Interoperability of Novell BorderManager with Other Novell Services
Articles and Tips: article
Software Consultant
Novell, Inc.
ssundar@novell.com
01 May 2002
This purpose of this AppNote is to help readers understand the interactions of Novell BorderManager with other services, and therefore manage and use Novell BorderManager more effectively. It also presents some common upgrade scenarios and provides tips and hints which customers should find useful.
- Introduction
- Technical Overview
- TCP/IP Interaction with Novell BorderManager
- eDirectory Interaction with Novell BorderManager
- NBM Product Maintenance Tips
- Upgrade Scenarios
- Conclusion
|
Topics |
Novell BorderManager, technical overview, upgrades, troubleshooting |
|
Products |
Novell BorderManager, Novell TCP/IP, Novell eDirectory |
|
Audience |
network administrators, integrators, support technicians |
|
Level |
beginner |
|
Prerequisite Skills |
familiarity with basic networking concepts |
|
Operating System |
n/a |
|
Tools |
none |
|
Sample Code |
no |
Introduction
Novell BorderManager (NBM) is one of Novell's premier access and security solutions. With its powerful directory-integrated features, you can control, accelerate, and monitor your users' Internet activities. Because NBM leverages identity-based access control and forward proxies, you can safeguard your network against undesirable Web content while maintaining exceptional performance levels. NBM also integrates VPN services, an industry-standard firewall, and a scalable content-filtering service. Ultimately, these features ensure that your network is protected and your users are productive.
NBM reduces the risk of internal users accessing or downloading Internet content that can jeopardize your network or expose your organization to liability. It is especially handy in situations where a single product may not fulfill all the needs of a customer, especially large organizations. NBM is a suite of products that offers solutions to our customers' most common problems.
NBM leverages the tight security and scalability of NetWare, and works with Windows NT/2000/XP and UNIX networks. (Some NBM components also work with Linux and Macintosh networks.) It is tightly integrated with the Novell Internet Access Server (NIAS) that provides RAS (Remote Access Services) and WAN (Wide Area Networking) services.
Technical Overview
To achieve a total access management solution, the NBM suite contains various modules. NBM is designed so that it can extend the required information and its related products and services to a large number of users without exposing its resources to unauthorized use.
Modules that Ship with Novell BorderManager
This section lists the modules that ship with NBM, all of which are vital to its proper operation.
Novell BorderManager Modules. The following table lists the NLMs that are part of NBM itself, divided into functionality areas.
|
Install/Configure/Monitor Modules |
BRDCFG.NLM BRDNON.NLM LICINST.NLM NISETUP.NLM PINSTALL.NLM BRDSRV.NLM |
|
Proxy/Gateway Modules |
PROXY.NLM PROXYCFG.NLM NBMALERT.NLM IPXIPGW.NLM CSATPXY.NLM CSSYSMSG.NLM CVPREDIR.NLM |
|
Virtual Private Network (VPN) and Network Address Translation (NAT) Modules |
VPMASTER.NLM AUTHGW.NLM AUTHCHK.NLM VPNCFG.NLM VPSLAVE.NLM VPTUNNEL.NLM VPNINF.NLM NAT.NLM |
|
BorderManager Authentication Services (BMAS) |
BMALMGR.NL BMASEXT.NLM RADCLNT.NLM BMSFLOG.NLM RADIUS.NLM ADM.NLM BMLICMGR.NLM |
|
Firewall Modules |
IPFILT.NLM IPFLT30.NLM IPFLT31.NLM FILTCFG.NLM FILTSRV.NLM |
TCP/IP and IPX/SPX Stack Modules. NBM is tightly coupled with the secure version of the TCP/IP stack and also with various encryption formats of the TCP/IP stack. These modules provide security solutions for VPN users of NBM. They are listed in the "TCP/IP Interaction with Novell BorderManager" section.
