Maintaining a Healthy NDS Tree: Part 1
Articles and Tips: article
Premium Support Engineer
Novell Technical Services
BEHZAD ANARAKI
Premium Support Engineer
Novell Technical Services
01 Aug 1997
You don't need a medical degree to diagnose the health of your NDS tree. All you need is a few handy utilities and the insights presented in this AppNote. This is the first in a two-part series.
Introduction
The purpose of this AppNote is to provide customers with a systematic routine for diagnosing and maintaining a healthy Novell Directory Services (NDS) tree. These tasks have been divided into three sections:
Tree Health Checks. Reference this section to determine the overall health of the tree.
Partition Health Checks. Reference this section before doing any partition operations.
Server Health Checks. Reference this section to identify health of replicas on a server.
Special thanks to John Mehl, Rob Ross, and Steve Woodruff of Novell for their help with this AppNote.
This AppNote is the first of two parts. The first part covers the Tree Health Checks and the Partition Health Checks. The second part will cover the Server Health Checks.
The following NDS utilities are used for performing these health checks:
DSREPAIR.NLM (comes with NetWare 4.x)
DSTRACE.NLM (comes with NetWare 4.x)
NDS Manager (Windows-based management utility that comes with NetWare 4.11)
SCANTREE.EXE. This program can be downloaded from the Novell Support Connection web site at http://support.novell.com. Search for file name SCANDS.EXE. (SCANTREE.EXE is not supported by Novell Technical Services.)
DSDIAG.NLM. As of this writing, this NDS diagnostics utility is in beta. Reference TID 2928396 for the Novell web site location to download this utility.
This AppNote assumes some familiarity with NDS terminology and operations. Refer to previous AppNotes and other Novell documents for background information on NDS.
Tree Health Checks
As a network administrator, you should establish a proactive health check of your NDS tree. To help you determine the frequency of the recommended checks, the occurrence of NDS tree changes can be classified as follows:
A dynamic tree is classified as an NDS tree with new partitions being created, or with new servers being added, or a combination of the two--on a frequent basis (perhaps two to three times a week). This classification would typically represent a company moving from a NetWare 3 environment or creating a new NDS tree.
A static NDS tree is classified as a NDS tree with a minimum number of changes--such as a new partition or server being added perhaps a couple timesa month. This classification would typically represent a company with an established NDS tree, where the majority of changes involve adding leaf objects and intermittently adding servers and creating new partitions.
Each section includes a dynamic/static timeframe for running the check. The time frames given for scheduled checks are only recommendations and should be tailored for your individual organization's needs.
Time Synchronization/NDS Version Check
Time frame: Dynamic Tree - Weekly / Static Tree - Monthly
Correct time synchronization is important because NDS partitions are replicated and need to be concurrent with one another. Each event that occurs in NDS is marked with a timestamp. The timestamps are used to order the events or changes that occur on multiple servers. Timestamping of events keeps all NDS changes in proper order. A time synchronization check must be done regularly to ensure that NDS functions correctly. If time is out of synchronization when performing a Change Replica Type partition operation, the operation will not complete.
It is also a good idea to check the version of NDS (DS.NLM) that is running on your servers to ensure you have the most up-to-date Directory Services software.
Load DSREPAIR.NLM on a server holding a replica of the [ROOT] partition.
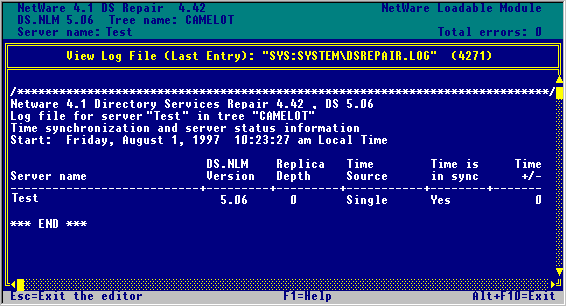
From the Available Options menu, select "TimeSynchronization." Verify that time is synchronized (see Figure 1).
Check the DS.NLM version, as shown in Figure 1.(As of this writing, the minimum version for NetWare 4.10 servers is DS.NLM v5.01; NTS recommends using DS.NLM v5.06. For NetWare 4.11 servers, the recommended DS version is currently v5.73.)
Figure 1: Sample DSREPAIR Time Synchronization report showing time in sync and DS.NLM version.
