Configuration Parameters for the Compatibility Mode Driver
Articles and Tips: article
Worldwide Support Engineer
Novell Customer Services
01 Apr 1999
The Compatibility Mode Driver allows NetWare 5's Pure IP environment to coexist with IPX. Find out how to configure the driver to get the results you need.
- Introduction
- Changing the CMD Network Number
- IPX CMD Mode Routing
- Configuring the Preferred Migration Agent on a CMD Server
- Binding to the Preferred IP Address
- Providing IP Backbone SupportTLE
- Enabling Filtering
- Viewing the Migration Agent List
- Updating the Router Table
- Viewing the CMD Server Statistics
- Conclusion
Introduction
This AppNote provides a detailed explanation of the configuration parameters available for the server component of the Compatibility Mode Driver (SCMD.NLM). These parameters can be configured on servers running NetWare 5 (with later than Support Pack 1a), intraNetWare 4.11 (with later than Support Pack 6), and NetWare 4.2. Check http://www.novell.com for the latest releases of the Support Packs. SCMD.NLM should be v1.59f or higher.
On NetWare 5 servers you can set the parameter values using either the Monitor utility, the SET command, or optional command-line parameters at the server console prompt. Keep in mind that on NetWare 5 servers, the "LOAD" keyword is optional when loading an NLM. On intraNetWare 4.11 or NetWare"4.2 servers, you must use the optional command-line parameters specified in this AppNote. When command-line options are used, the parameter values are not set permanently, but revert back to the default settings if you unload the SCMD module and reload it without specifying the new value.
It is assumed that the reader understands the functionality of the SCMD.NLM module and now wants to configure it in one of the following ways:
Changing the CMD network number
Indicating IPX or CMD mode of routing
Configuring the Preferred Migration Agent on a CMD Server
Binding to the preferred IP address
Providing IP backbone support
Enabling filtering
Viewing the Migration Agent list
Updating the router table
Viewing the CMD Server statistics
For background information on Compatibility Mode and NetWare 5, refer to "Migrating to Pure IP with NetWare 5" and "Compatibility Mode Installation and Configuration" in the September 1998 issue of Novell AppNotes.
Changing the CMD Network Number
IPX-based applications are supported on a Pure IP network by having a virtual IPX stack on the client and server nodes. The virtual IPX stack provides the IPX functionality to the applications (see Figure 1).
Figure 1: The virtual IPX stack supports IPX-based applications on a Pure IP network.
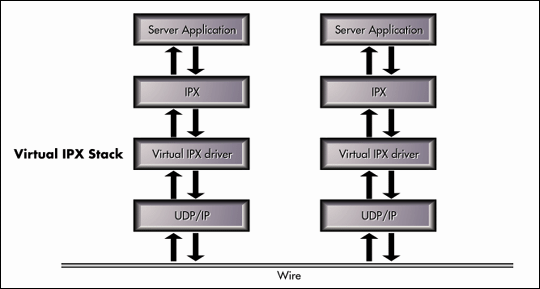
The virtual IPX driver in the stack interacts with the Service Location Protocol (SLP) to register and query service and route information. When the virtual IPX driver receives an IPX packet from an IPX-based server application, it processes the SAP/RIP information by interacting with SLP. It then encapsulates it into a data packet and forwards the packet to UDP/IP on the stack. Similarly, the virtual IPX driver on the client receives the UDP/IP packet, unencapsulates the packet, and forwards the SAP/RIP information to the IPX layer.
The virtual IPX driver behaves as a virtual LAN driver for the IPX router by binding itself to IPX with a unique IPX network number. Once it is bound to IPX with a unique network number, all outbound IPX packets destined for the network will be routed to this virtual LAN driver.
By default, the virtual IPX network number for the Compatibility Mode Driver (CMD) is set to FFFFFFFD. You can change this either through the Monitor utility or by using the following SET command-line parameter (where xxxxxxxx is the new network number for CMD):
SET CMD NETWORK NUMBER=xxxxxxxx
The SCMD.NLM module must be loaded before this value can be changed. You must subsequently unload and reload the module for the change to take effect. This option can be used when SCMD.NLM is running either in CMD Server or Migration Agent (MA) mode.