To provide packet filtering and gateway functionality on IPX platforms, NBM should have enough information about the IPX/SPX stack. The IPX/SPX modules include:
IPXCFG.NLM
IPXCON.NLM
IPXF.NLM
IPXFLT.NLM
IPXPING.NLM
IPXRTR.NLM
IPXRTRNM.NLM
DNS/DHCP and ManageWise Modules. NBM provides proxy functionality for a variety of services such as DNS, HTTP, FTP, Telnet, multimedia, mail, and so on. For host name resolution, it talks to the DNS/DHCP modules. NBM comes with its own statistics to provide information to users. To come up with its statistics and to provide BorderManager alert messages, NBM interacts with ManageWise- related modules. These modules include:
BOOTPFWD.NLM
DHCPD.NLM
DNLIB.NLM
DNLOAD.NLM
MWISE.NLM
NTREND.NLM
NWTRAP.NLM
SNMP.NLM
SNMPLOG.NLM
VGADISP.NLM
Security and Remote Management Modules. NBM leverages Novell eDirectory, the Proxy/Cache technology, and a variety of security services to provide improved productivity, faster and more secure access, and accelerated network performance. To provide these high-performance caching solutions, NBM leverages the Traditional File System functionality. For efficient authentication, NBM is integrated with Novell International Cryptographic Infrastructure (NICI) modules. The remote management modules ship with NBM to provide host resolution and remote management/alert services. These include:
NETDB.NLM
TELNETD.NLM
XCONSOLE.NLM
XCONSSRV.NLM
WAN and RAS Connectivity Modules. To provide support to third-party products, NBM has interfaces to talk with third-party hardware and software. Here are some of the important interfaces that are supported.
AIO Async Subsystem. AIO (Asynchronous Input/Output) is the architecture used for serial communication. This architecture facilitates the writing of driver-independent applications that use serial communication either through COM ports or through third-party cards. This subsystem includes the AIO architecture, some generic AIO drivers, AIO applications, and related configuration utilities. The related modules are:
AIO.NLM
AIOPAD.NLM
AIOPDCON.NLM
WHSMAIO.NLM
WHAIOCFG.NLM
AIOTSM.NLM
CPECFG.NLM
AIOCOMX.NLM
CAPI ISDN Subsystem. CAPI Manager is the architecture used for ISDN connectivity. This architecture facilitates the writing of driver-independent applications that use ISDN connectivity. This subsystem includes the CAPI Manager architecture and test, trace, and configuration utilities. It also includes a special CAPI application WHSMCAPI.LAN that is a pseudo-HSM driver. The related modules are:
CAPIMGR.NLM
CAPITRACE.NLM
CAPITEST.NLM
WHSMCAPI.NLM
WHCATCFG.NLM
WAN-HSM Drivers. This subsystem involves two WAN-HSM drivers (NW2000.LAN and SYNCPLUS.LAN). These drivers can be used by the PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) and Frame Relay protocols. These drivers are the interface between their respective cards and the PPP/Frame Relay protocols.
The NIASCFG.NLM configuration utility for WAN and RAS connectivity is included with NBM for configuring modem, remote access, and ports.
A variety of third-party NLMs are also included on the NBM CD to support various drivers related to RAS and WAN. To provide a listing of these modules is outside the scope of this AppNote.
Interaction with Novell BorderManager
Figure 1 is a block diagram showing how the various modules interact within a Novell BorderManager system.
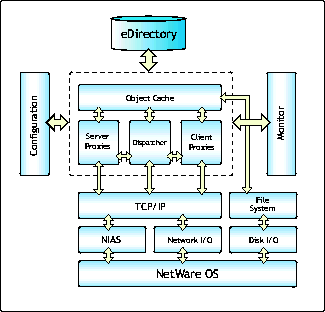
Interaction of various modules in Novell BorderManager.
The following paragraphs describe the flow of control starting from a request received by the proxy until the response is sent to the browser.