NDS Synchronization Check
Time frame: Dynamic Tree - Weekly / Static Tree - Monthly
To check NDS synchronization, run DSDIAG with the options described below.
Load DSDIAG.NLM on a server. (NTS recommends running DSDIAG.NLM on a non-production server that receives the 0278 tree SAP packets of the tree being checked).
At the Main Menu, select "Generate Report".

Select "Check Partition Status".
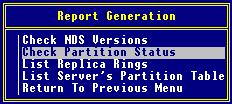
The "General Options" screen is displayed.
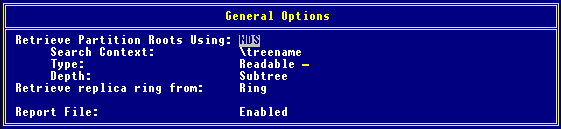
Use the following settings:
Retrieve Partition Roots Using: NDS(default)
Search Context: \tree_name
Type: Readable (default)
Depth:Subtree (default)
Retrieve replica ring from: Ring (default)
Report File: Enabled (Default filename SYS:SYSTEM\DPSTAT00.RPT)
Press <F6< to set Warnings options. Change "Display only partition roots/servers with warnings or errors" from Off to On. (This setting will show only partitions with problems, eliminating the need to review all partitions in the tree.)
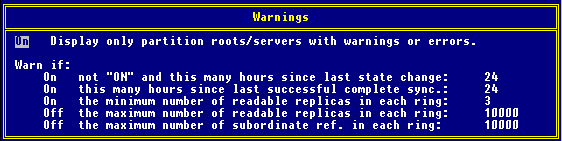
Press <F10< to start the report (there can be up to 10 reports running at one time).
The following is an example of the report output for the TEST tree. Refer to the README file that comes with DSDIAG for information about interpreting this report.
Report Title: DSD Partition Sync. Status
Report Version: 0.8
Base DN: \TEST
Identity: \[Public]
Start Date: Jul 31, 1997
5:56:57 pm MDT
Retrieved Partition Roots Form: NDS
Search Context: .
Type: Readable
Depth: Subtree
Retrieved replica ring from: Ring
Replica Synchronization Summary:
Status Warni Tota OK Acce Repl Repl Most-Recent
Complete Partition
Repl Repl Erro Erro Unkn Synchronization
Time Name
0 2 2 0 0 0 Jul 31, 1997
5:42:12 pm MDT \TEST
Replica Synchronization Total:
Status Warni Tota OK Acce Repl Repl Most-Recent
Complete
Repl Repl Erro Erro Unkn Synchronization
Time
0 H 2 2 0 0 0 Jun 9, 1997
12:57:42 pm MDT
Replicas found: 2
Partitions found: 1
Servers contacted with Partitions and Replicas: 2
Count Error Numbers Message
Count Warning Message
2 H Completed sync. has not occurred in the hours.
End Date: Jul 31, 1997 5:56:57 pm MDT
********************
Continuity Check 'generalreport'
Time frame: Dynamic Tree - Weekly / Static Tree - Monthly
This option in DSDIAG provides information that can be used to determine whether the NDS tree design adheres to Novell's recommended design rules for replica placement. These design rules should be observed as the tree changes and grows on your network. In summary, these rules are:
Always have three replicas for fault tolerance, but never more than ten replicas per partition.
Replicate locally.
The replica synchronization process must complete in under 30 minutes.
Note: To check this synchronization process, select a server with a replica of the partition and run DSTRACE with the parameters shown below: SET DSTRACE=ON (activates the trace screen for Directory Services transactions) SET DSTRACE=+S (Enables the debug error messages for synchronized objects between fileservers) SET DSTRACE=*H (starts the "heartbeat" process, which is the skulker synchronization process between file servers) Start timing the operation when all the DSTRACE parameters have been entered, and stop when all partitions are synchronized on the server. (For additional information about DSTRACE, see "Using the Directory Services Trace (DSTrace) Screen" in the February 1997 issue of AppNotes).
Always try to have fewer than 15 subordinate OUs under any single OU in the tree. This reduces the overall number of subordinate references.
To check NDS continuity, run DSDIAG with the options shown below.
Load DSDIAG on a server (NTS recommends running DSDIAG.NLM on a non-production server that receives the 0278 tree SAP packets of the tree being checked).
