.NLM at the console prompt, specifying the Fully Distinguished Name (FDN) and password of a user with supervisory rights at the Root level of the tree. The syntax is:
SCHEXT <user_FDN> <password>
For example: SCHEXT .CN=ADMIN.O=NOVELL PASSWORD
IP Filters Not Seen in FILTCFG Immediately After Reboot
Several customers have asked why IP filters do not show up in the FILTCFG utility immediately after reboot. If the eDirectory database is not initialized by the time FILTSRV/IPFLT loads, you will not be able to see the filters. However, FILTSRV.NLM tries to read filters from eDirectory every 30 seconds until it is successful. Until such time, temporary "Deny All" filters are added to protect all public interfaces of the system.
NBM Access Management Role Not Seen in iManager
After installing NBM 3.7 and logging in to iManager, you may not see the "NBM Access Management" role displayed in the left panel. To remedy this, log in to iManager with the same user name as the user who installed NBM 3.7 on the server or as the user who has been assigned the NBM Access Management role.
If you still do not see the NBM Access Management role, follow these steps:
In iManager, click on the Configure button.
Click on "Modify Role" under "Role Management" in the left panel.
Check to see if the "NBM Access Management" role is visible in the list of roles in the right panel. If so, it is likely that the jar file and folder for plug-ins are not named properly; it should be sys:\webapps\eMFrame\WEB-INF\lib\ bm.jar. ("bm.jar" and all folder names should be in lowercase.)
If the role is not visible, you need to run the "Install plugin" task to install bm.jar. Start by clicking on the iManager Configure button, selecting "Role Based Services Setup", and then "Install Plugin".
Select "bm" as the plug-in to install (see Figure 3).
Using the Object Selector, browse eDirectory and select "Role Based Service" as the Collection Container.
Click OK to complete the plug-in installation.
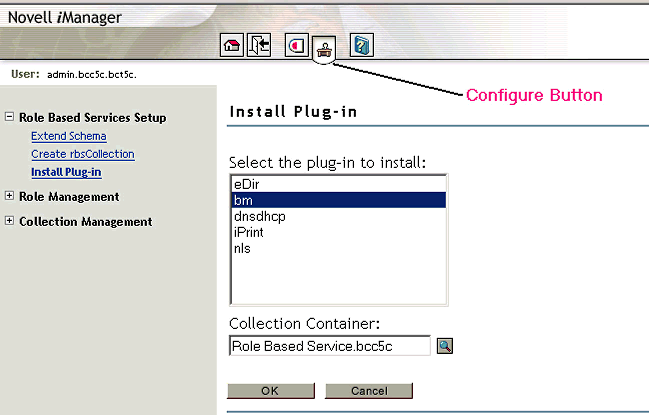
Manually installing the bm.jar plug-in to iManager.
Proxies on Non-Standard Ports No Longer Work After NBM 3.7 Upgrade
After upgrading to NBM 3.7, proxies listening on non-standard ports (other than 8080) may no longer work. NBM 3.7 opens some standard ports used by proxy (such as 8080, 21 and so on) and adds filters to protect the public interfaces. If you have configured your proxy to listen on some other port, you need to create filtering exceptions to allow the traffic through that port. This can be done using FILTCFG or iManager.
BRDCFG Doesn't Add NBM 3.7 Filters
The filters added by running BRDCFG and those added by installing NBM 3.7 are not the same. BRDCFG adds the BMEE 3.6 default filters, while NBM 3.7 adds all stateful filters. A modified version of BRDCFG that will add NBM 3.7 filters is planned for inclusion in Service Pack 1 (SP1) for NBM 3.7.
Updated Version of FILTSRV
When FILTSRV loads, it tries to read the filter configuration information (get object details) from eDirectory. If FILTSRV cannot read this information from eDirectory due to network communication problems, all packets will be allowed through the firewall. A new version of FILTSRV is available that will deny all packets through the firewall when eDirectory is down. This file is included in the BM37FLT.EXE patch that can be downloaded from http://support.novell.com.
iManager Doesn't Run and No One Is Listening on Port 2200
If iManager doesn't come up and it appears that no one is listening on port 2200, iManager may have become corrupt and will no longer allow access. Refer to TID #10065902 at http://support.novell.com for instructions on reinstalling iManager.
iManager Doesn't Run After Server IP Address Change
If iManager does not come up after you have changed the IP address of the NetWare 6 server, refer to TID #10067789 at http://support.novell.com.
General iManager Issues
If you are facing general issues with Novell iManager, refer to the following document: http://www.novell.com/documentation/lg/imanage10/index.html?imanage/data/ac1jn64.html.
Future Scope
The key change in NBM 3.7 isn't so much that the firewall is administered via iManager. What's more important is that the firewall configuration is now stored in eDirectory. This sets the stage for exciting possibilities in the future, such as firewall management via ZENworks policies and a user interface based more on the functionality that the customer wants to allow or deny, rather than on technical specifics such as ports and protocols.
Future benefits of this policy orientation may include the following:
Imagine being able to do things like select a User object, click a button, and see that user's "Effective Internet Access"!
Policies can be user- and workstation-centric rather than server-centric like they are now, giving you greater flexibility in assigning policies to users.
You can have the ability to specify which takes precedence, the user policy or the workstation policy. For example, by having the user policy take precedence, you can allow the CEO to always do everything she wants no matter where she is on the network. By having the workstation policy take precedence, the CEO can do anything in her office, but even the CEO wouldn't be able to access forbidden sites when in the open employee lounge.
You can have application firewall policies. The GroupWise Internet Agent (GWIA) is a good example to think about because it has so many ports and protocols that can be relevant. When you install the application, an Application Firewall Policy is created. Then, in this object, all you have to do is check the boxes of the services you want to use and associate the policy with the appropriate firewall server objects.
Conclusion
This AppNote has described TCP/IP packet filter configuration through iManager in NBM 3.7. For the latest updates to the information presented in this AppNote, refer to TID #10070403, available online at http://support.novell.com/cgi-bin/search/searchtid.cgi?/10070403.htm.
* Originally published in Novell AppNotes
Disclaimer
The origin of this information may be internal or external to Novell. While Novell makes all reasonable efforts to verify this information, Novell does not make explicit or implied claims to its validity.