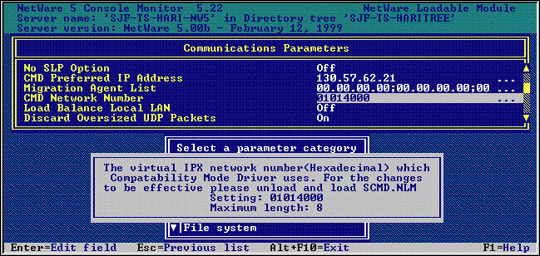
To change this parameter from the Monitor utility, select Server Parameters, then the Communications category, and then make the change in the field for CMD Network Number, as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2: You can set the CMD network number from the Monitor utility.
Another option is to change the CMD network number dynamically while loading the SCMD module. To do this, type the following at the console prompt:
LOAD SCMD /NET=xxxxxxxx
Note: LOAD command-line parameters are used primarily to set the values on intraNetWare 4.11 or NetWare 4.2 servers. Using this option changes the network number only temporarily. Once you unload SCMD.NLM and reload it without specifying the /NET option, it will reset to the original network number. On a NetWare 5 server, using this command-line option will change the network number permanently. If you unload SCMD.NLM on a NetWare 5 server and reload it without specifying the /NET option, it will not reset to the original network number.
IPX CMD Mode Routing
This autoconfigured parameter signifies whether the server is using the CMD mode of routing or IPX routing. SCMD.NLM sets the value as On or Off depending on the mode of operation. When SCMD.NLM is loaded in CMD Server mode, this parameter is set to On. When SCMD.NLM is loaded as a Migration Agent, it is set to Off. Users should not change the value of this parameter. Since the CMD Server or MA can provides the route information, this parameter is not required and will be removed in a future release of SCMD.NLM.
Configuring the Preferred Migration Agent on a CMD Server
When a CMD Server is configured on the network, it will register itself with SLP and issue an SLP service request to learn all the available registered SLP services of type MGW.NOVELL—the SLP service type for Migration Agents. From the SLP replies, the server will build a list of active MAs. (If there are no MAs present on the network, the CMD Server will issue SLP requests for SLP service type SAPSRV.NOVELL to update its router with the other SLP-registered CMD services.)
From this active MA list, the CMD Server will choose the nearest one based on the "IP distance" (whether the MA is in the same subnet, a different subnet, or a different network). The CMD Server then opens a permanent TCP connection with the nearest MA. Every 60 seconds, the MA will send SAP/RIP updates to the registered CMD server through a delta transfer. These updates continue until either side terminates the TCP connection. If the MA terminates the TCP connection, the CMD Server tries to establish the connection again with the same MA. If the MA is down, the CMD Server will re-target to the next MA in its active MA list, if any. If not, it will once again query SLP for MAs.
When multiple MAs are configured on the network, you can statically set the list of MAs to which the CMD Server has to register and retarget if the primary MA fails. This is mainly useful for load balancing purposes. To do this, type the following command at the console prompt:
SET PREFERRED MIGRATION AGENT LIST = <IP address of MA</
You can specify a maximum of five IP addresses in the list of Preferred MAs. Separate the addresses with semicolons ( ; ) and end the list with a slash (/ ). You will need to unload and load SCMD.NLM for the changes to be effective. This option can only be used when SCMD.NLM is running in the CMD Server mode.
Note: Currently, IP distance has no way to consider the link speed. An MA across a 56Kbps link could be determined to be closer or equal to an MA across a high-speed backbone. The above parameter helps in overcoming this limitation.