First the browser establishes a connection with the proxy. In so doing, a connection block is allocated and initialized. Requests may come in while the connection is being established; if so, they are allocated and initialized as they come in.
When a request is received, the TCPIP module services it. At this point the proxy authenticates and filters the request for access rules. HTTPS requests are handled differently from HTTP requests, secure requests go through the SSL interface, and so on.
Next, the cache is searched to see whether the requested data is available there. The cache look-up returns either a hit or a miss. If it is a hit, it sends the data after checking and processing. The proxy then transmits the data to the browser. If it is a miss, the HTTP Server component sends a request through the dispatcher. The dispatcher determines the protocol type and calls the appropriate client (such as the HTTP client for HTTP services) and starts the process of filling up the cache from the origin server.
Once the client proxy receives the requested data from the origin server, it processes the data and handles it appropriately. The data may be cached or sent directly to the browser, bypassing the cache.
TCP/IP Interaction with Novell BorderManager
The Novell TCP/IP protocol suite is contained in the following NetWare Loadable Module (NLM) programs that ship with NBM 3.7:
TCP.NLM (provides Transport-layer TCP and UDP interfaces)
TCPIP.NLM (provides IP, ICMP, IGMP, Routing, and other Network-layer protocols)
BSDSOCK.NLM (provides the BSD standard sockets interface)
NETLIB.NLM (a library of the entire stack-one version which runs with both the secure and non-secure versions of the above NLMs)
These TCP/IP binaries are available on the NBM 3.7 CD and are installed in the SYS:SYSTEM directory on the NetWare server. When NBM is installed, the server's TCPIP.NLM is replaced with the secure version of TCPIP.NLM.
Note: In NetWare 5.1 SP3 the TCP stack is one NLM: TCPIP.NLM. Likewise, BorderManager 3.6 ships with only one TCPIP.NLM. In NetWare 5.1 SP4 and NetWare 6 SP1, the TCPIP.NLM is split into the four NLMs listed above, which are shipped with BorderManager 3.7. Splitting the stack provides for better maintenance and extensibility of the product.
Multiprocessor-Enabled TCP and UDP
The Novell TCP/IP software is multiprocessor (MP)-enabled and multithreaded for NetWare 6 and NetWare 6 SP1, but not for NetWare 5.1 SP4 (the NBM install programs check for the OS version and install the correct TCP/IP stack). The Transport-layer modules (TCP and UDP) are completely MP-enabled so that the stack can process any TCP/UDP connections on any processor. This enhances performance and helps the stack scale more than it can on a single-processor machine.
Configuration Utilities
The following NLMs are used to configure the TCP/IP stack:
INETCFG.NLM (Internetworking Configuration utility, used for configuring network adapters, protocols, and bindings)
TCPCFG.NLM (a companion utility used to configure the TCP/IP stack)
For more information, see "A Technical Overview of Novell TCP/IP in NetWare 6" in the April 2002 issue of Novell AppNotes at http://support.novell.com/techcenter/articles/ana20020401.html.
eDirectory Interaction with Novell BorderManager
NBM relies on Novell eDirectory for the key functions listed in this section.
Filtering
NBM 3.7 stores the TCP/IP filters and filter exceptions in eDirectory. All other filters are still stored in the FILTERS.CFG file. Hence, the TCP/IP filters will be read from eDirectory, while the other filters will continue to be read from FILTERS.CFG by all applications. During installation of NBM 3.7, the filtering schema gets extended. Installation also creates the NBMRuleContainer object in the context where the NCP Server resides.
This gives rise to the following limitation. If you are using both iManager (the new snap-in for filtering) and FILTCFG (the existing snap-in for filtering) simultaneously to configure filters, changes done through iManager will not be reflected to IPFLT immediately.
For the proper functionality of the TCP/IP filters and filter exceptions created through BRDCFG (which are stored in the FILTERS.CFG file), this file should be migrated to eDirectory.