At the Main Menu, select "Generate Report."
Select "List Replica Rings."
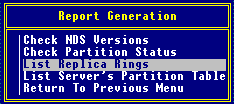
The "General Options" screen is displayed.
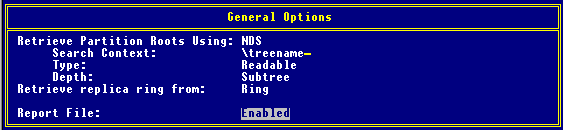
Use the following settings:
Retrieve Partition Roots Using: NDS (default)
Search Context: \tree_name
Type: Readable (default)
Depth: Subtree (default)
Retrieve replica ring from: Changefrom Single (default) to Ring to check every server in each replica ring.
Report File: Enabled (default filename SYS:SYSTEM\DPROOT00.RPT)
Press <F6< to set options for Warnings. Change "Display only partition roots/servers with warnings or errors" from Off to On. (This setting will show only partitions with problems, eliminating the need to review all partitions in the tree.)
Press <F8< to set Display options, and change Warnings from Off to On.
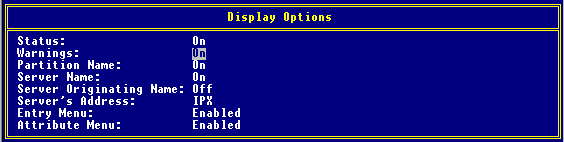
Press <F10< to start the report (up to 10 reports can run at one time).
The following is an example of the report output for the TEST tree. Refer to the README file that comes with DSDIAG for help in interpreting this report.
Report Title: DSD List Replica Rings
Report Version: 0.8
Base DN: \
Identity: \[Public]
Start Date: Jul 31, 1997
5:58:49 pm MDT
Retrieved Partition Roots Form: NDS
Search Context: \TEST
Type: Readable
Depth: Subtree
Retrieved replica ring from: Ring
Partition Name: \TEST
Server Name: \TEST\O=yahoo\OU=sw\CN=TEST-PSE-410
Server's Address: 01017FD9
Entry:
Status Warni Entry ID Repl Entry
Type Name
0 010000B4 RW \TEST
Partition Creation Time:
Status Warni Epoch Epoch
Repli
0 1 1
Replica:
Status Warni Repl Repl Replica Replica Server Address
Numb Type State Root ID Name
0 R 1 M On 010000B6
\TEST\O=novell\CN=TEST_DSE_411 335CBFB3
0 R 4 RW On 010000B4
\TEST\O=yahoo\OU=sw\CN=TEST-PSE-410 01017FD9
Partition Name: \TEST
Server Name: \TEST\O=novell\CN=TEST_DSE_411
Server's Address: 335CBFB3
Entry:
Status Warni Entry ID Repl Entry
Type Name
0 010000B6 M \TEST
Partition Creation Time:
Status Warni Epoch Epoch
Repli
0 1 1
Replica:
Status Warni Repl Repl Replica Replica Server Address
Numb Type State Root ID Name
0 R 1 M On 010000B6
\TEST\O=novell\CN=TEST_DSE_411 335CBFB3
0 R 4 RW On 010000B4
\TEST\O=yahoo\OU=sw\CN=TEST-PSE-410 01017FD9
Replicas found: 2
Partitions found: 1
Servers contacted with Partitions and Replicas: 2
Count Error Numbers Message
Count Warning Message
4 R Fewer than the minimum readable replicas found.
End Date: Jul 31, 1997 5:58:50 pm MDT
********************
Partition and Object Check
Time frame: Dynamic Tree - Every two weeks / Static Tree - Monthly
The partition and object check is recommended to provide the administrator with information about the number of objects in a partition and the tree. This check is useful in determining whether the NDS tree is within the recommended partitioning guidelines. Partitions should not exceed 2,000 objects.
The SCANTREE utility takes a snapshot of the NDS tree. SCANTREE is a DOS application designed to traverse an NDS tree and return a series of statistics. The results help to characterize an NDS tree by describing the width and depth of the tree, as well as the variety and characteristics of leaf objects.
Requirements for running SCANTREE are a 386 or higher processor, DOS 5 or higher, and at least 500 KB of available conventional RAM. You should have the Novell VLM Client software, version 1.20 revision B or higher.
|
Note: SCANTREE uses temporary files such as SCANTREE.nnn to store container information.These files reduce the possibility of running out of memory while analyzing large trees.This requires you to login as Admin or some other user with equivalent access rights beforerunning SCANTREE. |
From a workstation, log in as Admin or equivalent.