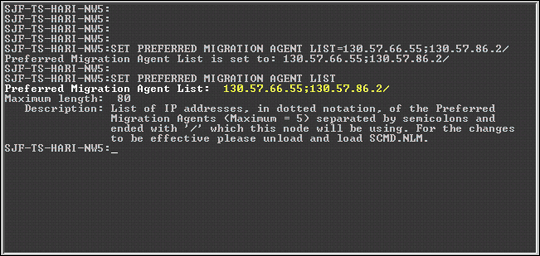
Figure 3 illustrates the use of this parameter. In this example, the IP addresses of two MAs have been entered: 130.57.66.55 and 130.57.86.2. Note that the addresses are separated by a semicolon and the command ends with a slash. Typing the complete SET parameter without any IP addresses will display the current MAs in the configured list.
Figure 3: This is an example of statisically setting the Preferred Migration Agents list on a CMD Server.
This parameter can also be changed from the Monitor utility. To do this, select Server Parameters, then select the Communications category, and change the value in the field for Preferred Migration Agent List.
Note: Since you don't need to run intraNetWare/NetWare 4.11 or 4.2 servers in CMD Server mode, you do not have any optional LOAD command-line parameter to configure the Preferred Migration Agent dynamically.
Binding to the Preferred IP Address
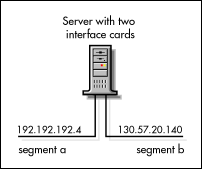
When multiple IP interfaces are installed in a single server, the CMD Server or MA will always bind itself to the IP address with the lowest value. For example, the server in Figure 4 has two IP interfaces: 192.192.192.4 and 130.57.20.140. In this case, the CMD Server or MA will always bind to address 130.57.20.140.
Figure 4: On a server with two IP interfaces, the CMD Server or MA will bind itself to the lowest address.
You can specify which interface you want CMD to bind to by using a SET parameter option. To bind to an interface with the address 192.192.192.4, for example, type the following command at the server console.
SET CMD PREFERRED IP ADDRESS = 192.192.192.4
On a NetWare 5 server, you can also change this setting from the Monitor utility. To do this, select Server Parameters, then select the Communications category, and then change the value in the field for Preferred IP Address. Be sure to enter the IP address in dotted decimal notation. This option can be used when SCMD.NLM is running in either CMD Server mode or MA mode.
The SCMD.NLM module must be loaded for this value to be set. You must subsequently unload and reload the module for the change to take effect.
Another option is to change the Preferred IP Address dynamically while loading the module. To do so, type a command similar to the following at the console prompt:
LOAD SCMD /PREFIP=192.192.192.4
Providing IP Backbone Support
When migrating a network from IPX to Pure IP, the need often arises to connect two IPX network segments across an IP network backbone. This scenario is illustrated in Figure 5, where IPX networks A and B are connected via an IP network, so they cannot communicate with each other in IPX. To facilitate communication between the two IPX segments, you need to enable IP Backbone Support on the MAs (also referred to as MA-MA protocol).
Figure 5: A network setup illustrating Migration Agents with IP backbone support.
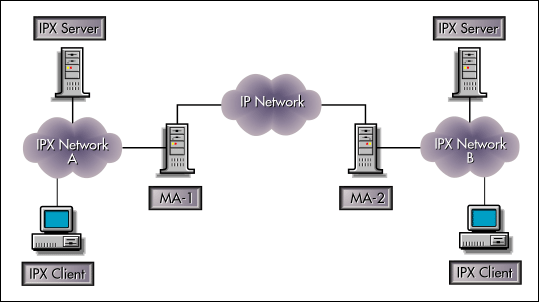
(For more information on installing SCMD.NLM to provide IP Backbone Support, refer to "Compatibility Mode Installation and Configuration" in the September 1998 issue of Novell AppNotes.)
By default, the IP Backbone feature is enabled when SCMD.NLM is loaded using the /MA option. In NetWare 5 with Support Packs later than 1a, the /MA (/G) and the /BS option functionalities have been combined. Loading SCMD.NLM with either of the options loads the MA with IP Backbone Support:
LOAD SCMD /MA [/BS] [/G]
For this configuration to work, ensure the following:
Each IPX disconnected network has at least one MA.
All MAs have NLSP routing enabled (IPXRTR routing = NLSP) and have the same CMD network number.
SLP visibility exists among all MAs.