Proxy/VPN Configuration
All proxy configurations done through the NWAdmin utility are stored in the NCP Server object in eDirectory. As far as VPN configuration is concerned, except for the security key data, all other configuration items (such as Protected Network list, Number of Slaves Configured, and so on) are stored in eDirectory. With NBM 3.7 the VPN-specific filters when VPN is being configured are stored in eDirectory.
Licenses
The NBM licenses are also stored in eDirectory in the NCP Server object. For NBM 3.7 there is only one license envelope for all services.
Note: With NBM 3.7, only eDirectory version 8.0 or later is supported.
NBM Product Maintenance Tips
Today NBM ships on a CD that contains the latest versions of all modules as of the time of the product's release. As is the case with many product suites, the CD contains various modules and NLMs that NBM is dependent upon but which are not owned by the NBM engineering team. This mode of NBM viability has certain inherent problems when it comes to applying updates to the product after its initial installation.
When a change is made in a file or NLM that is not owned by the NBM team, the modules that belong to other products have no way of getting onto the NBM CD until the next release of BorderManager or its support packs. Changes to all related modules can be difficult to track and roll into NBM support packs in a timely manner. It also takes time to do the in-depth testing that revised modules require to ensure that they work with the latest NBM modules.
The main thing to be aware of is that, if you re-install NBM from the CD, all files on the server will be overwritten with the information from the CD. This can cause problems, especially in the case of BM36SP1A (as explained in the section on TCP/IP and its interaction with BorderManager).
It is not a good idea for Novell to remove the NBM dependency on other modules or NLMs, as this may lead to the problem of NBM depending on other Novell products for its functionality. The maintenance of all such modules would become a costly affair for simple NBM users.
Use the following tips as rules of thumb before installing NBM onto your server to ensure that NBM installs and works as smoothly as it can.
Ensure that the NBM server has a local Read/Write replica of the partition containing the NBM server and its licenses.
Ensure that all concurrent patches and fixes are in place and in the correct order. (Refer to the "Upgrade Scenarios" section for more information.)
Ensure that all servers are on the same version of Novell Licensing Services (NLS).
If there is only one NBM server, specify that server as the preferred server in a NetWare Client Configuration (on the administrator's machine).
Upgrade Scenarios
Users of earlier versions of BorderManager may now want to upgrade to Novell BorderManager 3.7. This section presents the various kinds of upgrades available to users, and the considerations and recommendations they should keep in mind while upgrading. The case scenarios covered are:
Case 1: Upgrade from BM 3.5 to NBM 3.7
Case 2: Upgrade from BMEE 3.6 to NBM 3.7
Case 3: Upgrade from BM 3.5 on NetWare 5.1 to NBM 3.7 on NetWare 6.0
Case 4: Upgrade from BMEE 3.6 on NetWare 5.1 to NBM 3.7 on NetWare 6.