Map a search drive to the SYS:\PUBLIC\NLS directory.
Start the program by typing SCANTREE /d >[filename].
The SCANTREE options can include any of the following (multiple options may be included on the command line):
/?
Displays the help screen
<context<
Targets a specific context (in typeful format)
>[filename]
DOS redirection to a filename of your choice
/users
Reports only user objects
/d
Dumps all object and container names to standardoutput
To determine the number of objects in a partition, add the number of subordinates listed for each container. For example:
OBJECT NAME (SUBORDINATES, ATTRIBUTES, ATTRIBUTE SIZE) O=test. (10, 17, 2715)
In this tree, container O=test has 10 subordinate objects, 17 attributes, and an average attribute size of 2715. You would add up the number of subordinates given for each container in the partition to get the partition total.
For more details about SCANTREE, see "Understanding SCANTREE.EXE's Statistics" in the March 1996 issue of Novell Application Notes.
Partition Health Checks
To properly manage your NDS tree, various partition operations will be performed as needed. Two NetWare utilities are used to perform these partition operations: NDS Manager and DSREPAIR. NDS Manager is a Windows-based program that replaces Partition Manager. It enables you to control the partitioning and replication of the NDS database. It also provides other vital information such as synchronization and continuity. DSREPAIR is a server-based utility that is used to check time synchronization (as described earlier in this AppNote). You should always check the synchronization and continuity status of a replica and any child replicas both before and after the partition operation.
This section deals with the following operations:
Adding a Replica
Removing a Replica
Changing Replica Type
Splitting a Partition
Joining Two Partitions
Moving a Subtree
These instructions assume the user making the request has sufficient rights to perform the indicated operations.
Adding a Replica
The add replica operation creates a new copy of the partition information and stores it on the target server. The server receiving the replica will be added to the replica ring of the partition. If there are child partitions the server doesn't hold, NDS automatically adds a Subordinate Reference replica on this server and adds it to the child replica rings.
|
Note: If the partition where the target server will receive a replica has child partitions,always run a synchronization and continuity check of the partition and its child partitionsbefore starting the add replica operation. |
Key Steps. The client requests to add a replica to the target server. If there are child partitions, the Master server of the child partitions adds the target server to all children partition replica rings below the target partition. This is accomplished by adding a Subordinate Reference replica to the target server. The replica rings of the child partitions are modified to include the target server.
|
Note: For this step to complete, the child partitions must be synchronized withno errors. If the target server has a readable replica (master, Read-Write, or Read-Only) ofthe child partition, it will not need to have a Subordinate Reference replica added. |
|
If the partitionoperation hangs at replica state RS_NEW_REPLICA, the operation cannot be aborted in DSREPAIR. |
The Master server adds the target server to the partition by modifying the replica ring list. Specifically, it sets the replica state to RS_NEW_REPLICA. (DSTRACE will show the replica state as STATE=1.)
|
Ifthe partition operation hangs at replica stateRS_TRANSITION_ON, the operation cannot be aborted in DSREPAIR. |
When the Master server has notified all servers in the replica ring, the Master server will send the target server the contents of the partition. After the target server has received all the contents of the partition, the Master server changes the replica state from RS_NEW_REPLICA to RS_TRANSITION_ON. (DSTRACE will show the replica state as STATE=6.)
When the Master server has notified all servers in the replica ring of the change, the Master server will request each server in the replica ring to update the target server replica with any updates more recent than those of the Master server.
|
Note: If all servers in the replica ring do not reply to the Master server updaterequest, the replica state cannot advance. All servers involved in this partition operation must be up until the operation completes. |
After all the servers in the replica ring have updated the target server, the target server will send a request to the Master server to change the replica state to RS_ON. (DSTRACE will show the replica state as STATE=0.)
The Master server sets the replica state to RS_ON and synchronizes the change to each server. When the change completes, the operation is completed.
Procedure to Add a Replica using NDS Manager. Before starting the operation, check the partition synchronization status of the partition where the new replica will be added, and all child partitions. Verify that ALL PROCESSED =Yes. Also check the partition continuity status. Verify that the replica ring is consistent on all servers in the partition.