UDP communication (Port 2645) is enabled on all routers between all the MAs.
To check whether the IP Backbone Support feature is working, enter the following command to display all the services that the server is aware of:
DISPLAY SERVERS
The services discovered by MAs on either end of the IP backbone should be listed.
You can also check to see whether the MAs are visible by typing the following command to display the list of MAs the server has learned about from SLP:
LOAD SCMD /STAT
Refer to the section on "Viewing the CMD Server Statistics" later in this AppNote to learn more about the /STAT option.
Configuring for SLP Independent Backbone Support
By default, MAs use SLP to discover other MAs on the network. You can configure MAs not to be dependent on SLP for discovering other MAs on the network. This is referred to as "SLP Independent" backbone support or "MA in NOSLP mode." To enable this, you first need to turn off the SLP mode of discovery for the MA and provide a static MA list. Then you load the MA.
To turn off SLP support, enter the following command at the console prompt:
SET NO SLP OPTION = ON
In this mode of operation, it is recommended that you do not connect any CMD Server to the MA. This mode of working is only for the MA-MA feature; the other features of CMD are not recommended in this configuration.
To configure the MA list statically, enter the IP addresses of each other MA followed by a slash ( / ) on both these MAs:
SET MIGRATION AGENT LIST = <IP Address of MA</
You can specify up to five addresses, separated by semicolons and ending with a slash. You must unload and reload SCMD.NLM for the changes to be effective.
Note: The limitation of five MAs is only for setting the number of MAs in this list. It is not the maximum number of MAs this node can communicate with.
Using a DHCP Server to Get the MA List
Under SLP Independent mode, MAs can be configured to get the CMD parameters (MA list, CMD network number, and so on) from a DHCP Server.
To configure the IP address of the DHCP server, enter the following command at the console prompt:
SET DHCP IP ADDRESS = <IP Address of DHCP Server<
Optionally, you can specify the DHCP server's address when you load SCMD. To do so, enter the following command at the console prompt.
LOAD SCMD[/MA]/NOSLP/DHCPADDRESS =<IP Address of DHCP Server<
Note: The /DHCPADDRESS feature is currently not available, but it will be implemented in a future release of SCMD.NLM.
Setting MA-MA Communication Time
When the MA is operating in SLP Independent mode, you can set the time interval for the MAs to communicate with each other. This communication time setting is used for the MAs to discover each other and keep the MA lists current. It has nothing to do with the transfer of services (SAP) and network route (RIP) information between the MAs.
To set the communication time, enter the following command:
SET MA COMMUNICATION TIME = xMINUTES
The default value is 10 minutes, with a range of 1 to 3000 minutes. The communication time should be the same for all the MAs on the network.
Optionally, you can load MA in the SLP Independent mode and set the communication time for the MAs at the command line. To do so, type the following at the console prompt:
LOAD SCMD [/MA] /NOSLP /SYNCTIME = xMINUTES
You can also load SCMD and specify the MA addresses which this node will be using. To do so, type the following command at the console prompt:
LOAD SCMD [/MA] /NOSLP /MAADDR = <IP address of MA<
Or you can specify MA-MA communication time and the MA list together. The /SYNCTIME and /MAADDR switches must be typed after the /NOSLP switch. An example is shown below:
LOAD SCMD [/MA] /NOSLP /SYNCTIME= x MINUTES /MAADDR=<IP address of MA<
Note: The /MAADDR switch replaces the /PREFERREDMA switch in SLP Independent mode.
The SLP independent MA-MA protocol removes dependency from SLP only for the MA-MA feature. No other features in SCMD.NLM will work without SLP. SLP is a must for any CMD server or client to work with the MA. Since SLP is the basic protocol used in IP for dynamic service visibility and accessibility, the entire design of the CMD product relies on SLP. The MA-MA protocol is only a part of SCMD.NLM and the independence of this feature from SLP should not be misinterpreted as the ability of the whole SCMD product to be SLP independent.