Case 5: Upgrade Cyber Patrol to SurfControl
Case 6: Upgrading the Firewall
Case 1: Upgrading from BM 3.5 to NBM 3.7
Going from BM 3.5 to NBM 3.7 is simple, straightforward upgrade. As a base requirement, you must have NetWare 5.1 SP4 or NetWare 6.0 SP1 installed on the server before you start installing NBM 3.7. The upgrade process should follow this order, depending on which version of NetWare you have:
NetWare 5.1 > OS patches (if any) > NetWare 5.1 SP3 > OS patches (if any) > BM 3.5 > BM 3.5 SP3 > BM/OS patches (if any) > NetWare 5.1 SP4 > NBM 3.7
NetWare 6.0 > OS patches (if any) > BM 3.5 > BM 3.5 SP3 > BM/OS patches (if any) > NetWare 6.0 SP1 > NBM 3.7
Case 2: Upgrading from BMEE 3.6 to NBM 3.7
This case is similar to Case 1. It has the same base requirement of having NetWare 5.1 SP4 or NetWare 6.0 SP1 installed on the server before you start installing NBM 3.7. The upgrade process should follow this order, depending on which version of NetWare you have:
NetWare 5.1 > OS patches (if any) > NetWare 5.1 SP3 > OS patches (if any) > BMEE3.6 > BM/OS patches (if any) > BM36SP1A > NetWare 5.1 SP3 > NetWare 5.1 SP4 > NBM 3.7
NetWare 6.0 > OS patches (if any) > BMEE3.6 > BM/OS patches (if any) > BM36SP1A > NetWare 6.0 SP1 > NBM 3.7
Case 3: Upgrading from BM 3.5 on NetWare 5.1 to NBM 3.7 on NetWare 6.0
This case is similar to Case 1, again with the base requirement of NetWare 5.1 SP4 and NetWare 6.0 SP1. Case 3 includes the additional activity of upgrading to NetWare 6.0 after upgrading from BM 3.5 to NBM 3.7. It can also be done by upgrading BM 3.5 working on NetWare 6.0 and then upgrading BM 3.5 to NBM 3.7. In short, you can upgrade to NetWare 6.0 and then to NBM 3.7, or vice-versa. The upgrade process is given below for both scenarios:
NetWare 5.1 > OS patches (if any) > NetWare 5.1 SP3 > OS patches (if any) > BM 3.5 > BM 3.5 SP 3 > BM/OS patches (if any) > NetWare 5.1 SP4 > NBM3.7> NetWare 6.0 > NetWare 6.0 SP1
NetWare 5.1 > OS patches (if any) > NetWare 5.1 SP3 > OS patches (if any) > BM3.5 > BM 3.5 SP 3 > BM/OS patches (if any) > NetWare 5.1 SP4 > NetWare 6.0 > NetWare 6.0 SP1 > NBM 3.7
Case 4: Upgrading from BMEE 3.6 on NetWare 5.1 to NBM 3.7 on NetWare 6.0
The upgrade from BMEE 3.6 to NBM 3.7 is simple. Like the other cases, it has the base requirement of NetWare 5.1 SP4 and NetWare 6.0 SP1. As in Case 3, you can upgrade to NetWare 6.0 and then to NBM 3.7, or vice-versa. The upgrade process is given below for both scenarios:
NetWare 5.1 > OS patches (if any) > NetWare 5.1 SP3 > OS patches (if any) > BMEE 3.6 > BM36SP1A > NetWare 5.1 SP3 > NetWare 5.1 SP4 > NBM 3.7 > NetWare 6.0 > NetWare 6.0 SP1
NetWare 5.1 > OS patches (if any) > NetWare 5.1 SP3 > OS patches (if any) > BMEE 3.6 > BM36SP1A > NetWare 5.1 SP3 > NetWare 5.1 SP4 > NetWare 6.0 > NetWare 6.0 SP1 > NBM 3.7
As updating to NBM 3.7 would be the most common upgrade scenario, here are some tips to note:
BMEE 3.6 Abend Issue. With NetWare 5.1 SP4, any time a client-to-site VPN connection is initiated, your server might abend in TCP.NLM. To resolve this, install the BorderManager 3.6 Support Pack 1A (BM36SP1A) available at http://support.novell.com.
BMEE 3.6 Installation Issue. When installing BMEE 3.6, the server's TCPIP.NLM is replaced with a secure version of TCPIP.NLM. This version of TCPIP.NLM is not compatible with some of the files in NetWare 5.1 SP4. You must reinstall this Support Pack after installing BMEE3.6 to get the correct version of the secure TCPIP.NLM installed and to get the compatible files installed. Otherwise an error such as "File SYS:\SYSTEM\ BSDSOCK.NLM cannot be opened" will be displayed.
NMAS-Related Issue. If the BMEE 3.6 server is located in an eDirectory tree that also has the NMAS product installed (meaning there is a Login Policy object in the Security container), you must complete the steps listed below to allow users to authenticate to BorderManager services running on NetWare 5.1:
Load ADMATTRS.NLM.