Start the NDS Manager utility. You can add a replica of a partition to a server from either the Tree view or the list of Partitions and Servers.
Proceed with the add partition operation as follows:
Choose the partition that you want to replicate on a server.
Choose Add replica.
Click the Browse button to choose the server to place the replica on.
Choose the NetWare Server object from the browser and click OK.
Select either Read/Write or Read Only.
Click OK.
To verify that the partition operation has completed successfully, repeat the synchronization (ALL PROCESSED=Yes) and replica ring continuity checks on the parent partition and all child partitions.
Removing a Replica
The delete replica operation removes a replica of the partition information and converts all the contents of that partition to external references. If the replica being deleted is a replica of a parent partition on the target server, the Subordinate References on the target server will be removed.
|
Note: DSREPAIR should not be used to remove replicas from servers. UseNDS Manager, NWAdmin,or INSTALL.NLM (which removes servers from the tree.) |
|
The replica ringwill show the target server in a replica stateRS_DYING_ REPLICA and the other servers willbe in a replica state RS_ON. If the partition operationhangs at replica state RS_DYING_ REPLICA,the operation cannot be aborted in DSREPAIR. |
Key Steps. The client requests to remove the replica on the target server to the Master server. The Master server changes the replica stateto RS_DYING_ REPLICA on the target server and synchronizes the change to all servers in the replica ring. (DSTRACE will show the replica state as STATE=2.)
The target server converts the real entries of the partition to external references and sends a backlink request to the servers holding the real entry that the external references refer to. One of three options will be preformed:
If the target server holds a replica of the parent partition, the target server sends a request to the Master server that its replica type has changed to a subordinate reference, then goes to the next step. (For this operation to complete, the master replica of the parent partition needs to be operational and the parent partition must be synchronized.)
If the target server does not hold a replica of the parent partition, the operation goes to next step.
If the target server does not hold a replicaof the parent partition but there are child partitions below the target partition, the target server sends a request to the Master server of each child partition that it no longer holds a readable replica of the parent partition. The Master server removes the subordinate replica from that child partition replica ring, then goes to next step. (For this operation to complete, the master replica of each child partition must be operational and the child partitions must be synchronized.)
The Master server will make one of the following changes:
If the target server holds a replica of the parent partition, the Master server changes the target server replica state to RS_ON.
If the target server does not hold a replica of the parent partition, the Master server modifies the replica ring by removing the target server and synchronizing the change.(DSTRACE will show the replica state as STATE=0.) The replica state will not change because the target server is the only replica in a RS_DYING_REPLICA state.
Procedure to Delete a Replica using NDS Manager. Before starting, check the synchronization status of the partition to be deleted, and all child partitions. Verify that ALL PROCESSED=Yes. Also check the partition continuity status. Verify that the replica ring is consistent on all servers in the partition.
In NDS Manager, choose the partition that has a replica you want to delete.
From the replica pane on the right, choose the replica you want to delete.
Right-click and choose Delete.
To verify that the operation has completed successfully, repeat the synchronization (ALL PROCESSED=Yes) and replica ring continuity checks.
Changing Replica Type
This is a critical partition operation because, as stated before, the master replica is in charge of all partition operations. If any synchronization errors exist prior to the Change Replica Type operation, it could cause confusion between replicas in the partition and the operation could get stuck (preventing sequential partition operations from being preformed). For the Change Replica Type operation, time must be synchronized for the operation to complete!
To change a RW replica to Master successfully, the old master will change the replica type in two stages and synchronize the changes to the other replicas (including the new Master).
|
If the partition operationhangs at replica state RS_CRT_0, the operationcan usually beaborted in DSREPAIR. |
Key Steps. The client requests a change replica type for a target server, to change it to the Master server. The Master server changes the replica state to RS_CRT_0 and synchronizes the change to all servers in the replica ring. (DSTRACE will show the replica state as STATE=4.)
The Master server tells the target server it is now the new Master server for the partition. The target server waits until its time is ahead of the time stamp issued by the master replica.
|
If the partition operation hangsat replica state RS_CRT_1, the operation cannot be aborted in DSREPAIR. |
The target server (new Master server) changes the replica state to RS_CRT_1. (DSTRACE will show the replica stateas STATE=5.)