Enabling Filtering
You can configure the MA to filter some of the IPX services or/and networks between two MAs. This option can be used only when SCMD.NLM is running in the MA mode and filtering is applied on the SCMD virtual board (using the SCMD.LAN module included in the latest releases of the SCMD patch). Before using the filtering option, install the SCMD board as outlined below.
Installing the SCMD Board Using SCMD.LAN
At the server console prompt, enter:
[LOAD] NWCONFIG
Note: On intraNetWare 4.11 or NetWare 4.2 servers, type LOAD INSTALL.
Select Driver Options.
Select Configure Network Drivers.
To select a driver from all the available drivers, choose Load an Additional Driver.
Note: On intraNetWare 4.11 or NetWare 4.2 servers, choose Select an Additional Driver.
The screen displays a list of all available drivers
From the select drivers list, select SCMD.LAN.
Press <Enter< to continue when you are prompted with a message that control will be switched to the system console screen to load driver <Lan driver for SCMD<.
Press <Esc< when you are prompted to BIND IPX to SCMD.
Note: You don't need to bind an IPX network number. Do not confuse this with the CMD network number.
Select "No" and press "Enter" to skip binding IPX to SCMD.
On NetWare 5 servers, press <Enter< when you get a message <Driver SCMD was successfully loaded but not bound to any protocol stacks<.
Note: On intraNetWare 4.11 or NetWare 4.2 servers, this message will not be displayed.
Select "No" when you are prompted to select an additional network driver.
You should see SCMD listed as "Currently Loaded" in the Selected Network Drivers Menu.
Note: You can also install the SCMD board using the INETCFG utility.
Running the FILTCFG Utility
Run the FILTCFG utility to set the filters. MAs will support both inbound and outbound filtering on the SCMD virtual board across the MAs.
For more information on the use of FILTCFG, refer to the documentation available at the following URL:
http://www.novell.com/documentation/lg/nw5/docui/index.html#../uscomm/rtcf_enu/data/ha00g5ue.html
To enable filtering on an MA, enter the following command:
LOAD SCMD /FILTER
Note: The /FILTER option enables backbone functionality with filtering support. Make sure the NLSP state is "On" under the "NLSP bind options." To verify this, load INETCFG at the server console. From the "Internetworking Configuration" screen, select Bindings, then IPX, then Expert Bind Options. Under NLSP Bind Options, "NLSP State" should be "On." Also, under RIP Bind Options"RIP State" should be "Auto", and under SAP Bind Options, "SAP State" should be "Auto".
Viewing the Migration Agent List
You can identify the number of MAs the CMD Server knows about at any time. To view this information, enter the following command:
LOAD SCMD /MALIST
Figure 6 shows the output from the SCMD /MALIST and DISPLAY SLP SERVICES commands for service type MGW.NOVELL.
Figure 6: Output from the SCMD/MALIST and DISPLAY SLP SERVICES commands.
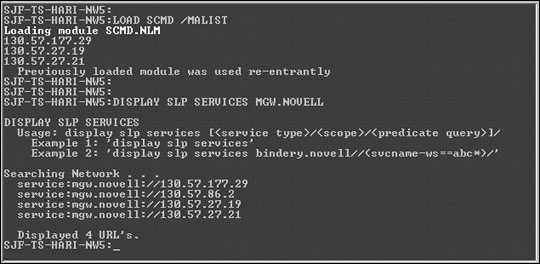
Note: The /MALIST option lists only those MAs that are active and known to this CMD Server and that have the same CMD network number.
Even though you see four MAs registered in SLP, this CMD Server knows only three MAs. This is because the MA at 130.57.86.2 is either not learned by the CMD Server or is running on a different CMD network number.
Updating the Router Table
The purpose of the /SYNC option is to force the CMD Server to discover the MAs in the network on demand and connect to one of them to get the SAP/RIP information to update the router table. The syntax for the command is:
LOAD SCMD /SYNC
When the CMD Server is already connected to an MA, SAPs and RIPs are always in sync and this option will not be useful. This option can be used only when SCMD.NLM is running in the CMD Server mode.