When prompted to log in as a user with rights to modify the Login Policy object, log in using the Administrator username and password.
Access NWAdmin from a client workstation.
Locate the Login Policy object and right-click to create rules to enable users to authenticate to BorderManager services.
Case 5: Upgrading Cyber Patrol to SurfControl
BM 3.5 and BMEE 3.6 are integrated with the Cyber Patrol product. NBM 3.7 now ships with SurfControl, a category-based filtering solution. SurfControl provides the ability to easily define and control user access to illegal or inappropriate Web sites. This solution can work in conjunction with NBM's powerful Access Control Rules and helps you to implement your organization's Internet usage policy.
After upgrading to NBM 3.7, follow these steps to upgrade Cyber Patrol to SurfControl:
Go to SYS:\ETC\CPFILTER and back up the CP_SETUP.EXE. This is Cyber Patrol's install program.
Go to SYS:\SURFCTRL and execute CP_SETUP.EXE. You can do this after mapping a drive from a client machine. Now the files related to Cyber Patrol, which exist in SYS:\ETC\CPFILTER, get backed up in the SYS:\ETC\CPFILTER.OLD directory. For ease of maintenance, you should also put the backed up copy of the Cyber Patrol install program (CP_SETUP.EXE) in this directory.
To start SurfControl, load CPFILTER NLM from the SYS:\ETC\CPFILTER directory and define the access rules through the NWAdmin utility. For live updates of SurfControl database, you need to load CSP_LIST NLM from the SYS:\ETC\CPFILTER directory.
Case 6: Upgrading the Firewall
If you chose to secure the public interfaces during installation of NBM 3.7, a set of default filters is configured at that time. If it is an upgrade, the existing filters are retained along with the default filter list.
Note: For the services selected during installation, default stateful filter exceptions are created. The definition of "public/private" interface is based on the configuration done in BRDCFG.NLM.
Compared to the earlier versions of BorderManager where all the filters are stored in a text file, NBM 3.7 leverages the advantages of eDirectory. TCP/IP filters are stored in eDirectory, whereas all others filters are stored in the FILTERS.CFG file. Hence, TCP/IP filters will be read from eDirectory and other filters will continue to be read from FILTERS.CFG by all applications.
Importing and Exporting Filters
Importing and exporting of filters to and from eDirectory is possible through commands from the system console.
Export. After installation of NBM 3.7, you can transfer all the filters from FILTERS.CFG to eDirectory by running the "FILTSRV MIGRATE" command. If you don't see any error messages, the command is successful. For this command to work, make sure that the FILTSRV.NLM is unloaded before you run the command.
For TCP/IP, the filters are read by FILTSRV not from the FILTERS.CFG file but from eDirectory, whereas for all other filters (except TCP/IP) the information is read from FILTERS.CFG.
Import. To get filters from eDirectory to a text file of the same format as FILTERS.CFG, run the following command at the system console prompt: FILTSRV_BACKUP_FILTERS <filename>. This stores all the TCP/IP filter configurations from eDirectory to the text file specified; it also copies all other filters from FILTERS.CFG to the filename specified in the SYS:\ETC directory. This gives you a consolidated list of filters. (The <filename> is optional; if none is specified, the filters are imported into the SYS:\ETC\FILTERS.BAK file by default.)
With NBM 3.7 and NetWare 6.0, Secure Remote Configuration is also possible through iManager.
Conclusion
This AppNote has discussed the interactions of Novell BorderManager with other services, as well as some usage guidelines for NBM. It has also covered some of the common upgrade scenarios with tips and hints which customers should find useful. A follow-up AppNote will cover additional interoperability areas such as NBM-Novell Modular Authentication Services (NMAS)-iChain, Novell Certificate Server, and Novell Client 32.
* Originally published in Novell AppNotes
Disclaimer
The origin of this information may be internal or external to Novell. While Novell makes all reasonable efforts to verify this information, Novell does not make explicit or implied claims to its validity.