The new Master server changes the old Master server to a RW replica. The old master changes it replica type to a RW replica. The old master changes its replica state to RS_CRT_1.
|
Note: The replica change sequence is usually where problems occur in this process.Be sure to run a continuity check to verify that the process has completed correctly. |
The new Master server changes the replica state to RS_ON and synchronizes the change. (DSTRACE will show the replica state as STATE=0.)
Procedure to Change Replica Type using NDS Manager. Before starting, check time synchronization of the tree (this is the only partition operation that requires the target server time to be in sync with the network). Check the synchronization of the partition where the replica type change is being made, and all child partitions. Verify that ALL PROCESSED=Yes. Also check the replica ring consistency of the replica.
In NDS Manager, you can change a replica type from either the Tree view or the list of Partitions and Servers.
Choose a partition or a server.
From the replica panel, choose the replica you want to change.
Choose Change replica type.
Choose a new type and click OK.
To verify that the partition operation has completed successfully, repeat the synchronization (ALL PROCESSED=Yes) and replica ring continuity checks.
Splitting a Partition
This operation happens when any container in Partition Manager is marked as a new partition. In other words, the container is already part of another partition and it gets split off as a new partition. This process establishes the new partition boundary. A new child partition is created with respect to the parent. By default, the servers that hold a copy of the parent partition will receive the copy of the new child partition, with the same replica ring as parent. That makes sense, since only servers that have a real copy of all the objects in the child partition will get a copy.
In the split partition operation:
The master of the partition issues the split call to all the replicas in the list.
The master of the parent becomes the master of the new child partition.
RW copies of the parent will receive a RW copy of the new child partition.
Subordinate References of the parent don't get involved in the operation.
A partition can be split as long as the new partition will have a container entry as its root entry. This partition operation changes the partition boundary using the same servers that have readable replicas (Master, Read-Write and Read-Only) of the parent partition. The traffic generated is the replica pointer (partition root), partition control and synchronization to the replicas. All the objects under the container are part of the new partition. Upon completion of the split, replica placement may need to be modified.
Key Steps. The client sends a request to split the partition to the Master server. The Master server verifies the request, changes the replica state of the partition to RS_SS_0, and sends this change to all servers in the replica ring. (DSTRACE will show the replica state as STATE=30.)
|
Before the partitionoperation can proceed, all servers in thereplica ring must reply to the Master serverthat their partition state has been changedto RS_SS_0. If the partition operation hangsat replica state RS_SS_0, the operation canusually be aborted in DSREPAIR. |
The Master server processes all obituaries that have not completed in the partition root container and containers that are in the new partition. This process removes obituaries that will no longer be associated with the parent partition. If the obituaries are unable to be processed, this partition operation may not proceed.
Upon completion of the obituary process, the Master server changes the replica state to RS_SS_1. (DSTRACE will show the replica state as STATE=31.)
|
If the partition operation hangs at replica state RS_SS_1, the operation cannotbe aborted in DSREPAIR. |
The Master server sends a DSALowLevelSplit request to each server in the replica ring. Each receiving replica splits its local replica. When completed, the server will reply indicating the process has completed successfully.
|
Note: The DSALowLevelSplit request is sent only to readable replicas, which excludessubordinate references. After the split, servers in the replica ring (excluding subordinatereplicas) of the original partition will hold the same replica type in the split partition. |
The master replica advances the replica state to RS_ON and sends the change to all servers in the parent and child partition. (DSTRACE will show the replica state as STATE=0.)
Procedure to Split a Partition using NDS Manager. Before starting, check the synchronization of the partition. Verify that ALL PROCESSED=Yes. Also check the replica ring continuity for the partition.
In NDS Manager, you can create a partition only from the Tree view.
Choose Tree view.
From the browser, choose the container you want to create as a partition.
Choose Create Partition.
To verify that the partition operation has completed successfully, repeat the synchronization and continuity checks. Check the status of the parent and new child partition involved in the operation. Verify that ALL PROCESSED=Yes. Also check the partition continuity of the parent and new child partition. Verify that the replica ring is correct on all servers in partition.
Joining Two Partitions
In a join partition operation, the existing child partition is merged back into the parent partition. Since it is not possible to delete the partition, you must merge it to the parent. This process destroys the partition boundary, then removes all the partition properties, as well as the record. Thus, the container is simply an object in the tree that can hold other objects. The container object can then be deleted if it doesn't hold any objects.