Viewing the CMD Server Statistics
SCMD.NLM provides two command-line switches to view statistics related to the CMD Server or MA:
The /STAT or "Status" switch
The /SEARCH switch
The CMD Server statistics are displayed on a separate screen named the CMD Information screen.
Using the /STAT Switch
The /STAT switch displays the following information:
CMD network number the server is using
IP Address the CMD Server or MA is bound to
Whether the server is running in CMD Server or MA mode
In CMD Server mode, the IP address of the MA in contact
In MA mode, the IP address of CMD Servers connected to this MA
IP addresses of all MAs learned on the network
Whether MA filtering is enabled or disabled
MA mode of discovery (SLP or NOSLP mode)
If MA is in NOSLP mode, information on the IP address of the DHCP server used to get the CMD parameter values (If a DHCP server is not configured, it would display "DHCP server NOT configured" on the statistics screen.)
To view the statistics on the CMD information screen, first type the following command at the console prompt:
LOAD SCMD /STAT
Note: You will be switched over to the "CMD Information Screen." Press the "Alt"+"Esc" keys to return to the console prompt.
Figure 7 shows an example of the statistics displayed for a CMD Server. Notice that the CMD network number is 01014000, the IP address bound is 130.57.20.112, the CMD Server is in the MA mode of discovery and is registered with the MA at 130.57.57.19. It has also learned about two MAs on the network.
Figure 7: Example of CMD Server statistics.

Figure 8 shows an example of the statistics displayed for an MA in SLP mode of discovery. Notice that the CMD network number is 01014000, the IP address of the MA is 130.57.20.112, and that no CMD Servers are connected to this MA. It has learned about two MAs (130.57.27.19 and 130.57.27.21) on the network.
Figure 8: Example of Migration Agent statistics.
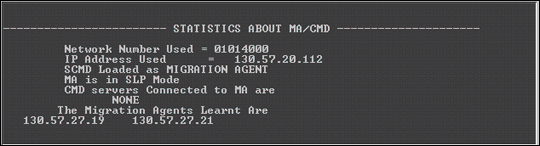
Figure 9 shows an example of the statistics displayed for an MA in SLP independent mode. Notice that the CMD network number is 01014000, the IP address of the MA is 130.57.20.112, and that no CMD Servers are connected to this MA. It has learned about two MAs (130.57.27.19 and 130.57.27.21) on the network. The MA is configured to get the CMD parameters from a DHCP server with IP address 130.57.20.105.
Figure 9: Example of statistics for Migration Agent in SLP Independent mode.
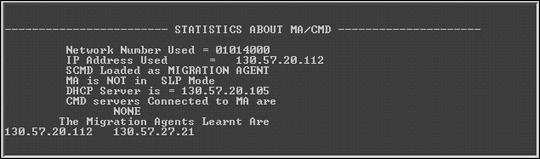
If you do not have a DHCP server configured, the screen would display the message "DHCP Server NOT Configured."
You can redirect the information to a file by entering the following command:
LOAD SCMD /STAT /DUMP
The information will be written to the CMDSTAT.DAT file in the SYS:\ETC\ directory. CMDSTAT.DAT can be opened with any text editor.
Note: With the /DUMP option, statistics will not be displayed in the CMD Information screen.
Using the /SEARCH Option
You can use the /SEARCH option to list the names of the services the CMD Server or the MA has located. You can also search for the network number of the CMD Server or MA. The /SEARCH option displays the following information:
Under Service Information [with NAME option]
SAP Type
Service Name
IPX Network Address
Socket number
Number of Hops to reach the service
Time to reach this service in Ticks
Total number of services known to the CMD network
Matching number of services
Under Network Information [with NET option]
IPX Network Address
IP Address of the reporting CMD Server or MA
Number of Hops to reach this network
Time to reach this network in Ticks
IP Subnet of the reporting CMD Server or MA
Number of SAPs reported by this IPX Network
Validity of the record (a value of 1 means the record is valid)
To use this option, enter the following command:
LOAD SCMD /SEARCH [NAME=Service Name] [NET=Network Number] [/DUMP]
The Service Name parameter can take one of the following values:
The wildcard *, which will locate all the services in the network
The exact name of the service (for example, SVE-EF)
A portion of the name, followed by a * (for example, SV*)
For the Net Number parameter, you can enter FFFFFFFF to list all the services in the network, or you can enter a specific network number to match.
With the /DUMP option, the information will be written to the CMDSTAT.DAT file in the SYS:\ETC\ directory. CMDSTAT.DAT can be opened with any text editor. If you specify the /DUMP option, information is not displayed on the CMD Information screen.
Figure 10 shows an example of the use of this command. In this example, we are searching for a server under all networks whose name starts with SV. The output is redirected to the SYS:ETC\CMDSTAT.DAT file.
Figure 10: Example of the SCMD/SEARCH command.
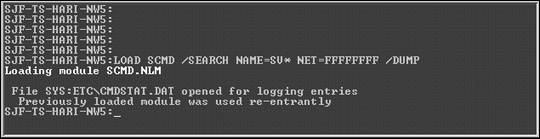
The contents of the CMDSTAT.DAT file generated from this command are listed below. Note that the command found two matching services and a total of 11 network numbers.
LOAD SCMD /SEARCH NAME=SV* NET=FFFFFFFF /DUMP
Contents of SYS:ETC\CMDSTAT.DAT FILE
SEARCH FOR NETWORK SERVICES
|
Type
|
Service Name
|
Net Addr
|
Socket number
|
Hops
|
Ticks
|
|
0004 |
SVE-FLAPHOGS |
440A3907 |
0451 |
06 |
01 |
|
026B |
SVE-FLAPHOGS-TREE_G D@@@@@D PJ |
440A3907 |
0023 |
06 |
01 |
|
0278 |
SVE-FLAPHOGS-TREE_ G D@@@@@D PJ |
440A3907 |
1340 |
06 |
01 |
SEARCH FOR NETWORK NUMBERS
|
Net Addr
|
IP Addr
|
Hops
|
Ticks
|
IP Subnet
|
Number of SAPs
|
Validity
|
|
01CE2E06 |
130.57.82.122 |
6 |
36 |
130.57.80.0 |
3 |
1 |
|
62912801 |
130.57.82.10 |
6 |
36 |
130.57.80.0 |
5 |
1 |
|
FDFE1C07 |
130.57.177.15 |
6 |
36 |
130.57.176.0 |
3 |
1 |
|
09CA5601 |
130.57.82.123 |
6 |
36 |
130.57.80.0 |
3 |
1 |
|
5CDAFC02 |
130.57.179.2 |
4 |
24 |
130.57.176.0 |
3 |
1 |
|
04400101 |
130.57.86.2 |
2 |
13 |
130.57.80.0 |
1 |
1 |
|
424FD40F |
130.57.66.5 |
6 |
36 |
130.57.66.0 |
3 |
1 |
|
440A3907 |
130.57.82.142 |
6 |
36 |
130.57.80.0 |
3 |
1 |
|
45CD8D0B |
130.57.82.114 |
6 |
36 |
130.57.80.0 |
5 |
1 |
|
B450A204 |
130.57.177.18 |
6 |
36 |
130.57.176.0 |
3 |
1 |
|
FBAEF635 |
130.57.86.2 |
2 |
13 |
130.57.80.0 |
4 |
1 |
Matching number of networks = 11
Total Number of networks known = 11
Conclusion
This AppNote has outlined the various configuration parameters for the server component of the Compatibility Mode Driver. It has also given several examples of how these parameters can be used to implement and maintain CMD on a NetWare network.
For current technical updates and a compilation of links to other Compatibility Mode documents, refer to TID 2944065 at:
http://support.novell.com/cgi-bin/search/tidfinder.cgi?2944065
* Originally published in Novell AppNotes
Disclaimer
The origin of this information may be internal or external to Novell. While Novell makes all reasonable efforts to verify this information, Novell does not make explicit or implied claims to its validity.