By default, the join operation makes the replica ring the same for both the parent and child partition, excluding the Subordinate References from the parent's replica ring. In other words, any server that holds a readable copy of the child or parent replica will get a RW copy of either one. This is probably the most time consuming part of the process; it can create network traffic, especially if the partitions are large. Upon completion of the merge, replica placement may need to be modified. On a server holding a subordinate reference of the child partition, the subordinate reference will be changed to a Read Only replica during the join operation.
Before you make any modifications to the replica ring, make sure the partition is synchronized and continuity is correct. The Master servers of the parent partition and child partition being joined are responsible for the operation.
|
Note: The data for both the parent and child partitions must exist on all serversin the parent ring for a merge partition operationto complete. Merging partitions is easier if both replica rings, the parent and child,are identical--meaning that where a read/write replica of the parent exists, a read write replica of the child does also, and so on. |
|
If the partitionoperation hangs at replica state RS_JS_0,the operation can usually be aborted in DSREPAIR. |
Key Steps. The client sends a request to join the child partition with the parent partition to the Master server of the child partition. The Master server of the child partition contacts the master of the parent partition to start the join process. The Master server of the parent partition sets the replica state to RS_JS_0 for the parent partition and sends this to all servers in the replica ring. (DSTRACE will show the replica state as STATE=40.)
The Master server of the child partition sets the replica state to RS_JS_0 for the child partition and sends this to all servers in the replica ring. The Master servers of the parent and child partitions compare replica rings to determine which servers they must add replicas to. Servers containing replicas of the child partition, but not the parent, receive new replicas of the parent partition. Servers containing replicas of the parent partition, but not the child partition, receive new replicas of the child partition. Servers with subordinate references of the child partition being joined to the parent partition will be changed to Read-Only replicas.
|
Note: Servers holding subordinate references of the child partition after this processwill hold Read-Write replicas. |
|
If the partitionoperation hangs at replica state RS_JS_1,the operation cannot be aborted in DSREPAIR. |
The Master servers of the parent partition sets the replica state to RS_JS_1 for all replicas (parent and child partition) and sends this to all servers in the replica ring. (DSTRACE will show the replica state as STATE=41.)
The Master server of the parent partition sends are quest to each server with replicas to erase their partition boundaries. All entries from both partitions will be in one partition.
|
If the partition operation hangsat replica state RS_JS_2, the operation cannot be aborted in DSREPAIR. If a replica is stuckin a join state, check the replica rings for parent and child to make sure they are thesame. The data for both the parent and child partitions must exist on all servers in theparent ring for a merge partition operation to complete. Contact Novell Technical Servicesif you are unable to resolve the problem. |
The Master server of the parent partition sets the replica state to RS_JS_2 and sends this to all servers in the replica ring. (DSTRACE will show the replica state as STATE=66.)
The Master server sets all replica states to RS_ON. (DSTRACE will show the replica state as STATE=0.)
The Master server becomes the master of the new partition. The child's master and RW replicas become RW copy of the new partition. These changes are sent to all servers in the replica ring.
Procedure to Join Partitions using NDS Manager. Before starting, check the partition synchronization of parent and child partitions. Verify that ALL PROCESSED=Yes.Also check the continuity of the partitions. Verify that the replica ring is consistent on all servers in the partition.
In NDS Manager, you can merge a partition from either the Tree view or the list of Partitions and Servers.
Choose the partition you want to merge with its parent partition.
Choose Merge partition.
To verify that the partition operation has completed successfully, repeat the synchronization (ALL PROCESSED=Yes) and replica ring continuity checks.
Moving a SubTree
The move subtree operation moves a partition with all its child entries as a unit to another logical location in the tree. The replicas of the partition being moved are held on the same servers they were held on previously. In other words, NDS moves the subtree logically, not physically. However, the objects' full names in the partition will change.
Any move subtree operation can be done under any container that meets the schema rules. Two conditions must exist:
The container being moved must be a partition.
The partition root object (which is a container object)cannot have any subordinate partitions (subtrees).
This partition operation can generate network traffic, depending on the number of entries in the partition and the parent partition servers involved. This partition operation does obituary functions. If there is a problem with obituaries not cleaning up in the partition, the operation may not complete. Or if this operation completes but leaves obit_move inhibit obituaries, the next partition operation involving these partitions will not start.
It is recommended that you add replicas of the new parent partition on the servers that hold replicas of the partition being moved, before doing the actual partition operation. The servers that hold replicas of the subtree will still hold replicas after the operation completes. The servers in the parent partition where the subtree will be moved will be added as subordinate replicas, and servers in the original parent partition will be removed as subordinate replicas. For this partition operation to complete correctly, the original parent partition, the subtree partition, and the new parent partition must be synchronized and replicarings must be correct on all servers.
Two master replicas are involved and responsible for specific parts of the operation. The master replica of the subtree partition being moved (the source partition) is responsible for completing the operation. In the move subtree operation, there is a destination server and a source server: The destination serveris the server holding the master replica of the parent partition under which the child partition is moving. The source server is the server holding the master replica of the partition that is moving.
Key Steps. The client sends a move subtree request to the destination Master server where the subtree partition (source partition) will be moving.
The destination Master server starts a 10 minute timer. (If the operation does not complete within 10 minutes, the Master server will clear the request from its memory.)
|
If the partition operation hangsat replica state RS_MS_0, the operation can usually be aborted in DSREPAIR in the earlystages of the operation. |
The destination Master server sets the replica state to RS_MS_0 and sends this change to all servers in the replica ring. (DSTRACE will show the replica state as STATE=50.)
The source Master server adds an OBT_TREE_OLD_RDN obituary of the partition=sold distinguished name, which will be deleted later.
The source Master server sets the replica state to RS_MS_0 and sends this change to all servers in the replica ring.
The source server forms a list of servers that will participate in the subtree move.
|
Note: If a replica is stuck in a join state, check the replica rings for parentand child to make sure they are the same. The data for both the parent and child partitions must exist on all servers in the parent ringfor a merge partition operation to complete. Contact Novell Technical Services if you are unable to resolve the problem. |
The source Master server adds an OBT_MOVE_TREE obituary on each of the servers in the above list. (The obituary process is critical for the completion of this operation. This process assures the partition operations has links to the original parent partition and obituaries are correctly cleaned up when the operation no longer needs them. External references changes will be processed during this operation.)
The source Master server sends a request to each server list. The change to each server depends on the replicas it hold. For example, servers holding a master or RW replica of the original parent partition, but not a readable replica of the source partition, will have the subordinate reference replica of the source partition removed.
The source Master server sends a request to each server on the notification list the move operation has completed. It then sends a request to each server on the notification list to change the obituary flag to OBF_PURGEABLE and reply.
The Master server of the source server sends an unlock request to the original parent partition of the source partition and destination partition. Each Master server of the original parent partition of the source partition and destination partition sets the replica state to RS_ON and sends this change to all servers in the replica ring. (DSTRACE will show the replica state as STATE=0.)
The source Master server sets the replica state to RS_ON for its partition and sends this change to all servers in the replica ring. (DSTRACE will show the replica state as STATE=0.)
|
Note: If the obituaries don't clean up correctly, the next partition operationinvolving the partition involved in the move subtree operation may get an Error- 637 in DSTRACE or an error FD83 " "Previous Move in Progress" in NWAdmin, NETDMIN, PARTMGR, or NDS Manager. To troubleshoot, referenceTID 2923724. |
Procedure to Move SubTree using NDS Manager. Check the partition synchronization status of each partition involved in the operation (original parent partition, source partition, and destination partition). Verify that ALL PROCESSED=Yes. Also check the continuity status of each partition involved in the operation (original parent partition, source partition, and destination partition). Verify that the replica ring is correct on all servers in each partition.
In NDS Manager, you can move a partition from either the Tree view or the list of Partitions and Servers.
Choose the partition you want to move.
Choose Move partition.
(Optional) To move the partition to a context besides [Root], either type a new context in To Context, or choose the browse icon and select the destination partition from the browser.
(Optional) Check Create an alias for this container object. This option will create an alias container and leaf objects. This is useful until users' workstation login contexts can be changed to match the new context.
Choose Yes.
To verify that the operation has completed successfully, repeat the synchronization (ALL PROCESSED=Yes) and replica ring continuity checks on each partition involved in the operation.
* Originally published in Novell AppNotes
Disclaimer
The origin of this information may be internal or external to Novell. While Novell makes all reasonable efforts to verify this information, Novell does not make explicit or implied claims to its validity.